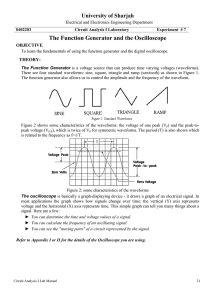
Types of Circuits
... A) What is the total voltage above? B) What is the voltage from B to F? C) What is the resistance from B to F? D) Find the current flowing from B to F (label it on the diagram). ...
... A) What is the total voltage above? B) What is the voltage from B to F? C) What is the resistance from B to F? D) Find the current flowing from B to F (label it on the diagram). ...
Part A: Multiple Choice / 18 marks - hhs-snc1d
... Circle the best answer for each question. 1. Which of the following would be a good conductor? a) Fur b) Oxygen gas c) Plastic d) Aluminum 2. Four 2V dry cells are connected in series. What would the voltage going through the circuit be? a) 2V b) 4V c) 8V d) 42V 3. 4 light bulbs are connected in par ...
... Circle the best answer for each question. 1. Which of the following would be a good conductor? a) Fur b) Oxygen gas c) Plastic d) Aluminum 2. Four 2V dry cells are connected in series. What would the voltage going through the circuit be? a) 2V b) 4V c) 8V d) 42V 3. 4 light bulbs are connected in par ...
Lab 7
... V est , I(t) = CsV est = Iest . Hence V = ZC I, where ZC = 1/(sC). The current-voltage relationship for inductance is V (t) = L(dI(t)/dt). As above consider V (t) = V est . Then I(t) = LsV est = Iest . So V = ZL I, where ZL = sL. You can apply the same analysis to a resistance R to obtain V = IR. So ...
... V est , I(t) = CsV est = Iest . Hence V = ZC I, where ZC = 1/(sC). The current-voltage relationship for inductance is V (t) = L(dI(t)/dt). As above consider V (t) = V est . Then I(t) = LsV est = Iest . So V = ZL I, where ZL = sL. You can apply the same analysis to a resistance R to obtain V = IR. So ...
DN74 - Techniques for Deriving 3.3V from 5V Supplies
... input to 3.3V with an output tolerance of only 3% (100mV). The LT1129-3.3 can handle up to 700mA in surface mount configurations, and includes both 16µA shutdown and 50µA standby currents for system sleep modes. Unlike other linear regulators, the LT1129-3.3 combines both low dropout and low voltage ...
... input to 3.3V with an output tolerance of only 3% (100mV). The LT1129-3.3 can handle up to 700mA in surface mount configurations, and includes both 16µA shutdown and 50µA standby currents for system sleep modes. Unlike other linear regulators, the LT1129-3.3 combines both low dropout and low voltage ...
College of Micronesia-FSM
... a. Why current is the same in all parts of a series circuit. 9 hrs b. Calculating total resistance, current, the voltage drops, and total power. c. Series aiding and series opposing voltages d. Analyzing series circuit e. Effect of an open circuit in a series path f. Switches represent the AND logic ...
... a. Why current is the same in all parts of a series circuit. 9 hrs b. Calculating total resistance, current, the voltage drops, and total power. c. Series aiding and series opposing voltages d. Analyzing series circuit e. Effect of an open circuit in a series path f. Switches represent the AND logic ...
Circuits Lab - University of Michigan SharePoint Portal
... The current and voltage of a circuit are measured in the fashion shown below. Voltage: Voltage is the electrical “push” from the battery to produce current. Voltage is measured across the device, because we want to know the potential difference above and below the device. This is a direct current (D ...
... The current and voltage of a circuit are measured in the fashion shown below. Voltage: Voltage is the electrical “push” from the battery to produce current. Voltage is measured across the device, because we want to know the potential difference above and below the device. This is a direct current (D ...
Check Your Understanding – Parallel Circuits – KEY (see highlights)
... a. The current at Y is greater than the current at Q. Less than b. The current at Y is greater than the current at P. less than c. The current at Y is greater than the current at Z. equal d. The current at P is greater than the current at Q. e. The current at Q is greater than the current at P. less ...
... a. The current at Y is greater than the current at Q. Less than b. The current at Y is greater than the current at P. less than c. The current at Y is greater than the current at Z. equal d. The current at P is greater than the current at Q. e. The current at Q is greater than the current at P. less ...
Note-A-Rific: Kirchhoff
... The power of these rules comes when you need to analyze a more complicated circuit that has a combination of series and parallel circuits together. • Kirchhoff’s rules still work, you just need to be careful about how you use them. • Unfortunately, there is no guaranteed way to always analyze a cir ...
... The power of these rules comes when you need to analyze a more complicated circuit that has a combination of series and parallel circuits together. • Kirchhoff’s rules still work, you just need to be careful about how you use them. • Unfortunately, there is no guaranteed way to always analyze a cir ...
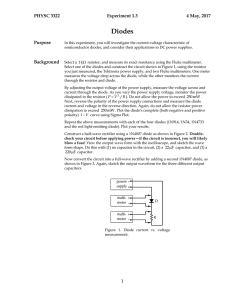
Experiment 1-3
... Discuss and compare the I V curves for the different diodes. A simplified model for forward conduction in a semiconductor diode relates the current and voltage by ...
... Discuss and compare the I V curves for the different diodes. A simplified model for forward conduction in a semiconductor diode relates the current and voltage by ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.