Experiment 2: Resistors in Series and Parallel
... 2.5 COMMENTS AND CONCLUSIONS Discuss the reasons for any differences in Table 2.1. Use Ohm’s Law to calculate the current flowing in the circuit It and hence calculate the voltage drop expected across each resistor (e.g. voltage drop across R1 is calculated as VR1 = ItR1, etc). Use the values as ind ...
... 2.5 COMMENTS AND CONCLUSIONS Discuss the reasons for any differences in Table 2.1. Use Ohm’s Law to calculate the current flowing in the circuit It and hence calculate the voltage drop expected across each resistor (e.g. voltage drop across R1 is calculated as VR1 = ItR1, etc). Use the values as ind ...
What is included in a circuit diagram? Circuit Diagrams
... • If one bulb burns out in a series circuit, it becomes an open circuit. • The bulbs in a circuit are a source of resistance. Adding bulbs to a series circuit increases the resistance. The current decreases, and each bulb shines less brightly. ...
... • If one bulb burns out in a series circuit, it becomes an open circuit. • The bulbs in a circuit are a source of resistance. Adding bulbs to a series circuit increases the resistance. The current decreases, and each bulb shines less brightly. ...
SGA6589Z 数据资料DataSheet下载
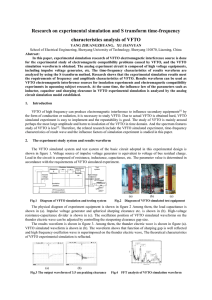
... responsibility is assumed by RF Micro Devices, Inc. ("RFMD") for its use, nor for any infringement of patents, or other rights of third parties, resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of RFMD. RFMD reserves the right to change comp ...
... responsibility is assumed by RF Micro Devices, Inc. ("RFMD") for its use, nor for any infringement of patents, or other rights of third parties, resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of RFMD. RFMD reserves the right to change comp ...
Document
... A circuit family C is an infinite list of circuits, (C0 , C1 , C2 ,) where Cn has n inputs A circuit family is said to be uniform if there is a log-space Turing machine that on the input of n 1s produces the circuit Cn For example, for computing the sum of two integers (of unlimited length), we nee ...
... A circuit family C is an infinite list of circuits, (C0 , C1 , C2 ,) where Cn has n inputs A circuit family is said to be uniform if there is a log-space Turing machine that on the input of n 1s produces the circuit Cn For example, for computing the sum of two integers (of unlimited length), we nee ...
PWA_Mod02_Prob05_v04
... • If you picked another method, such as writing a set of equations using KVL and KCL, it does not make that much difference. One advantage of the approach taken here is that we do not have to solve simultaneous equations. However, if we have access to a good calculator or a computer, the solution ca ...
... • If you picked another method, such as writing a set of equations using KVL and KCL, it does not make that much difference. One advantage of the approach taken here is that we do not have to solve simultaneous equations. However, if we have access to a good calculator or a computer, the solution ca ...
Building your Own Zapper
... The frequency is not dependant on the voltage. A 9 Volts battery is a convenient way to power it for portability. A standard 9v battery will last approximately 9days with this design. The frequency and duty cycle (ratio of On and Off time) are defined by the resistors R1, R2 and capacitor C2. When R ...
... The frequency is not dependant on the voltage. A 9 Volts battery is a convenient way to power it for portability. A standard 9v battery will last approximately 9days with this design. The frequency and duty cycle (ratio of On and Off time) are defined by the resistors R1, R2 and capacitor C2. When R ...
Kirchhoff`s Laws
... generate the voltage and current equations for the circuit. Each person in a lab group should choose a different circuit to work with. Each person should choose only one circuit. There may be some circuits in the figure that are not used. If you have trouble generating the equations, consult with th ...
... generate the voltage and current equations for the circuit. Each person in a lab group should choose a different circuit to work with. Each person should choose only one circuit. There may be some circuits in the figure that are not used. If you have trouble generating the equations, consult with th ...
PENGENALAN FILTER AKTIF
... There are 3 basic categories of active filters: 1. Low-pass filters 2. High-pass filters 3. Band-pass filters Each of these filters can be built by using op-amp as the active element combined with RC, RL or RLC circuit as the passive elements. ...
... There are 3 basic categories of active filters: 1. Low-pass filters 2. High-pass filters 3. Band-pass filters Each of these filters can be built by using op-amp as the active element combined with RC, RL or RLC circuit as the passive elements. ...
Analysis of electrical equivalent circuit of metal–insulator–semiconductor structure based on admittance measurements
... The estimation of the equivalent circuit parameters was performed by the Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm [11] of simultaneous fitting of capacitance and normalized conductance curves to experimental data using the OriginLab software. The best fitted values of the equivalent circuit parameters are pres ...
... The estimation of the equivalent circuit parameters was performed by the Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm [11] of simultaneous fitting of capacitance and normalized conductance curves to experimental data using the OriginLab software. The best fitted values of the equivalent circuit parameters are pres ...
Lecture 9
... voltage is suddenly removed. • In general, when an applied current or voltage suddenly changes, the voltages and currents in an RL or RC circuit will change exponentially with time, from their initial values to their final values, with the characteristic time constant t: ...
... voltage is suddenly removed. • In general, when an applied current or voltage suddenly changes, the voltages and currents in an RL or RC circuit will change exponentially with time, from their initial values to their final values, with the characteristic time constant t: ...
Resistors in Parallel A 9.0 V battery is connected to four resistors of
... 3. An 18.0 Ω, 9.00 Ω, and 6.00 Ω resistor are connected in parallel to an emf source. A current of 4.00 A is in the 9.00 Ω resistor. a. Calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit. ...
... 3. An 18.0 Ω, 9.00 Ω, and 6.00 Ω resistor are connected in parallel to an emf source. A current of 4.00 A is in the 9.00 Ω resistor. a. Calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit. ...
Adaptive signal sampling for high throughput, broadband
... invariant amplitude. A marked difference is that in Fig.4 only a part of a transient response is considered and not a steady state signal. Having a high sampling frequency at the beginning is essential while with longer time after the step no further information appear. Therefore, the sampling rate ...
... invariant amplitude. A marked difference is that in Fig.4 only a part of a transient response is considered and not a steady state signal. Having a high sampling frequency at the beginning is essential while with longer time after the step no further information appear. Therefore, the sampling rate ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.