The National Eye Institute Supercourse
... diseases and conditions that in majority have a genetic basis ...
... diseases and conditions that in majority have a genetic basis ...
投影片 1
... Poly A binding protein (PABPI), interact with both mRNA poly A and Eif4g Two ends is very close together, then ribosome subunit easy to bind. ...
... Poly A binding protein (PABPI), interact with both mRNA poly A and Eif4g Two ends is very close together, then ribosome subunit easy to bind. ...
Mechanisms of Glucocorticoid-Regulated Gene Transcription
... the majority of GR binding is at promoter-distal locations [53–56]. One representative study showed that for genes that are up regulated in response to glucocorticoid treatment (likely GR target genes), 50 % of the binding sites were located at a distance greater than 10 kb from the transcriptional ...
... the majority of GR binding is at promoter-distal locations [53–56]. One representative study showed that for genes that are up regulated in response to glucocorticoid treatment (likely GR target genes), 50 % of the binding sites were located at a distance greater than 10 kb from the transcriptional ...
RECOMBINANT HUMAN INSULIN-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR I
... Shipping: Products may be shipped on ice pack or dry ice. ...
... Shipping: Products may be shipped on ice pack or dry ice. ...
Snímek 1
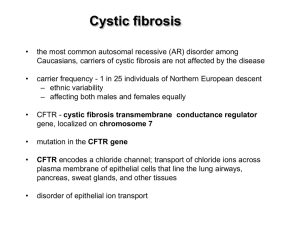
... • transport of chloride ions across plasma membrane of epithelial cells (lungs, pancreas, sweat glands, and other tissues) • mutations in the CFTR gene ...
... • transport of chloride ions across plasma membrane of epithelial cells (lungs, pancreas, sweat glands, and other tissues) • mutations in the CFTR gene ...
FAD
... triacylglycerol—glycosidic linkage C. nucleic acid—phosphodiester linkage D. protein—ester linkage E. steroid—peptide bond 27. When a nucleic acid undergoes hydrolysis, the resulting subunits are: A. amino acids B. monosaccharides C. nucleotides D. fatty acids E. carotenoids 28. ATP is important in ...
... triacylglycerol—glycosidic linkage C. nucleic acid—phosphodiester linkage D. protein—ester linkage E. steroid—peptide bond 27. When a nucleic acid undergoes hydrolysis, the resulting subunits are: A. amino acids B. monosaccharides C. nucleotides D. fatty acids E. carotenoids 28. ATP is important in ...
Chapter 16.2 - DNA Replication Details 2 - kyoussef-mci
... Primer removed but cannot be replaced with DNA because no 3 end available for DNA polymerase ...
... Primer removed but cannot be replaced with DNA because no 3 end available for DNA polymerase ...
DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis PPT
... 2.RNA polymerase (enzyme) binds to a region of DNA called the promoter which has the start codon AUG to code for the amino acid methionine 3.Promoters mark the beginning of a DNA chain in prokaryotes, but mark the beginning of 1 to several related genes in eukaryotes 4.The 2 DNA strands separate, bu ...
... 2.RNA polymerase (enzyme) binds to a region of DNA called the promoter which has the start codon AUG to code for the amino acid methionine 3.Promoters mark the beginning of a DNA chain in prokaryotes, but mark the beginning of 1 to several related genes in eukaryotes 4.The 2 DNA strands separate, bu ...
خلف زيدان قدوري .م كلية تكريت جامعة – االسنان طب
... structures with three or four strands can form. Nucleic acids are linear polymers (chains) of nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of three components: a purine or pyrimidine nucleobase (sometimes termed nitrogenous base or simply base), a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. The substructure cons ...
... structures with three or four strands can form. Nucleic acids are linear polymers (chains) of nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of three components: a purine or pyrimidine nucleobase (sometimes termed nitrogenous base or simply base), a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. The substructure cons ...
20_Lecture_Presentation
... Bacterial restriction enzymes cut DNA molecules at specific DNA sequences They protect the bacterial cell by cutting foreign DNA from other organisms or phages Hundreds have been identified, they are highly specific and recognize a particular sort DNA sequence or Restriction site Most restric ...
... Bacterial restriction enzymes cut DNA molecules at specific DNA sequences They protect the bacterial cell by cutting foreign DNA from other organisms or phages Hundreds have been identified, they are highly specific and recognize a particular sort DNA sequence or Restriction site Most restric ...
A new phagemid vector for positive selection of recombinants based
... the six inserted amino acids Glu-Phe-Gln-Lys-Ser-Leu instead of Val-36 [1,10]. The modi¢ed regions of this construct pBa-2 (Fig. 1) were sequenced and its toxicity for lacIq -negative E. coli TOP10 cells was tested. However, pBa-2 turned out to be non-toxic and even the size of colonies was not redu ...
... the six inserted amino acids Glu-Phe-Gln-Lys-Ser-Leu instead of Val-36 [1,10]. The modi¢ed regions of this construct pBa-2 (Fig. 1) were sequenced and its toxicity for lacIq -negative E. coli TOP10 cells was tested. However, pBa-2 turned out to be non-toxic and even the size of colonies was not redu ...
Shetti, a simple tool to parse, manipulate and search large datasets
... sequences. The Shetti tool can be used to search for a sequence, species, protein/gene or pattern/motif. Moreover, it can also be used to construct a universal consensus or molecular signatures for proteins based on their physical characteristics. Shetti is an efficient and fast tool that can deal w ...
... sequences. The Shetti tool can be used to search for a sequence, species, protein/gene or pattern/motif. Moreover, it can also be used to construct a universal consensus or molecular signatures for proteins based on their physical characteristics. Shetti is an efficient and fast tool that can deal w ...
5 end
... seem to make it easier to move mRNA out of the nucleus They protect mRNA from hydrolytic (causing hydrolysis) enzymes They help ribosomes attach to the 5 end Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... seem to make it easier to move mRNA out of the nucleus They protect mRNA from hydrolytic (causing hydrolysis) enzymes They help ribosomes attach to the 5 end Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Crystal Structure of a 70 Subunit Fragment from
... RNAP binding within E. coli s 54, an alternative s factor that is not a member of the s70 family (Wong et al., 1994; Tintut and Gralla, 1995). The largest concentration of mutations causing loss of core RNAP binding fell within or just adjacent to a short stretch of residues that bears resemblance t ...
... RNAP binding within E. coli s 54, an alternative s factor that is not a member of the s70 family (Wong et al., 1994; Tintut and Gralla, 1995). The largest concentration of mutations causing loss of core RNAP binding fell within or just adjacent to a short stretch of residues that bears resemblance t ...
DNA STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... Why do we need to cool the mixture? DNases or enzymes that destroy DNA are present in the cell’s cytoplasm. They are there to protect the cell from invasion by viruses. Once the nuclear membrane is destroyed by the soap the DNA is now susceptible to the DNases and will quickly be degraded. However, ...
... Why do we need to cool the mixture? DNases or enzymes that destroy DNA are present in the cell’s cytoplasm. They are there to protect the cell from invasion by viruses. Once the nuclear membrane is destroyed by the soap the DNA is now susceptible to the DNases and will quickly be degraded. However, ...
Application of Molecular Techniques to Improved Detection of
... genotype, unlike the best assays, which include the feature of testing response to control agents. Primary discriminating dose assays provide response data. In addition, DNA diagnostics are limited by their specificity; more than one mutation might confer the same resistant phenotype. However, most ...
... genotype, unlike the best assays, which include the feature of testing response to control agents. Primary discriminating dose assays provide response data. In addition, DNA diagnostics are limited by their specificity; more than one mutation might confer the same resistant phenotype. However, most ...
Biosynthesis of heme in mammals
... In contrast to ALAS, there is only a single ALAD gene in humans, located on chromosome 9q34 [32], which consists of two alternatively spliced non-coding exons (1A and 1B) and eleven coding exons (Fig. 4) [33]. The translational start site (ATG) is located in exon 2. A “housekeeping” promoter is loca ...
... In contrast to ALAS, there is only a single ALAD gene in humans, located on chromosome 9q34 [32], which consists of two alternatively spliced non-coding exons (1A and 1B) and eleven coding exons (Fig. 4) [33]. The translational start site (ATG) is located in exon 2. A “housekeeping” promoter is loca ...
3 - Rudner Lab - Harvard University
... structure to late gene expression? The flagellum is a hollow tube-like structure. Construction of the flagellum (both the hook-basal body and the flagellar filament) occurs at the distal tip by secretion of proteins through the conduit where they are added onto the growing structure (Chilcott and Hu ...
... structure to late gene expression? The flagellum is a hollow tube-like structure. Construction of the flagellum (both the hook-basal body and the flagellar filament) occurs at the distal tip by secretion of proteins through the conduit where they are added onto the growing structure (Chilcott and Hu ...
IL-1β +3953 C/T
... • involved in control of proliferation, differentiation and function of IS cells • involved in inflammatory processes and neuronal, hematopoietic and embryonic development of an organism • pleiotropic ...
... • involved in control of proliferation, differentiation and function of IS cells • involved in inflammatory processes and neuronal, hematopoietic and embryonic development of an organism • pleiotropic ...
PDF file
... is associated to the initiator and gives rise to unbranched amylose chains. Glycogen formation is completed by the so-called branching enzyme, that ramifies the amylose glucan (Tolmasky and Krisman, 1987; Tolmasky et al., 1998) to form mature glycogen molecules. No insect homologue of mammalian or y ...
... is associated to the initiator and gives rise to unbranched amylose chains. Glycogen formation is completed by the so-called branching enzyme, that ramifies the amylose glucan (Tolmasky and Krisman, 1987; Tolmasky et al., 1998) to form mature glycogen molecules. No insect homologue of mammalian or y ...
Using Fruit Flies to Investigate a Cancer Metastasis
... It is unclear whether the acid sequence for the WPD loop in fruit flies is different enough to cause a phenotype change. To begin to test the need for the WPD loop, human PRL-3 (hPRL-3) will be transferred into fruit flies because hPRL-3 has a conserved version of the WPD loop. The transgenic fruit ...
... It is unclear whether the acid sequence for the WPD loop in fruit flies is different enough to cause a phenotype change. To begin to test the need for the WPD loop, human PRL-3 (hPRL-3) will be transferred into fruit flies because hPRL-3 has a conserved version of the WPD loop. The transgenic fruit ...