EXAM1
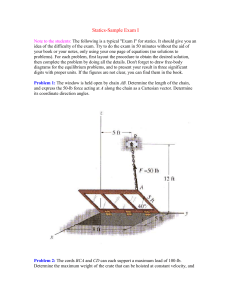
... idea of the difficulty of the exam. Try to do the exam in 50 minutes without the aid of your book or your notes, only using your one page of equations (no solutions to problems). For each problem, first layout the procedure to obtain the desired solution, then complete the problem by doing all the d ...
... idea of the difficulty of the exam. Try to do the exam in 50 minutes without the aid of your book or your notes, only using your one page of equations (no solutions to problems). For each problem, first layout the procedure to obtain the desired solution, then complete the problem by doing all the d ...
MS-Word File
... 10.An employee is filling out an expense report using her receipts. Should she use Exact or Approximate numbers? 11. A company wants to compare their sales to all of their competitors sales. What type of graph would be most appropriate 12. A bar Graph 13. Has a mass of about 1 gram ...
... 10.An employee is filling out an expense report using her receipts. Should she use Exact or Approximate numbers? 11. A company wants to compare their sales to all of their competitors sales. What type of graph would be most appropriate 12. A bar Graph 13. Has a mass of about 1 gram ...
Section 6.1: Law of Sines
... measures of the triangle – two sides, two angles, or one angle and one side. The breaks down into the following four cases: 1. Two angles and any side (AAS or ASA). 2. Two sides and an angle opposite one of them (SSA). 3. Three sides (SSS). 4. Two sides and their included angle (SAS). The first two ...
... measures of the triangle – two sides, two angles, or one angle and one side. The breaks down into the following four cases: 1. Two angles and any side (AAS or ASA). 2. Two sides and an angle opposite one of them (SSA). 3. Three sides (SSS). 4. Two sides and their included angle (SAS). The first two ...
Weber problem

In geometry, the Weber problem, named after Alfred Weber, is one of the most famous problems in location theory. It requires finding a point in the plane that minimizes the sum of the transportation costs from this point to n destination points, where different destination points are associated with different costs per unit distance.The Weber problem generalizes the geometric median, which assumes transportation costs per unit distance are the same for all destination points, and the problem of computing the Fermat point, the geometric median of three points. For this reason it is sometimes called the Fermat–Weber problem, although the same name has also been used for the unweighted geometric median problem. The Weber problem is in turn generalized by the attraction–repulsion problem, which allows some of the costs to be negative, so that greater distance from some points is better.