A low-phase-noise LC-VCO with an enhanced
... GNSS signal by 10–25 dBm. To enable positioning and navigation under forest canyons, in urban areas, and even inside buildings, high-sensitivity GNSS receivers should be able to receive signals below –155 dBm, which requires that the receiver’s local oscillator phase noise is smaller than –120 dBc/H ...
... GNSS signal by 10–25 dBm. To enable positioning and navigation under forest canyons, in urban areas, and even inside buildings, high-sensitivity GNSS receivers should be able to receive signals below –155 dBm, which requires that the receiver’s local oscillator phase noise is smaller than –120 dBc/H ...
103_unit_2
... format table. The number 5 x10-9 Farads could be written as 5 nano Farads and could also be written as 5 nF. The second conversion will be more difficult. Just remember that the number, when converted, should be a whole number and not a decimal number. To convert the scientific notation format into ...
... format table. The number 5 x10-9 Farads could be written as 5 nano Farads and could also be written as 5 nF. The second conversion will be more difficult. Just remember that the number, when converted, should be a whole number and not a decimal number. To convert the scientific notation format into ...
wk.22.tuesday.hmwk.equivalent resistance
... parallel circuits have higher current 5. 0.1 A or 100 mA 6. The total current through the circuit is 0.20 amps. resistors in parallel divide current and since these resistors are the same value they divide the current equally. Therefore each resistor carries 0.10 amps or 0.1 mA. Notice that this is ...
... parallel circuits have higher current 5. 0.1 A or 100 mA 6. The total current through the circuit is 0.20 amps. resistors in parallel divide current and since these resistors are the same value they divide the current equally. Therefore each resistor carries 0.10 amps or 0.1 mA. Notice that this is ...
Slide 1
... voltage and current. This equals the magnitude of the impedance, Z, when represented in a two-dimensional room spanned by real and imaginary vectors. In addition, we also want to know the phase shift (q) ...
... voltage and current. This equals the magnitude of the impedance, Z, when represented in a two-dimensional room spanned by real and imaginary vectors. In addition, we also want to know the phase shift (q) ...
Discrete devices: FETs - UBC Engineering Physics Project Lab
... • Gain Bandwidth product ~ 3 MHz. This would limit the bandwidth of the amplifier from DC up to 30 Hz (i.e. not a very ...
... • Gain Bandwidth product ~ 3 MHz. This would limit the bandwidth of the amplifier from DC up to 30 Hz (i.e. not a very ...
Elec 499 Final Report - Electrical and Computer Engineering
... A switching frequency of 50 kHz was achieved, and the method of soft switching implemented was zero voltage transition (ZVT). The use of a PWM boost converter allows for a variable input and constant output. The output is regulated by the control circuit which adjusts the duty cycle of the gating pu ...
... A switching frequency of 50 kHz was achieved, and the method of soft switching implemented was zero voltage transition (ZVT). The use of a PWM boost converter allows for a variable input and constant output. The output is regulated by the control circuit which adjusts the duty cycle of the gating pu ...
Section 1 Simple Circuits: Practice Problems
... In a series circuit, the current is opposed by each resistance in turn. The total resistance is the sum of the resistors. In a parallel circuit, each resistance provides an additional path for current. The result is a decrease in total resistance. 41. Compare the amount of current entering a junctio ...
... In a series circuit, the current is opposed by each resistance in turn. The total resistance is the sum of the resistors. In a parallel circuit, each resistance provides an additional path for current. The result is a decrease in total resistance. 41. Compare the amount of current entering a junctio ...
Kuliah 3(a) - FCSIT @ UM
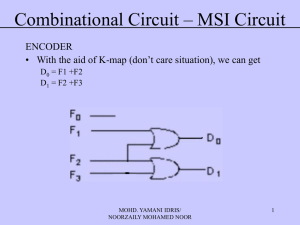
... MULTIPLEXER (Function Execution) • Boolean Function can be executed using multiplexer • 2n:1 multiplexer can execute Boolean function with n input variable as the following – Expression in SOM Example: ...
... MULTIPLEXER (Function Execution) • Boolean Function can be executed using multiplexer • 2n:1 multiplexer can execute Boolean function with n input variable as the following – Expression in SOM Example: ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.











![Figure 2.3 S-Parameter 2-port networks. [4 ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010416205_1-285fce7f5a801efdfe825c40ece3fe16-300x300.png)