Spring 2007 - Antelope Valley College
... DNA synthesis in the direction that goes away from the replication fork is called ____________________________ strand synthesis. ...
... DNA synthesis in the direction that goes away from the replication fork is called ____________________________ strand synthesis. ...
E coli
... • Most prokaryotic genes are arranged in units called operons • These are transcribed together and allow several genes’ activities to be co-ordinated, e.g. the genes in a pathway responsible for the metabolism of a specific compound, e.g. lactose, tryptophan • Figure 28-5 in Lehninger ...
... • Most prokaryotic genes are arranged in units called operons • These are transcribed together and allow several genes’ activities to be co-ordinated, e.g. the genes in a pathway responsible for the metabolism of a specific compound, e.g. lactose, tryptophan • Figure 28-5 in Lehninger ...
DNA and RNA
... information, form specific structures in a cell or carry out specific roles in a cell. Found in all living things and viruses.* The two most common are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). ...
... information, form specific structures in a cell or carry out specific roles in a cell. Found in all living things and viruses.* The two most common are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). ...
DNA and Central Dogma Study Guide
... 9. Summarize the flow of genetic information starting with DNA. 10. When does DNA replicate? 11. What does DNA replication make? 12. What do we mean when we say DNA replication is semi-conservative? Use percent values in your response. ...
... 9. Summarize the flow of genetic information starting with DNA. 10. When does DNA replicate? 11. What does DNA replication make? 12. What do we mean when we say DNA replication is semi-conservative? Use percent values in your response. ...
The Chromosome
... called chromatin, while the structure formed by two turns of DNA around one histone is called a nucleosome. A chromosomal DNA molecule contains three specific nucleotide sequences which are required for replication: a DNA replication origin; a centromere to attach the DNA to the mitotic spindl ...
... called chromatin, while the structure formed by two turns of DNA around one histone is called a nucleosome. A chromosomal DNA molecule contains three specific nucleotide sequences which are required for replication: a DNA replication origin; a centromere to attach the DNA to the mitotic spindl ...
E1-3 NotesProtein Synth
... d. thymine (T) 6. DNA – double helix (like a spiral staircase) a. discovered by Watson and Crick 7. Covalent bonds B/T sugar and phosphate 8. Nitrogen bases connect to sugar-phosphate backbone 9. 2 Nitrogen bases attach in the middle a. cytosine always pairs with guanine b. adenine always pairs with ...
... d. thymine (T) 6. DNA – double helix (like a spiral staircase) a. discovered by Watson and Crick 7. Covalent bonds B/T sugar and phosphate 8. Nitrogen bases connect to sugar-phosphate backbone 9. 2 Nitrogen bases attach in the middle a. cytosine always pairs with guanine b. adenine always pairs with ...
gene synthesis traditional cloning
... Gene Synthesis is simple and straightforward. Just submit the sequence of your gene of interest to GENEWIZ and we will take care of the rest. ...
... Gene Synthesis is simple and straightforward. Just submit the sequence of your gene of interest to GENEWIZ and we will take care of the rest. ...
ara Operon
... • Study of biological processes (example: synthesis of proteins) • Localization and regulation of gene expression • Cell movement • Cell fate during development ...
... • Study of biological processes (example: synthesis of proteins) • Localization and regulation of gene expression • Cell movement • Cell fate during development ...
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN
... The discovery of ribozymes rendered obsolete the idea that all biological catalysts are proteins. Introns may play a regulatory role in the cell. Specific functions have not been identified for most introns, but some contain sequences that regulate gene expression, and many affect gene products ...
... The discovery of ribozymes rendered obsolete the idea that all biological catalysts are proteins. Introns may play a regulatory role in the cell. Specific functions have not been identified for most introns, but some contain sequences that regulate gene expression, and many affect gene products ...
Supplementary Methods (doc 30K)
... Supplemental methods DNA Constructs and reagents The NF-кB p65 and p50 expression plasmids were used to produce full-length p65 and p50 protein. It was made by cloning PCR products into the HindIII and EcoRV sites of pFlag-CMV-2 expression vector as described before. (Hertlein E et al. 2005). The NF ...
... Supplemental methods DNA Constructs and reagents The NF-кB p65 and p50 expression plasmids were used to produce full-length p65 and p50 protein. It was made by cloning PCR products into the HindIII and EcoRV sites of pFlag-CMV-2 expression vector as described before. (Hertlein E et al. 2005). The NF ...
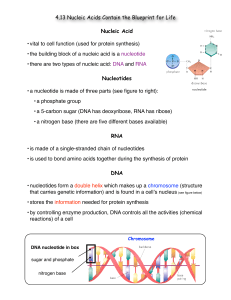
4.13 notes
... • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded cha ...
... • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded cha ...
pGLO transformation lab notes-2007
... 3. Heat-shock Increases permeability of membranes 4. Nutrient broth incubation Allows beta-lactamase expression ...
... 3. Heat-shock Increases permeability of membranes 4. Nutrient broth incubation Allows beta-lactamase expression ...
RNA and protein synthesis
... Protein synthesis occurs in two major parts transcription and translation. 1. Transcription: Process where DNA serves as a template to produce complementary mRNA 2. Translation: Process in which mRNA is used to link amino acids together to synthesize proteins. Involves tRNA and rRNA DNA ...
... Protein synthesis occurs in two major parts transcription and translation. 1. Transcription: Process where DNA serves as a template to produce complementary mRNA 2. Translation: Process in which mRNA is used to link amino acids together to synthesize proteins. Involves tRNA and rRNA DNA ...
genetic engineering and recombinant dna technology
... B. Genetic engineering can be conducted in a variety of ways. II. RESTRICTION ENZYMES-special enzymes that can be used to isolate and remove a specific DNA fragments and genes. These have become very useful in genetic engineering studies. III. RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY-involves the use of DNA from ...
... B. Genetic engineering can be conducted in a variety of ways. II. RESTRICTION ENZYMES-special enzymes that can be used to isolate and remove a specific DNA fragments and genes. These have become very useful in genetic engineering studies. III. RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY-involves the use of DNA from ...
Chapter 17 Presentation
... carries the genetic information from the DNA to the protein synthesizing machinery. RNA polymerase pries apart the DNA and joins RNA nucleotides together in the 5’-->3’ direction (adding, again, to the free 3’ end). RNA polymerase is just like DNA ...
... carries the genetic information from the DNA to the protein synthesizing machinery. RNA polymerase pries apart the DNA and joins RNA nucleotides together in the 5’-->3’ direction (adding, again, to the free 3’ end). RNA polymerase is just like DNA ...
More Exam Practice - Iowa State University
... into CO2 and pyruvate. In this way, C4 plants maintin a concentrtation of CO2 in their bundle sheath cells as an adaption to hot, dry climates. If they were to open their stomata to take in CO2 during the day, they would also lose too much water. This way, they can keep their stomata partially close ...
... into CO2 and pyruvate. In this way, C4 plants maintin a concentrtation of CO2 in their bundle sheath cells as an adaption to hot, dry climates. If they were to open their stomata to take in CO2 during the day, they would also lose too much water. This way, they can keep their stomata partially close ...
DNA and RNA - Mrs-Lamberts-Biology
... Chromosomes in Eukaryotic Cells: • Eukaryotic cells have 1,000 times as much DNA as prokaryotes. • It is packed tightly in the nucleus of the cell. • DNA is a long molecule – the nucleus of a human cell contains 1 meter (3 feet) of DNA. • Chromosomes are composed of DNA wrapped tightly around prote ...
... Chromosomes in Eukaryotic Cells: • Eukaryotic cells have 1,000 times as much DNA as prokaryotes. • It is packed tightly in the nucleus of the cell. • DNA is a long molecule – the nucleus of a human cell contains 1 meter (3 feet) of DNA. • Chromosomes are composed of DNA wrapped tightly around prote ...
Prokaryotic Gene Regulation | Principles of Biology from Nature
... consists of an operator and a promoter. The promoter is the region of the DNA that has a specific sequence that the RNA polymerase binds to for initiation of transcription. The ability of RNA polymerase to access the promoter is regulated by the operator and transcription factors. An operator is a s ...
... consists of an operator and a promoter. The promoter is the region of the DNA that has a specific sequence that the RNA polymerase binds to for initiation of transcription. The ability of RNA polymerase to access the promoter is regulated by the operator and transcription factors. An operator is a s ...
A primer on the structure and function of genes
... corresponds exactly to the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide. Often several protein coding genes are regulated and expressed as a single unit; this is called an OPERON (see figure below). The mRNA for these adjacent coding sequences is synthesized in one piece. The operon includes regulator ...
... corresponds exactly to the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide. Often several protein coding genes are regulated and expressed as a single unit; this is called an OPERON (see figure below). The mRNA for these adjacent coding sequences is synthesized in one piece. The operon includes regulator ...
Genetics and Protein Synthesis
... The complex then shifts along the mRNA to the next triplet, opening the A site. The new tRNA enters at the A site. When the codon in the A site is a termination codon, a releasing factor binds to the site, stopping translation and releasing the ribosomal complex and mRNA. ...
... The complex then shifts along the mRNA to the next triplet, opening the A site. The new tRNA enters at the A site. When the codon in the A site is a termination codon, a releasing factor binds to the site, stopping translation and releasing the ribosomal complex and mRNA. ...
Protein Synthesis
... • Clover-leaf shape • Single stranded molecule with attachment site at one end for an amino acid • Found out in the cytoplasm • Brings amino acid to ribosome ...
... • Clover-leaf shape • Single stranded molecule with attachment site at one end for an amino acid • Found out in the cytoplasm • Brings amino acid to ribosome ...
Chapter 8 Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes 6
... The mammalian activator E2F binds sites upstream of its target genes. A second protein, the repressor Rb, controls the activity of E2F by binding E2F, thus blocking activation and recruiting a deacetylase enzyme that represses the target genes. Phosphorylation of Rb causes release of Rb from E2F, an ...
... The mammalian activator E2F binds sites upstream of its target genes. A second protein, the repressor Rb, controls the activity of E2F by binding E2F, thus blocking activation and recruiting a deacetylase enzyme that represses the target genes. Phosphorylation of Rb causes release of Rb from E2F, an ...
Ch 5
... mRNA has codons – a sequence of 3 nucleotides that codes for an amino acid. tRNA has anticodons that are complementary to mRNA’s codons. AUG is the universal ‘start’ codon that tells the ribosome to start translating. There are three ‘stop’codons – UAA, UAG and UGA – that tell the ribosome to stop t ...
... mRNA has codons – a sequence of 3 nucleotides that codes for an amino acid. tRNA has anticodons that are complementary to mRNA’s codons. AUG is the universal ‘start’ codon that tells the ribosome to start translating. There are three ‘stop’codons – UAA, UAG and UGA – that tell the ribosome to stop t ...
Summary
... the archaeal chromatin proteins HMfA and HMfB). These studies suggest that the DNA binding properties of these proteins are altered by physico-chemical conditions corresponding with different cellular environments. Due to the alteration of their DNA binding properties these proteins’ cellular functi ...
... the archaeal chromatin proteins HMfA and HMfB). These studies suggest that the DNA binding properties of these proteins are altered by physico-chemical conditions corresponding with different cellular environments. Due to the alteration of their DNA binding properties these proteins’ cellular functi ...