Computer Aided Design
... NODESET1 is a one-pin symbol which helps calculate the bias point by providing a initial guess for some net. NODESET2 is a two-pin symbol which helps calculate the bias point between two nets. Some or all of the circuit nets may be given an initial guess. NODESET symbols are effective for the bias ...
... NODESET1 is a one-pin symbol which helps calculate the bias point by providing a initial guess for some net. NODESET2 is a two-pin symbol which helps calculate the bias point between two nets. Some or all of the circuit nets may be given an initial guess. NODESET symbols are effective for the bias ...
RB721Q-40 - Digi-Key
... No technical content pages of this document may be reproduced in any form or transmitted by any means without prior permission of ROHM CO.,LTD. The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Up ...
... No technical content pages of this document may be reproduced in any form or transmitted by any means without prior permission of ROHM CO.,LTD. The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Up ...
lecture3
... If a linear circuit is excited by more that one independent source, then the total response is simply the sum of the responses of the individual sources. Voltage sources - short circuit Current source - open circuit ...
... If a linear circuit is excited by more that one independent source, then the total response is simply the sum of the responses of the individual sources. Voltage sources - short circuit Current source - open circuit ...
AC_Circuits1
... During the positive half-cycle of the voltage waveform, plate X of the capacitor becomes positively charged and plate Y negatively charged. During the negative half-cycle, X receives a negative charge and Y a positive one. There is therefore an alternating flow of charge or alternating current, i, t ...
... During the positive half-cycle of the voltage waveform, plate X of the capacitor becomes positively charged and plate Y negatively charged. During the negative half-cycle, X receives a negative charge and Y a positive one. There is therefore an alternating flow of charge or alternating current, i, t ...
Electronic Engineering
... connected between it’s input and output then this is equivalent to the amplifier with one capacitor connected from its input to ground and another between its output and ground. The value of the input capacitor is C (A + 1) and the output capacitor is given by C (A + 1)/A ...
... connected between it’s input and output then this is equivalent to the amplifier with one capacitor connected from its input to ground and another between its output and ground. The value of the input capacitor is C (A + 1) and the output capacitor is given by C (A + 1)/A ...
Electric Circuit`s
... parallel. 2 Resistors two and three are connected in parallel to each other. They are then connected in series to resistor four. This combination is in series to resistor one. 3 Resistors two and three are connected in series to each other. They are connected in parallel to resistor four. This combi ...
... parallel. 2 Resistors two and three are connected in parallel to each other. They are then connected in series to resistor four. This combination is in series to resistor one. 3 Resistors two and three are connected in series to each other. They are connected in parallel to resistor four. This combi ...
Exam Solutions
... (21 pts) Z-bus: A three-bus network is operating so that all buses have voltage magnitudes equal to 1.0 pu. Each bus is connected to the other two buses via branches having impedance of j0.1 pu. The Z-bus of the network is given as: ...
... (21 pts) Z-bus: A three-bus network is operating so that all buses have voltage magnitudes equal to 1.0 pu. Each bus is connected to the other two buses via branches having impedance of j0.1 pu. The Z-bus of the network is given as: ...
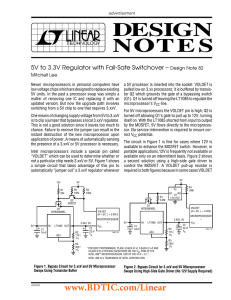
DN82 - 5V to 3.3V Regulator with Fail-Safe Switchover
... For certain families of microprocessors, 3.3V is required. The circuits shown in Figures 1 and 2 are fully compatible with 3.3V applications by simply substituting a fixed 3.3V version of the regulator (use an LT10853.3). Higher current operation is also possible. The LT1085 is suitable for 3A appli ...
... For certain families of microprocessors, 3.3V is required. The circuits shown in Figures 1 and 2 are fully compatible with 3.3V applications by simply substituting a fixed 3.3V version of the regulator (use an LT10853.3). Higher current operation is also possible. The LT1085 is suitable for 3A appli ...
EE 321 Analog Electronics, Fall 2013 Homework #5 solution
... (a) In this case the input voltage is above ground, and the op-amp will attempt to adjust by drawing current in. It can draw current through D1 , and then D2 will not be conducting. Thus, vA = −VD = −0.7 V, v− = 0 V. For the ground we realize that no current flows through the loop containing ground, ...
... (a) In this case the input voltage is above ground, and the op-amp will attempt to adjust by drawing current in. It can draw current through D1 , and then D2 will not be conducting. Thus, vA = −VD = −0.7 V, v− = 0 V. For the ground we realize that no current flows through the loop containing ground, ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.