Enantioselective Synthesis of Cyclic Ethers through a Vanadium
... the chemoselectivity of the oxidation reaction was observed. The vanadium-catalyzed oxidation of 1, using CHCl3 as the solvent and L1 (Table 1, entry 2) or L2 (Table 1, entry 4) as the ligand, cleanly afforded 2,5-trans-THP 2 (THP = tetrahydropyran; d.r. = > 95:5) with excellent diastereoselectivity ...
... the chemoselectivity of the oxidation reaction was observed. The vanadium-catalyzed oxidation of 1, using CHCl3 as the solvent and L1 (Table 1, entry 2) or L2 (Table 1, entry 4) as the ligand, cleanly afforded 2,5-trans-THP 2 (THP = tetrahydropyran; d.r. = > 95:5) with excellent diastereoselectivity ...
Amino acids and prot..
... are either (D- or L-). They are named D or L according to arrangement of the groups COOH, R, NH2 and H. around the chiral α carbon atom. Sighting with the hydrogen atom away from the viewer, if these groups are arranged clockwise around the carbon atom, then it is the D-form. If counter-clockwise, i ...
... are either (D- or L-). They are named D or L according to arrangement of the groups COOH, R, NH2 and H. around the chiral α carbon atom. Sighting with the hydrogen atom away from the viewer, if these groups are arranged clockwise around the carbon atom, then it is the D-form. If counter-clockwise, i ...
Chem 150 Unit 4 - Chemical Properties I Chemical Reactions
... element. Thus, the atoms in O2, O3, P4, S8, and aluminum metal all have an oxidation number of 0. * The oxidation number of monatomic ions is equal to the charge on the ion. The oxidation number of sodium in the Na+ ion is +1, for example, and the oxidation number of chlorine in the Cl- ion is -1. * ...
... element. Thus, the atoms in O2, O3, P4, S8, and aluminum metal all have an oxidation number of 0. * The oxidation number of monatomic ions is equal to the charge on the ion. The oxidation number of sodium in the Na+ ion is +1, for example, and the oxidation number of chlorine in the Cl- ion is -1. * ...
EX. Draw the structure of
... In a _____________ combustion reaction, a hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water vapour and energy. When fuels are burned with insufficient oxygen, _________________ combustion takes place. In these reactions, carbon monoxide (CO(g)) and even carbon soot (C(s)) can be produc ...
... In a _____________ combustion reaction, a hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water vapour and energy. When fuels are burned with insufficient oxygen, _________________ combustion takes place. In these reactions, carbon monoxide (CO(g)) and even carbon soot (C(s)) can be produc ...
Document
... aldehydes or alkynes with marginal covalent triple bond. E. Aldehydes and ketones are oxidized with Tollens’ reagent to the corresponding carboxylic acids. 23. The following statements regarding carbonyl compounds are correct: A. The compounds obtained by the condensation of two molecules of acetone ...
... aldehydes or alkynes with marginal covalent triple bond. E. Aldehydes and ketones are oxidized with Tollens’ reagent to the corresponding carboxylic acids. 23. The following statements regarding carbonyl compounds are correct: A. The compounds obtained by the condensation of two molecules of acetone ...
Oxidation Reactions
... DMP is a very mild oxidant and is especially useful for oxidising molecules containing very sensitive functionality. In the following example taken from Evans' synthesis of cytovaricin, Dess-Martin periodinane oxidised the only available secondary alcohol to the corresponding ketone in excellent yie ...
... DMP is a very mild oxidant and is especially useful for oxidising molecules containing very sensitive functionality. In the following example taken from Evans' synthesis of cytovaricin, Dess-Martin periodinane oxidised the only available secondary alcohol to the corresponding ketone in excellent yie ...
Lab 7
... alpha to the carbonyl group in cyclohexanone. When this bond is cleaved, Step 1, we replace the H atom with an –OH group. The generalized methodology is to place –OH groups on open valences where bonds break. The -H atom is the one nearest the O atom in cyclohexanone. Replacing it with an –OH group ...
... alpha to the carbonyl group in cyclohexanone. When this bond is cleaved, Step 1, we replace the H atom with an –OH group. The generalized methodology is to place –OH groups on open valences where bonds break. The -H atom is the one nearest the O atom in cyclohexanone. Replacing it with an –OH group ...
10 bioenergetics 03
... methanogenesis is from proton translocation via electron transfer to the methyl group generated during metabolism. Methanogenesis = anaerobic methyl respiration ...
... methanogenesis is from proton translocation via electron transfer to the methyl group generated during metabolism. Methanogenesis = anaerobic methyl respiration ...
Chemistry for the Health Sciences II
... activity. The course covers topics that parallel organic compounds with biochemical molecules, pairing such groups as the oxygen containing organic molecules with carbohydrates, carboxylic acids with lipids and amines with amino acids and proteins. CHEM 1520 begins during the second part of the quar ...
... activity. The course covers topics that parallel organic compounds with biochemical molecules, pairing such groups as the oxygen containing organic molecules with carbohydrates, carboxylic acids with lipids and amines with amino acids and proteins. CHEM 1520 begins during the second part of the quar ...
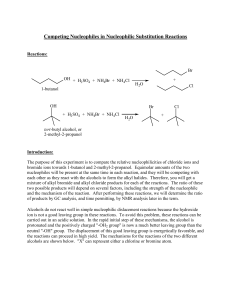
Competing Nucleophiles in Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
... Experimental Procedure for 1-butanol: The sulfuric acid, ammonium bromide, and ammonium chloride will be provided to you as a solvent-nucleophile medium. One mL of this solution contains 0.42 mL of sulfuric acid, 0.1056 g of ammonium chloride, and 0.1944 g of ammonium bromide. From this information, ...
... Experimental Procedure for 1-butanol: The sulfuric acid, ammonium bromide, and ammonium chloride will be provided to you as a solvent-nucleophile medium. One mL of this solution contains 0.42 mL of sulfuric acid, 0.1056 g of ammonium chloride, and 0.1944 g of ammonium bromide. From this information, ...
Carbohydrates as versatile platforms in the construction
... Indeed, most aminoglycosides from natural sources contain either the neamine (16) or deoxystreptamine (17) motif. Diastereomeric 1,3-diaminocyclitol derivatives can, therefore, be obtained only through organic synthesis. Our synthetic strategy toward this goal is inspired by recent work from Madsen ...
... Indeed, most aminoglycosides from natural sources contain either the neamine (16) or deoxystreptamine (17) motif. Diastereomeric 1,3-diaminocyclitol derivatives can, therefore, be obtained only through organic synthesis. Our synthetic strategy toward this goal is inspired by recent work from Madsen ...
Full answers
... product and clearly indicate the reagent(s) required for each reaction. The following list of suggested reagents is sufficient to accomplish all necessary reactions, but you may use other reagents if you wish. One of the intermediates is shown for you. Suggested reagents: ...
... product and clearly indicate the reagent(s) required for each reaction. The following list of suggested reagents is sufficient to accomplish all necessary reactions, but you may use other reagents if you wish. One of the intermediates is shown for you. Suggested reagents: ...
Faculteit der Natuurwetenschappen, Wiskunde en Informatica
... diastereomeric ratios are obtained; from 55:45 to 93:7. It should be noted that using bulkier Grignard reagents in the addition leads to higher diastereomeric ratios. This is most likely because bulkier substituents are more sterically hindered and causes the Grignard reagent to only attack the side ...
... diastereomeric ratios are obtained; from 55:45 to 93:7. It should be noted that using bulkier Grignard reagents in the addition leads to higher diastereomeric ratios. This is most likely because bulkier substituents are more sterically hindered and causes the Grignard reagent to only attack the side ...
Acids and bases
... A base has an electron-pair in a HOMO of suitable symmetry to interact with the LUMO of the acid ...
... A base has an electron-pair in a HOMO of suitable symmetry to interact with the LUMO of the acid ...
unit (11) molecules of life
... Linolenic acid (18:3) …… 3 double bonds The glyceride has a total of 5 double bonds, (0 + 2 + 3 = 5). Each double bond requires one molecule of H2. So for 1 mol glyceride, we need 5 moles of H2. ...
... Linolenic acid (18:3) …… 3 double bonds The glyceride has a total of 5 double bonds, (0 + 2 + 3 = 5). Each double bond requires one molecule of H2. So for 1 mol glyceride, we need 5 moles of H2. ...
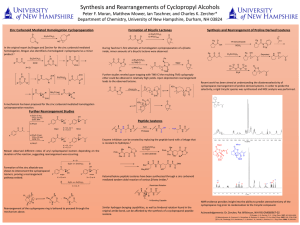
Here is the Original File - University of New Hampshire
... ether could be obtained in relatively high yields. Upon deprotection rearrangement leads to the observed lactone. ...
... ether could be obtained in relatively high yields. Upon deprotection rearrangement leads to the observed lactone. ...
Uses and Sources of some Organic Molecules C11-5-14
... Esters Most esters have pleasant odors. Esters are responsible for the fragrances of many flowers and the pleasant tastes of ripened fruits. Bananas contain the ester amyl acetate, and oranges the ester octyl acetate. Beeswax and other waxes are composed of esters, as are animal and vegetable fats ...
... Esters Most esters have pleasant odors. Esters are responsible for the fragrances of many flowers and the pleasant tastes of ripened fruits. Bananas contain the ester amyl acetate, and oranges the ester octyl acetate. Beeswax and other waxes are composed of esters, as are animal and vegetable fats ...
Development of Novel Catalytic Asymmetric Reactions using
... Metal enolates of carbonyl compounds are highly versatile nucleophilic reagents that can be used in reactions with various electrophilic agents. They are regarded as essential synthetic intermediates in organic chemistry. 1 Conventionally, two main approaches have been directed to develop asymmetric ...
... Metal enolates of carbonyl compounds are highly versatile nucleophilic reagents that can be used in reactions with various electrophilic agents. They are regarded as essential synthetic intermediates in organic chemistry. 1 Conventionally, two main approaches have been directed to develop asymmetric ...
$doc.title
... water molecule • Esters undergo hydrolysis reac4on in water to generate alcohol and carboxylic acid • This is the reverse reac4on of esterifica4on • Hydrolysis is slow at neutral pH • Small amount of ...
... water molecule • Esters undergo hydrolysis reac4on in water to generate alcohol and carboxylic acid • This is the reverse reac4on of esterifica4on • Hydrolysis is slow at neutral pH • Small amount of ...
CHAPTER 11 BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE:
... adds to the carbon with the most hydrogen. For alkynes, the addition is always two mole to one mole of alkyne, the product being a substituted alkane. If hydrogen gas is added, the process is called hydrogenation. ...
... adds to the carbon with the most hydrogen. For alkynes, the addition is always two mole to one mole of alkyne, the product being a substituted alkane. If hydrogen gas is added, the process is called hydrogenation. ...
Arrows - Rutgers Chemistry
... nucleophile) the reaction is reversible. In step 3 one of the adjacent methyl groups moves to the cationic site. We signify this by a curved two-‐spiked arrow pointing to the carbon bearing the pos ...
... nucleophile) the reaction is reversible. In step 3 one of the adjacent methyl groups moves to the cationic site. We signify this by a curved two-‐spiked arrow pointing to the carbon bearing the pos ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.