Chapter 6: Electricity
... If the atom acquires an electron, the atom becomes negatively charged because there are now more electrons than protons • When an atom gains an electron it acquires a negative (-) charge Charge is measured in units called coulombs (C) 1 electron has a charge of 1.60 x 10-19C, and it requires 6 ...
... If the atom acquires an electron, the atom becomes negatively charged because there are now more electrons than protons • When an atom gains an electron it acquires a negative (-) charge Charge is measured in units called coulombs (C) 1 electron has a charge of 1.60 x 10-19C, and it requires 6 ...
What can a Non Load Break Switch do?
... Remember it is a game as to how fast I can establish my dielectric verses how fast the voltage builds Besides pulling the contacts apart very fast I can help myself by bottling up the arc until current zero then letting the arc energy move the dielectric media very fast into where the arc was. Brea ...
... Remember it is a game as to how fast I can establish my dielectric verses how fast the voltage builds Besides pulling the contacts apart very fast I can help myself by bottling up the arc until current zero then letting the arc energy move the dielectric media very fast into where the arc was. Brea ...
Chapter 4
... The voltage output of an AC for voltage output with the source is given by the general form expression ∆v = ∆ Vmax sinωt, we see ∆v = (200 V) sin ωt. that ∆ Vmax = 200 V. Thus, the Find the rms current in the rms voltage is circuit when this source is connected to a 100 Ohm resistor. ...
... The voltage output of an AC for voltage output with the source is given by the general form expression ∆v = ∆ Vmax sinωt, we see ∆v = (200 V) sin ωt. that ∆ Vmax = 200 V. Thus, the Find the rms current in the rms voltage is circuit when this source is connected to a 100 Ohm resistor. ...
characteristics of passive circuit elements (r,l,c)
... An inductor generally consists of a coil of a good conductor, (usually copper) wound on an insulating cylindrical former, which may or may not have a ferromagnetic core. The winding may be singlelayer, multilayer or honeycomb. Note the construction of the different inductors given to you and write d ...
... An inductor generally consists of a coil of a good conductor, (usually copper) wound on an insulating cylindrical former, which may or may not have a ferromagnetic core. The winding may be singlelayer, multilayer or honeycomb. Note the construction of the different inductors given to you and write d ...
R-L-C AC Circuits •
... Chapter 3). The response of a circuit to a complicated waveform (e.g. a square wave) can be understood by analyzing each of the individual sine or cosine components that make up the complicated waveform. Usually only a few of these components are important in determining the circuit's response to th ...
... Chapter 3). The response of a circuit to a complicated waveform (e.g. a square wave) can be understood by analyzing each of the individual sine or cosine components that make up the complicated waveform. Usually only a few of these components are important in determining the circuit's response to th ...
P21 Homework Set #7
... Assess: This is a large current indeed, and it would require large transmission lines; we could make the current smaller by sending the power down the transmission lines at an even higher voltage. ...
... Assess: This is a large current indeed, and it would require large transmission lines; we could make the current smaller by sending the power down the transmission lines at an even higher voltage. ...
chapter28class
... changes, following the chosen loop 2. Current follows the direction of direction. electric field, hence the decrease of potential. ...
... changes, following the chosen loop 2. Current follows the direction of direction. electric field, hence the decrease of potential. ...
(A) Find the current in the circuit.
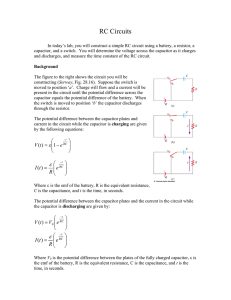
... RC Circuits A direct current circuit may contain capacitors and resistors, the current will vary with time When the circuit is completed, the capacitor starts to charge The capacitor continues to charge until it reaches its maximum charge (Q = Cε) Once the capacitor is fully charged, the cu ...
... RC Circuits A direct current circuit may contain capacitors and resistors, the current will vary with time When the circuit is completed, the capacitor starts to charge The capacitor continues to charge until it reaches its maximum charge (Q = Cε) Once the capacitor is fully charged, the cu ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.