Tuesday
... focuses the light down to extremely small regions on the chip - similar to how a microscope’s lens lets us see tiny things by focusing light, but in reverse. The chemical in the small illuminated region changes, and then a solvent washes away the chemical but some regions stay because of the light t ...
... focuses the light down to extremely small regions on the chip - similar to how a microscope’s lens lets us see tiny things by focusing light, but in reverse. The chemical in the small illuminated region changes, and then a solvent washes away the chemical but some regions stay because of the light t ...
text lc inverter oscillator
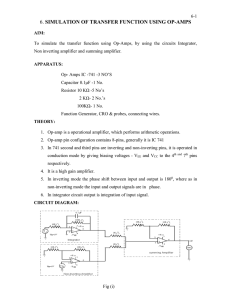
... For input voltages less than half the power supply voltage the output is high and for voltages greater than half the power supply voltage the output is zero. The transition between the two states is for the input equal to half the power supply voltage. The power consumed by the ideal INVERTER is zer ...
... For input voltages less than half the power supply voltage the output is high and for voltages greater than half the power supply voltage the output is zero. The transition between the two states is for the input equal to half the power supply voltage. The power consumed by the ideal INVERTER is zer ...
Chapter 4
... Source transformation rules • Note that the arrow of the current source is directed towards the positive terminal of the voltage source • Source transformation is not possible when R=0 for an ideal voltage source • For a realistic source, R0 • For an ideal current source, R= also prevents the use ...
... Source transformation rules • Note that the arrow of the current source is directed towards the positive terminal of the voltage source • Source transformation is not possible when R=0 for an ideal voltage source • For a realistic source, R0 • For an ideal current source, R= also prevents the use ...
AdvLessons#11
... then no current will flow (infinite impedance). In an AC circuit, it is possible to oscillate the direction of the current fast enough that the capacitor never fills up. At very high frequencies it is as if the capacitor isn’t even there (zero impedance). The larger the Capacitance, the less l ...
... then no current will flow (infinite impedance). In an AC circuit, it is possible to oscillate the direction of the current fast enough that the capacitor never fills up. At very high frequencies it is as if the capacitor isn’t even there (zero impedance). The larger the Capacitance, the less l ...
network theorems module
... When zeroing a voltage source, it becomes a short circuit. When zeroing a current source, it becomes an open circuit. We can find the Thévenin resistance by zeroing the sources in the original network and then computing the resistance between the terminals. ...
... When zeroing a voltage source, it becomes a short circuit. When zeroing a current source, it becomes an open circuit. We can find the Thévenin resistance by zeroing the sources in the original network and then computing the resistance between the terminals. ...
Determination of Small-Signal Equivalent Circuit Elements and
... We combine measurements of test patterns and the device itself at different bias points for this task. The most serious problem arises from the distributed nature of the base electrode which results in the feedback capacitance Cfb. There are various approaches to deal with this capacitance. The valu ...
... We combine measurements of test patterns and the device itself at different bias points for this task. The most serious problem arises from the distributed nature of the base electrode which results in the feedback capacitance Cfb. There are various approaches to deal with this capacitance. The valu ...
First Circuit Breaker for Terminal Blocks
... harmless short-term surges, such as in-rush current associated with motor startup. For this reason, a fuse can be replaced by an 1180 circuit breaker of lower current rating, increasing the level of overload protection for devices that control factory equipment such as assembly lines, robots, heater ...
... harmless short-term surges, such as in-rush current associated with motor startup. For this reason, a fuse can be replaced by an 1180 circuit breaker of lower current rating, increasing the level of overload protection for devices that control factory equipment such as assembly lines, robots, heater ...
L4 series and parallel resistors
... Replace R in the circuit shown in Figure 1 with three resistors in parallel as shown in Fig.3. Set the supply voltage so that there is a 3 volt p.d. across the parallel network of resistors. Measure the total current I flowing in the circuit and the currents flowing in each branch with the ammeter. ...
... Replace R in the circuit shown in Figure 1 with three resistors in parallel as shown in Fig.3. Set the supply voltage so that there is a 3 volt p.d. across the parallel network of resistors. Measure the total current I flowing in the circuit and the currents flowing in each branch with the ammeter. ...
Metal Detectors
... (metres as opposed to centimetres) different techniques are required. One method of detecting large ferrous objects buried deep in the ground is to look for localised variation in the earth’s magnetic field. Sensitive magnetometers may be used to measure variations of this type. Because field variat ...
... (metres as opposed to centimetres) different techniques are required. One method of detecting large ferrous objects buried deep in the ground is to look for localised variation in the earth’s magnetic field. Sensitive magnetometers may be used to measure variations of this type. Because field variat ...
lect18_f03
... • in the low frequency limit, XL 0 and XC . • Therefore, as w 0, the current will flow mostly through the inductor; the current through the capacitor approaches 0. • in the high frequency limit, XL and XC 0 . • Therefore, as w , the current will flow mostly through the capacitor, ap ...
... • in the low frequency limit, XL 0 and XC . • Therefore, as w 0, the current will flow mostly through the inductor; the current through the capacitor approaches 0. • in the high frequency limit, XL and XC 0 . • Therefore, as w , the current will flow mostly through the capacitor, ap ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.