analog multimeter
... • Analog meters use a graduated scale with a pointer • Digital meters provide a direct readout • A multimeter combines a voltmeter, ammeter, and ohmmeter into one package • A VOM is an analog multimeter • A DMM is a digital multimeter ...
... • Analog meters use a graduated scale with a pointer • Digital meters provide a direct readout • A multimeter combines a voltmeter, ammeter, and ohmmeter into one package • A VOM is an analog multimeter • A DMM is a digital multimeter ...
A High Linearity Darlington Intermediate Frequency (IF
... Design for Stability Typical specifications dictate unconditionally stable operation up to 18 GHz. This amplifier is designed for unconditionally stable operation, including the external components and biasing under all conditions. For this purpose, various stability design techniques have been empl ...
... Design for Stability Typical specifications dictate unconditionally stable operation up to 18 GHz. This amplifier is designed for unconditionally stable operation, including the external components and biasing under all conditions. For this purpose, various stability design techniques have been empl ...
DC Circuits
... 1) The current circuit elements wired in series is constant. 2) The voltage can change across a circuit element wired in series. 3) The sum of voltage drops across individual circuit elements equals the voltage of the power supply. 4) The equivalent resistance of a circuit with more than one circuit ...
... 1) The current circuit elements wired in series is constant. 2) The voltage can change across a circuit element wired in series. 3) The sum of voltage drops across individual circuit elements equals the voltage of the power supply. 4) The equivalent resistance of a circuit with more than one circuit ...
The CrickSAT Mission connections to math, electricity and electronis
... (mW), 1mW = 0.001W. For example an LED uses about 40mW and a bleeper uses about 100mW, even a lamp such as a torch bulb only uses about 1W. The typical power used in mains electrical circuits is much larger, so this power may be measured in kilowatts (kW), 1kW = 1000W. For example a typical main ...
... (mW), 1mW = 0.001W. For example an LED uses about 40mW and a bleeper uses about 100mW, even a lamp such as a torch bulb only uses about 1W. The typical power used in mains electrical circuits is much larger, so this power may be measured in kilowatts (kW), 1kW = 1000W. For example a typical main ...
Exp_Ohmic Circuit Elements
... Charge cannot accumulate at any point along the circuit path. This is the law of conservation of charge. In a direct-current (DC) circuit the current always flows in one direction and is usually constant. In an alternating current (AC) circuit the current oscillates, flowing in one direction and the ...
... Charge cannot accumulate at any point along the circuit path. This is the law of conservation of charge. In a direct-current (DC) circuit the current always flows in one direction and is usually constant. In an alternating current (AC) circuit the current oscillates, flowing in one direction and the ...
PHYSICS II: Kirchhoff`s Rules
... 1. Before connecting the circuit, turn on the power supply and adjust output A to 10 volts & then turn off the power supply. Also set the decade box values to R1500, & R3800 and use the ohm scale of your DVM to carefully measure R1, R2 & R3 [generally your FLUKE DVM is more accurate than the dec ...
... 1. Before connecting the circuit, turn on the power supply and adjust output A to 10 volts & then turn off the power supply. Also set the decade box values to R1500, & R3800 and use the ohm scale of your DVM to carefully measure R1, R2 & R3 [generally your FLUKE DVM is more accurate than the dec ...
circuit for continuous motional series resonant frequency and
... The system was calibrated and characterized by connecting ten different selected resistances, covering a range from 100 Ω to 5000 Ω, in place of the sensor. Values of α =-228.8mV and β=3420mV were obtained were obtained which minimized the sum of squared relative errors between the values of Rm obta ...
... The system was calibrated and characterized by connecting ten different selected resistances, covering a range from 100 Ω to 5000 Ω, in place of the sensor. Values of α =-228.8mV and β=3420mV were obtained were obtained which minimized the sum of squared relative errors between the values of Rm obta ...
Ohm, Ohm On The Range
... Concepts associated with electricity often require formal reasoning. Observations can be made more concrete by using flashlight bulbs instead of resistors. The resistances will not be known, but they will be the same and the brightness of the bulbs will decrease with then decreasing currents in part ...
... Concepts associated with electricity often require formal reasoning. Observations can be made more concrete by using flashlight bulbs instead of resistors. The resistances will not be known, but they will be the same and the brightness of the bulbs will decrease with then decreasing currents in part ...
Electrical Engineering 105
... V IR1 IR2 I ( R1 R2 ) The current is the same through each resistor because any charge flowing through one resistor must also flow through the other. ...
... V IR1 IR2 I ( R1 R2 ) The current is the same through each resistor because any charge flowing through one resistor must also flow through the other. ...
Circuit/System Testing LNF Engine 1. Verify that a test lamp
... 1. Verify that a test lamp illuminates between the G13 generator B+ terminal 1 X2 and ground. ⇒ If the test lamp does not illuminate and the circuit fuse is good 1.1 Ignition OFF. 1.2 Test for less than 2 Ω in the B+ circuit end to end. ⇒ If 2 Ω or greater, repair the open/high resistance in the cir ...
... 1. Verify that a test lamp illuminates between the G13 generator B+ terminal 1 X2 and ground. ⇒ If the test lamp does not illuminate and the circuit fuse is good 1.1 Ignition OFF. 1.2 Test for less than 2 Ω in the B+ circuit end to end. ⇒ If 2 Ω or greater, repair the open/high resistance in the cir ...
Experiment 1: Index of refraction
... Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II—AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated than Ohm’s law for resistance. In this laboratory you will study timevarying electrical si ...
... Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II—AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated than Ohm’s law for resistance. In this laboratory you will study timevarying electrical si ...
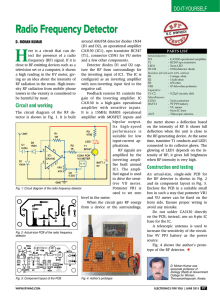
Radio Frequency Detector
... the RF-generating device. At the same time, transistor T1 conducts and LED1 connected to its collector glows. The glowing of LED1 depends on the intensity of RF; it gives full brightness when RF intensity is very high. ...
... the RF-generating device. At the same time, transistor T1 conducts and LED1 connected to its collector glows. The glowing of LED1 depends on the intensity of RF; it gives full brightness when RF intensity is very high. ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.