DVM with the ICL7106
... of passive components combine to generate the clock signal used to gate the auto-ranging logic. A closer look at the inner workings of the ICL7106 will help clarify the discussion of this circuit. The analog section of the ICL7106 is shown in Figure 3. It can be shown that CREF low (pin 33 of ICL710 ...
... of passive components combine to generate the clock signal used to gate the auto-ranging logic. A closer look at the inner workings of the ICL7106 will help clarify the discussion of this circuit. The analog section of the ICL7106 is shown in Figure 3. It can be shown that CREF low (pin 33 of ICL710 ...
1.5 GHz Low Noise Silicon MMIC Amplifier Technical Data INA-52063
... INA-52063 Applications Information Introduction The INA-52063 is a silicon RFIC amplifier that is designed with an internal resistive feedback network to provide a 50 Ω input and 50 Ω output impedance. With a Third Order Intercept Point of +20 dBm and a low Noise Figure of 4 dB, the INA-52063 is esp ...
... INA-52063 Applications Information Introduction The INA-52063 is a silicon RFIC amplifier that is designed with an internal resistive feedback network to provide a 50 Ω input and 50 Ω output impedance. With a Third Order Intercept Point of +20 dBm and a low Noise Figure of 4 dB, the INA-52063 is esp ...
Slide 1 - sm.luth.se
... Figure 4.9 Cross-section of a CMOS integrated circuit. Note that the PMOS transistor is formed in a separate n-type region, known as an n well. Another arrangement is also possible in which an n-type body is used and the n device is formed in a p well. Not shown are the connections made to the p-ty ...
... Figure 4.9 Cross-section of a CMOS integrated circuit. Note that the PMOS transistor is formed in a separate n-type region, known as an n well. Another arrangement is also possible in which an n-type body is used and the n device is formed in a p well. Not shown are the connections made to the p-ty ...
Series and Parallel Resistive Circuits
... 2. Repeat step 1 for the remaining resistors. 3. Select the Constant Voltage block. On the 'Inspector' tab, set the V voltage parameter to 14 V. 4. Select the Constant Current block. Set the I current to 21 A. 5. Attach a probe to the line from the bottom resistor. On the 'Inspector' tab, deselect t ...
... 2. Repeat step 1 for the remaining resistors. 3. Select the Constant Voltage block. On the 'Inspector' tab, set the V voltage parameter to 14 V. 4. Select the Constant Current block. Set the I current to 21 A. 5. Attach a probe to the line from the bottom resistor. On the 'Inspector' tab, deselect t ...
Slide 1 - Cobb Learning
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
Electric Current
... • In general, the resistance of materials goes up as the temperature goes up, due to thermal effects. This property can be used in ...
... • In general, the resistance of materials goes up as the temperature goes up, due to thermal effects. This property can be used in ...
TDE1747
... applications, specifically to drive lamps, relays, stepping motors. This device is essentially blow-out proof. Current limiting is available to limit the peak output current to safe values. Adjustment only requires one external resistor. In addition, thermal shut down is provided to keep the IC from ...
... applications, specifically to drive lamps, relays, stepping motors. This device is essentially blow-out proof. Current limiting is available to limit the peak output current to safe values. Adjustment only requires one external resistor. In addition, thermal shut down is provided to keep the IC from ...
APPLICATION NOTE U-102 UC1637/2637/3637 SWITCHED MODE
... (Eq. 17) is shown. The plot shows that as the frequency increases, the tach output decreases and the phase lag increases towards a maximum of 180°. This means that although we can introduce plenty of gain at very low frequencies, where the phase lag is low, the added gain must be reduced at the high ...
... (Eq. 17) is shown. The plot shows that as the frequency increases, the tach output decreases and the phase lag increases towards a maximum of 180°. This means that although we can introduce plenty of gain at very low frequencies, where the phase lag is low, the added gain must be reduced at the high ...
Phys 345 Electronics for Scientists
... • Any two-terminal linear circuit can be replaced with a current source and a parallel resistor which will produce the same effects at the terminals • IN is the short-circuit current ISC of the circuit that the Norton generator is replacing • Again, RN is the ratio of VOC to the short-circuit curren ...
... • Any two-terminal linear circuit can be replaced with a current source and a parallel resistor which will produce the same effects at the terminals • IN is the short-circuit current ISC of the circuit that the Norton generator is replacing • Again, RN is the ratio of VOC to the short-circuit curren ...
DC Analysis
... Thus no iterative process is necessary. With the Ymatrix of the components, i.e. now a complex matrix, and the appropriate extensions it is necessary to solve the equation system similar to the (linear) DC analysis. ...
... Thus no iterative process is necessary. With the Ymatrix of the components, i.e. now a complex matrix, and the appropriate extensions it is necessary to solve the equation system similar to the (linear) DC analysis. ...
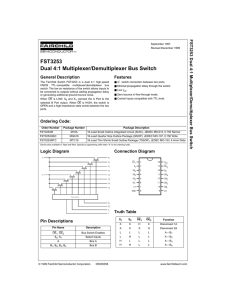
FST3253 Dual 4:1 Multiplexer/Demultiplexer Bus Switch FST3 253
... Note 4: Typical values are at VCC = 5.0V and T A = +25°C Note 5: Measured by the voltage drop between A and B pins at the indicated current through the switch. On resistance is determined by the lower of the voltages on the two (A or B) pins. ...
... Note 4: Typical values are at VCC = 5.0V and T A = +25°C Note 5: Measured by the voltage drop between A and B pins at the indicated current through the switch. On resistance is determined by the lower of the voltages on the two (A or B) pins. ...