2011. Lecture 2
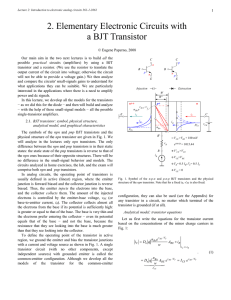
... physical structure of the npn transistor are given in Fig. 1. We will analyze in the lectures only npn transistors. The only difference between the npn and pnp transistors is in their static states: the static state of the pnp transistors is reverse to that of the npn ones because of their opposite ...
... physical structure of the npn transistor are given in Fig. 1. We will analyze in the lectures only npn transistors. The only difference between the npn and pnp transistors is in their static states: the static state of the pnp transistors is reverse to that of the npn ones because of their opposite ...
7 chapter 6
... of operation. Notice, also, that the transistors are labeled Q 1 and Q2. Loading Effects: In determining the voltage gain of the first stage, you must consider the loading effect of the second stage. Because the coupling capacitor C3 effectively appears as a short at the signal frequency, the total ...
... of operation. Notice, also, that the transistors are labeled Q 1 and Q2. Loading Effects: In determining the voltage gain of the first stage, you must consider the loading effect of the second stage. Because the coupling capacitor C3 effectively appears as a short at the signal frequency, the total ...
Circuit Building Lab
... 8. Build a parallel circuit with two bulbs and have your voltage source set at 3 volts. 9. If you add another bulb to this circuit in parallel, what do you think will happen to the brightness of the bulbs? ...
... 8. Build a parallel circuit with two bulbs and have your voltage source set at 3 volts. 9. If you add another bulb to this circuit in parallel, what do you think will happen to the brightness of the bulbs? ...
Practice Work #1
... understand that the voltage dropped across a current-conducting diode does change with the amount of current going through it, but that this change is fairly small over a wide range of currents. This is why many textbooks simply say the voltage drop across a conducting, semiconductor diode remains c ...
... understand that the voltage dropped across a current-conducting diode does change with the amount of current going through it, but that this change is fairly small over a wide range of currents. This is why many textbooks simply say the voltage drop across a conducting, semiconductor diode remains c ...
Instructor`s Guide - The Described and Captioned Media Program
... circuit has a single path for current flow but has more than one resistor. A parallel circuit is yet more complex with more than one resistor, each with its own pathway for current. ...
... circuit has a single path for current flow but has more than one resistor. A parallel circuit is yet more complex with more than one resistor, each with its own pathway for current. ...
Simple circuits worksheet
... In applications where the voltage source possesses very little internal resistance of its own, the current surge resulting from such a short-circuit may be huge. Very large surges of electric current are capable of heating wires to the point where their insulation bursts into flames, as well as caus ...
... In applications where the voltage source possesses very little internal resistance of its own, the current surge resulting from such a short-circuit may be huge. Very large surges of electric current are capable of heating wires to the point where their insulation bursts into flames, as well as caus ...
Ford Motor Company - Automotive Systems Training
... The ease or difficulty with which electrons flow ...
... The ease or difficulty with which electrons flow ...
Chapter 13: Electric Circuits 1. A household circuit rated at 120 Volts
... 24. A 100 watt bulb is rated for use in a 120 volt line. During a brownout the actual voltage drops to 100 V. The actual power dissipated in the bulb under these conditions is A. 120 W. B. 100 W. C. 83.3 W. D. 69.4 W. E. 48.2 W. Answer: D 25. A heater is rated to dissipate 1800 W when connected to ...
... 24. A 100 watt bulb is rated for use in a 120 volt line. During a brownout the actual voltage drops to 100 V. The actual power dissipated in the bulb under these conditions is A. 120 W. B. 100 W. C. 83.3 W. D. 69.4 W. E. 48.2 W. Answer: D 25. A heater is rated to dissipate 1800 W when connected to ...
A Modified Bipolar Translinear Cell with Improved Linear Range and
... front end of a second-generation current controlled conveyor (CCCII) [2] and an operational transconductance amplifier (OTA) [3], [4]. It can also be used as current controlled floating and/or grounded resistor [5], [6], [7] to help setting the operating condition in an electronic circuit such as os ...
... front end of a second-generation current controlled conveyor (CCCII) [2] and an operational transconductance amplifier (OTA) [3], [4]. It can also be used as current controlled floating and/or grounded resistor [5], [6], [7] to help setting the operating condition in an electronic circuit such as os ...
Laboratory Manual for DC Electrical Circuits
... indispensible in the prototyping of electronic circuits and extremely useful when examining the operation of DC systems. Of equal importance is the handheld digital multimeter or DMM. This device is designed to measure voltage, current, and resistance at a minimum, although some units may offer the ...
... indispensible in the prototyping of electronic circuits and extremely useful when examining the operation of DC systems. Of equal importance is the handheld digital multimeter or DMM. This device is designed to measure voltage, current, and resistance at a minimum, although some units may offer the ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.