Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 14 – Ethers
... • Because of their intermediate polarity, ethers are good solvents. They can dissolve nonpolar, polar, and even some ionic compounds. Although ether molecules cannot hydrogen bond with each other, they can act as hydrogen bond donors. The lone pairs of electrons can stabilize electron-deficient comp ...
... • Because of their intermediate polarity, ethers are good solvents. They can dissolve nonpolar, polar, and even some ionic compounds. Although ether molecules cannot hydrogen bond with each other, they can act as hydrogen bond donors. The lone pairs of electrons can stabilize electron-deficient comp ...
NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91391) 2013
... Carboxylic acid (butanoic acid) is obtained by reacting a mixture of butan-1ol with acidified potassium dichromate solution (under reflux conditions) until all of the reactant has been converted to butanoic acid. Observations: orange Cr2O72– to green /, purple MnO4– to colourless / aldehyde condense ...
... Carboxylic acid (butanoic acid) is obtained by reacting a mixture of butan-1ol with acidified potassium dichromate solution (under reflux conditions) until all of the reactant has been converted to butanoic acid. Observations: orange Cr2O72– to green /, purple MnO4– to colourless / aldehyde condense ...
reactions.html Reaction 1. Electrophilic addition of
... lithium metal in ammonia for trans product ...
... lithium metal in ammonia for trans product ...
Organic Compounds Containing C, H and O
... Ans. i. a. Nitro (-NO2) group is an electron withdrawing whereas methoxy (-OCH3) group is electron releasing in nature. o-nitrophenol produces H+ ions easily but methoxyphenol does not. This is because o-nitrophenoxide ion is stabilised due to resonance. This is not true with o-methoxyphenoxide ion. ...
... Ans. i. a. Nitro (-NO2) group is an electron withdrawing whereas methoxy (-OCH3) group is electron releasing in nature. o-nitrophenol produces H+ ions easily but methoxyphenol does not. This is because o-nitrophenoxide ion is stabilised due to resonance. This is not true with o-methoxyphenoxide ion. ...
Additional file 1
... 1-Acenaphthen-5-yl-ethanone (3): Pyridinium dichromate (3.0 g, 9.0 mmol) was added to a stirred solution of alcohol 2 (1.8 g, 9.0 mmol) and powdered 4Å molecular sieve (0.75 g) in anhydrous CH2Cl2 (50 mL) at 0°C. After the addition was complete, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 h, t ...
... 1-Acenaphthen-5-yl-ethanone (3): Pyridinium dichromate (3.0 g, 9.0 mmol) was added to a stirred solution of alcohol 2 (1.8 g, 9.0 mmol) and powdered 4Å molecular sieve (0.75 g) in anhydrous CH2Cl2 (50 mL) at 0°C. After the addition was complete, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 h, t ...
Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones
... Benedict’s Test Benedict’s test • gives a positive result with compounds that have an aldehyde functional group and an adjacent hydroxyl group. • utilizes Benedict’s solution, which contains Cu2+ (CuSO4). When the solution is added to this type of aldehyde and heated, a brick-red solid of Cu2O form ...
... Benedict’s Test Benedict’s test • gives a positive result with compounds that have an aldehyde functional group and an adjacent hydroxyl group. • utilizes Benedict’s solution, which contains Cu2+ (CuSO4). When the solution is added to this type of aldehyde and heated, a brick-red solid of Cu2O form ...
CHM 3200 - Miami Dade College
... c. Illustrating methodologies for the synthesis of ketones (via oxidation of secondary alcohols). d. Identifying and illustrating reactions of aldehydes and ketones (nucleophilic addition reactions, hydration, acetal formation, Grignard reaction, conjugate addition, α-substitution reactions, nucleop ...
... c. Illustrating methodologies for the synthesis of ketones (via oxidation of secondary alcohols). d. Identifying and illustrating reactions of aldehydes and ketones (nucleophilic addition reactions, hydration, acetal formation, Grignard reaction, conjugate addition, α-substitution reactions, nucleop ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 PART-A
... 11. Give an example for α, β, γ and δ-elimination reaction. 12. State and explain the Hammond postulate to the bromination of n-propane. 13. How will you determine the reaction mechanism of hydrolysis of an ester using isotoping labeling method? 14. Write and explain the Steven’s rearrangement. 15. ...
... 11. Give an example for α, β, γ and δ-elimination reaction. 12. State and explain the Hammond postulate to the bromination of n-propane. 13. How will you determine the reaction mechanism of hydrolysis of an ester using isotoping labeling method? 14. Write and explain the Steven’s rearrangement. 15. ...
CHEMISTRY 1000
... We’ve already seen one reaction which organic chemists would consider to be a reduction reaction – the nucleophilic addition of hydrogen to a carbonyl (using NaBH4 or LiAlH4 as the source of nucleophilic hydrogen). This was a chemoselective reaction – in other words, the reducing agent only reduced ...
... We’ve already seen one reaction which organic chemists would consider to be a reduction reaction – the nucleophilic addition of hydrogen to a carbonyl (using NaBH4 or LiAlH4 as the source of nucleophilic hydrogen). This was a chemoselective reaction – in other words, the reducing agent only reduced ...
Chapter 13 Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
... • The –OH group is polar and capable of hydrogen bonding. • This makes low molecular weight alcohols highly soluble in water. • Hydrogen bonding in a water-methanol solution: ...
... • The –OH group is polar and capable of hydrogen bonding. • This makes low molecular weight alcohols highly soluble in water. • Hydrogen bonding in a water-methanol solution: ...
Enhanced diastereoselectivity of an ene hydroperoxidation reaction
... performing singlet oxygen ene reactions, with significant enhancement of product regioselectivity.1 It is found that, in the intrazeolite photooxygenation of geminal dimethyl trisubstituted alkenes, formation of the new double bond in the ene adducts occurs preferentially at the methyl groups.2 Labe ...
... performing singlet oxygen ene reactions, with significant enhancement of product regioselectivity.1 It is found that, in the intrazeolite photooxygenation of geminal dimethyl trisubstituted alkenes, formation of the new double bond in the ene adducts occurs preferentially at the methyl groups.2 Labe ...
CHM_221_201620 - Oakton Community College
... of enthalpy and activation energy. 8. Draw mechanisms and their transition states for radical reactions and polar reactions as well as the interconversion of resonance structures using curvedarrow notation. 9. Predict the products of and conditions required for: addition reactions to alkenes and alk ...
... of enthalpy and activation energy. 8. Draw mechanisms and their transition states for radical reactions and polar reactions as well as the interconversion of resonance structures using curvedarrow notation. 9. Predict the products of and conditions required for: addition reactions to alkenes and alk ...
CHM_223_201620 - Oakton Community College
... of enthalpy and activation energy. 8. Draw mechanisms and their transition states for radical reactions and polar reactions as well as the interconversion of resonance structures using curvedarrow notation. 9. Predict the products of and conditions required for: addition reactions to alkenes and alk ...
... of enthalpy and activation energy. 8. Draw mechanisms and their transition states for radical reactions and polar reactions as well as the interconversion of resonance structures using curvedarrow notation. 9. Predict the products of and conditions required for: addition reactions to alkenes and alk ...
CH_10_5_Functional_Groups
... An ether contains an oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms (COC) functional group. Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, Eleventh Edition ...
... An ether contains an oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms (COC) functional group. Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, Eleventh Edition ...
Zn mediated regioselective Barbier reaction of propargylic bromides
... alcohols but unsubstituted propargyl halides always gave the corresponding propargylic alcohols with high selectivity [9]. It was reported recently that allenic alcohols were obtained with high selectivity by indium-mediated coupling of propargylic halides with aldehydes in aqueous media [7]. The zi ...
... alcohols but unsubstituted propargyl halides always gave the corresponding propargylic alcohols with high selectivity [9]. It was reported recently that allenic alcohols were obtained with high selectivity by indium-mediated coupling of propargylic halides with aldehydes in aqueous media [7]. The zi ...
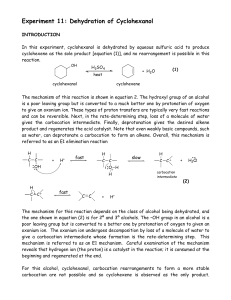
Dehydration of Cyclohexanol
... carbocations derived from certain 2°alcohols may undergo rearrangement to form more stable carbocations. This can result in the formation of rearranged isomeric alkenes. Both 2° and 3° alcohols primarily undergo the E1 reaction under these conditions, whereas for 1° alcohols and methyl alcohol, symm ...
... carbocations derived from certain 2°alcohols may undergo rearrangement to form more stable carbocations. This can result in the formation of rearranged isomeric alkenes. Both 2° and 3° alcohols primarily undergo the E1 reaction under these conditions, whereas for 1° alcohols and methyl alcohol, symm ...
alcohols - profpaz.com
... These compounds are important molecules in living cells and include carbohydrates. · Two simple and important polyhydroxy alcohols are ethylene glycol and glycerol. ...
... These compounds are important molecules in living cells and include carbohydrates. · Two simple and important polyhydroxy alcohols are ethylene glycol and glycerol. ...
Ethers and Epoxides
... • Diethyl ether is used industrially as a solvent • Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a solvent that is a cyclic ether • Epoxides contain a C-O-C unit which make-up a ...
... • Diethyl ether is used industrially as a solvent • Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a solvent that is a cyclic ether • Epoxides contain a C-O-C unit which make-up a ...
H3PO4 in a Direct Synthesis of Oligo–Poly(ethylene phosphate)
... the macromolecular backbones. These most likely are formed by the wrong addition with nucleophilic attack on the carbon atom, resulting in dealkylation (Scheme 2). This is only one example of many similar reactions that could proceed at different sites of macromolecules and at different degrees of p ...
... the macromolecular backbones. These most likely are formed by the wrong addition with nucleophilic attack on the carbon atom, resulting in dealkylation (Scheme 2). This is only one example of many similar reactions that could proceed at different sites of macromolecules and at different degrees of p ...
doc
... What contributes to the stability of the allylic radical? _____________________ Why does bromination occur exclusively at the allylic position? Compare bond dissociation energies at the other positions – alkyl, allylic, and vinylic. ...
... What contributes to the stability of the allylic radical? _____________________ Why does bromination occur exclusively at the allylic position? Compare bond dissociation energies at the other positions – alkyl, allylic, and vinylic. ...
Learning Guide for Chapter 16
... What other compounds have this band? How can they be distinguished from ethers? esters - also have C=O band alcohols - also have OH band anhydrides - also have 2 C=O bands NMR Spectra of Ethers What chemical shift are the H's next to the O in an ether? 3-4 ppm H ...
... What other compounds have this band? How can they be distinguished from ethers? esters - also have C=O band alcohols - also have OH band anhydrides - also have 2 C=O bands NMR Spectra of Ethers What chemical shift are the H's next to the O in an ether? 3-4 ppm H ...
Download PDF
... Course Textbook: “Organic Chemistry,” by Smith, 4th ed; class interaction “CPS RF keypad” to be registered to the course; will be used for daily in-class quizzes. “Connect” on-line or take home problem sets will be assigned about every 3rd day to be turned in on specific dates and graded. Optional C ...
... Course Textbook: “Organic Chemistry,” by Smith, 4th ed; class interaction “CPS RF keypad” to be registered to the course; will be used for daily in-class quizzes. “Connect” on-line or take home problem sets will be assigned about every 3rd day to be turned in on specific dates and graded. Optional C ...
carbonyl chemistry 1
... Below is the preparation of a ketone sequentially from a primary alcohol (through an intermediate aldehyde): ...
... Below is the preparation of a ketone sequentially from a primary alcohol (through an intermediate aldehyde): ...
Elias James Corey

Elias James ""E.J."" Corey (born July 12, 1928) is an American organic chemist. In 1990, he won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry ""for his development of the theory and methodology of organic synthesis"", specifically retrosynthetic analysis. Regarded by many as one of the greatest living chemists, he has developed numerous synthetic reagents, methodologies and total syntheses and has advanced the science of organic synthesis considerably.