File
... Organic Chemistry Classifying Organic Compounds (Read pages 4 and 51) Define the following terms: organic chemistry aromatic hydrocarbon functional group dipole-dipole force ether aldehyde amide ...
... Organic Chemistry Classifying Organic Compounds (Read pages 4 and 51) Define the following terms: organic chemistry aromatic hydrocarbon functional group dipole-dipole force ether aldehyde amide ...
Answers
... Aldehydes, ketones and alcohols such as propanal, CH3CH2CHO; propanone, CH3COCH3, and 1-propanol, CH3CH2CH2OH are all liquids at room temperature. When a liquid boils the intermolecular forces that hold the molecules in the liquid phase must be overcome to allow the molecules to enter the vapour pha ...
... Aldehydes, ketones and alcohols such as propanal, CH3CH2CHO; propanone, CH3COCH3, and 1-propanol, CH3CH2CH2OH are all liquids at room temperature. When a liquid boils the intermolecular forces that hold the molecules in the liquid phase must be overcome to allow the molecules to enter the vapour pha ...
cape chemistry unit ii module i
... CH3COR and therefore give a positive iodoform test. In the formula CH3CH(OH)R: The alpha carbon is CH3. The alpha carbon is one carbon away from the carbon with the functional group. Iodoform is CHI3: Tri-iodomethane (fine yellow crystals with characteristic smell) Stage 1: alcohol is oxidized to a ...
... CH3COR and therefore give a positive iodoform test. In the formula CH3CH(OH)R: The alpha carbon is CH3. The alpha carbon is one carbon away from the carbon with the functional group. Iodoform is CHI3: Tri-iodomethane (fine yellow crystals with characteristic smell) Stage 1: alcohol is oxidized to a ...
Chapter 1 Chemical Bonding and Chemical Structure
... • Recall priorities: carboxylic acid > anhydride > ester > acid halide > amide > nitrile > aldehyde > ketone > alcohol (phenol) > thiol > amine 16.1 Nomenclature of Benzene Derivatives ...
... • Recall priorities: carboxylic acid > anhydride > ester > acid halide > amide > nitrile > aldehyde > ketone > alcohol (phenol) > thiol > amine 16.1 Nomenclature of Benzene Derivatives ...
Carbonyl α-substitution and Condensation Reactions
... Carbonyl compounds can behave as either electrophiles or nucleophiles. In a nucleophilic addition reaction or a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction, the carbonyl group behaves as an electrophile by accepting electrons from an attacking nucleophile. In an a-substitution reaction, the carbonyl com ...
... Carbonyl compounds can behave as either electrophiles or nucleophiles. In a nucleophilic addition reaction or a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction, the carbonyl group behaves as an electrophile by accepting electrons from an attacking nucleophile. In an a-substitution reaction, the carbonyl com ...
chm238f02.exam2
... (c) Which reagent(s) would you use if you wanted to substitute the alcohol with bromide in the same position and with inversion of configuration, without any rearrangement. ...
... (c) Which reagent(s) would you use if you wanted to substitute the alcohol with bromide in the same position and with inversion of configuration, without any rearrangement. ...
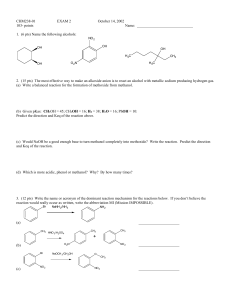
CHM238-01 EXAM 2 October 14, 2002 103
... that occurs under acidic conditions. Consider the situation shown below. (a) Provide arrows and necessary lone pairs to complete the reaction flow for the unexpected alcohol substitution reaction: H H3C ...
... that occurs under acidic conditions. Consider the situation shown below. (a) Provide arrows and necessary lone pairs to complete the reaction flow for the unexpected alcohol substitution reaction: H H3C ...
Porphyrin Complex - Center for Biomimetic Systems
... presence of H218O, 50% of the oxygen atom in the triphenylmethanol product derived from the labeled water (Scheme 1A). Furthermore, when the triphenylmethane hydroxylation was carried out under 18O2 atmosphere, less than 2% 18O was incorporated into the triphenylmethanol product (Scheme 1B). The res ...
... presence of H218O, 50% of the oxygen atom in the triphenylmethanol product derived from the labeled water (Scheme 1A). Furthermore, when the triphenylmethane hydroxylation was carried out under 18O2 atmosphere, less than 2% 18O was incorporated into the triphenylmethanol product (Scheme 1B). The res ...
Alcohols
... Carbonyl Compounds The mechanisms involve the addition of a nucleophilic hydride ion (:H-) to the positively polarized, electrophilic carbon atom of the carbonyl group • The initial product is an alkoxide ion, which is protonated by addition of H3O+ in a second step to yield the alcohol product ...
... Carbonyl Compounds The mechanisms involve the addition of a nucleophilic hydride ion (:H-) to the positively polarized, electrophilic carbon atom of the carbonyl group • The initial product is an alkoxide ion, which is protonated by addition of H3O+ in a second step to yield the alcohol product ...
8.1 Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
... ketones, the “–e” is dropped from the alkane containing the carbonyl group and replaced with the suffix “-one”. The location of the carbonyl group must be specified in ketones containing five or more carbons. The chain is numbered in a manner which places the lowest number on the carbon containing t ...
... ketones, the “–e” is dropped from the alkane containing the carbonyl group and replaced with the suffix “-one”. The location of the carbonyl group must be specified in ketones containing five or more carbons. The chain is numbered in a manner which places the lowest number on the carbon containing t ...
Alcohols and Phenols
... Review: Cis-1,2-diols from hydroxylation of an alkene with OsO4 followed by reduction with NaHSO3 Trans-1,2-diols from acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of epoxides ...
... Review: Cis-1,2-diols from hydroxylation of an alkene with OsO4 followed by reduction with NaHSO3 Trans-1,2-diols from acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of epoxides ...
Organic Chemistry
... Mechanism of Reaction with Base/H2O – Esters • Step 1: Attack of hydroxide ion (a nucleophile) on the carbonyl carbon (an electrophile). (Addition) • Step 2: Collapse of the TCAI. (Elimination) • Step 3: Proton transfer to the alkoxide ion; this step is irreversible and drives saponification to com ...
... Mechanism of Reaction with Base/H2O – Esters • Step 1: Attack of hydroxide ion (a nucleophile) on the carbonyl carbon (an electrophile). (Addition) • Step 2: Collapse of the TCAI. (Elimination) • Step 3: Proton transfer to the alkoxide ion; this step is irreversible and drives saponification to com ...
Unit-8-Alcohols-Aldehydes
... • Markovnikov’s Rule can be used to predict which of the two products is predicted to be the major product. -The hydrogen from the water in a hydration reaction is added to the double-bonded carbon atom that originally carried the most hydrogen atoms. ...
... • Markovnikov’s Rule can be used to predict which of the two products is predicted to be the major product. -The hydrogen from the water in a hydration reaction is added to the double-bonded carbon atom that originally carried the most hydrogen atoms. ...
friedel-craft reaction: a review - Advance Institute of Biotech
... alkyl complexes, which are regarded as the active species of the alkene polymerization. The bulky anion, formed from the above reaction of MAO with the halogeno ligand, does not coordinate the cationic transition metal firmly and enhances coordination of the monomer to the metal center. Thus, high L ...
... alkyl complexes, which are regarded as the active species of the alkene polymerization. The bulky anion, formed from the above reaction of MAO with the halogeno ligand, does not coordinate the cationic transition metal firmly and enhances coordination of the monomer to the metal center. Thus, high L ...
Communications to the Editor - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... also be converted to a mixture in which 6b predominated by base treatment. We assumed that 6a and 6b are the endo (syn to carbonyl) and exo (anti to carbonyl) isomers, respectively. However, the correctness of this assignment was not proven until the completion of the synthesis when the synthetic pr ...
... also be converted to a mixture in which 6b predominated by base treatment. We assumed that 6a and 6b are the endo (syn to carbonyl) and exo (anti to carbonyl) isomers, respectively. However, the correctness of this assignment was not proven until the completion of the synthesis when the synthetic pr ...
Oxidation of Benzyl Ethers to Benzoate Esters Using a Novel
... by 7. The unstable gem-diol decomposes to give 11. Alternatively, conversion of the α-alkoxy radical intermediate 5 to benzaldehyde (11) could occur through a second H-abstraction, this time by the odd electron moiety in 6. Both paths provide the desired carbonyl compound along with an iodosobenzoic ...
... by 7. The unstable gem-diol decomposes to give 11. Alternatively, conversion of the α-alkoxy radical intermediate 5 to benzaldehyde (11) could occur through a second H-abstraction, this time by the odd electron moiety in 6. Both paths provide the desired carbonyl compound along with an iodosobenzoic ...
Copper perchlorate: Efficient acetylation catalyst
... Some of the advantages associated are noted here: solvent free and ambient reaction conditions, rapid reaction, quantitative yield, and no by-product formation from possible Fries rearrangement in the case of phenols. There is also a selectivity among the functional groups to get acylated if the rea ...
... Some of the advantages associated are noted here: solvent free and ambient reaction conditions, rapid reaction, quantitative yield, and no by-product formation from possible Fries rearrangement in the case of phenols. There is also a selectivity among the functional groups to get acylated if the rea ...
ppt
... 1°, 2°, and 3° amines all have similar reactivity; the initially formed monoalkylation product can undergo further reaction to yield a mixture of alkylated products ...
... 1°, 2°, and 3° amines all have similar reactivity; the initially formed monoalkylation product can undergo further reaction to yield a mixture of alkylated products ...
Chemdraw B&W - Chemistry Courses
... Electron-donating substituents (such as CH3, NH2, OCH3) increase the basicity of the corresponding arylamine Electron-withdrawing substituents (such as Cl, NO2, CN) decrease arylamine basicity ...
... Electron-donating substituents (such as CH3, NH2, OCH3) increase the basicity of the corresponding arylamine Electron-withdrawing substituents (such as Cl, NO2, CN) decrease arylamine basicity ...
104 Chapter 22: Amines. Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH3
... Arylamines are much less basic than alkylamines. The lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen of aniline are conjugated to the π-electrons of the aromatic ring and are therefore less available for acid-base chemistry. Protonation disrupts the conjugation. Substitutents can greatly influence the basic ...
... Arylamines are much less basic than alkylamines. The lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen of aniline are conjugated to the π-electrons of the aromatic ring and are therefore less available for acid-base chemistry. Protonation disrupts the conjugation. Substitutents can greatly influence the basic ...
Alkyl Aryl Ether Bond Formation with PhenoFluor
... bond formation is appealing and orthogonal to other crosscoupling approaches. The Mitsunobu reaction has been developed for this purpose, and a large substrate scope has been demonstrated.[6, 7] However, several substrate classes, such as salicylaldehydes, are not tolerated, and general alcohol–alco ...
... bond formation is appealing and orthogonal to other crosscoupling approaches. The Mitsunobu reaction has been developed for this purpose, and a large substrate scope has been demonstrated.[6, 7] However, several substrate classes, such as salicylaldehydes, are not tolerated, and general alcohol–alco ...
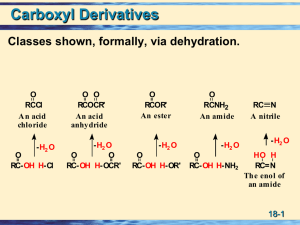
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
... More electrophilic carbonyl groups are more reactive to addition ◦ (acyl halides are most reactive, amides are least) ...
... More electrophilic carbonyl groups are more reactive to addition ◦ (acyl halides are most reactive, amides are least) ...
A GRIGNARD REACTION: SYNTHESIS OF 2-METHYL-2
... 2. The Grignard reagent is mixed with a compound that has an electron-deficient carbonyl carbon. In this case, acetone is used. The electron-rich C attacks the electron-poor C forming a new C-C bond. Simultaneously, the carbonyl oxygen atom takes up one pair of electrons, creating the anion of an al ...
... 2. The Grignard reagent is mixed with a compound that has an electron-deficient carbonyl carbon. In this case, acetone is used. The electron-rich C attacks the electron-poor C forming a new C-C bond. Simultaneously, the carbonyl oxygen atom takes up one pair of electrons, creating the anion of an al ...
carbohydrates: monosaccharides. oligo
... Solution. Pentoses and hexoses are the most common in nature. Usually they have unbranched chains, so quantity of the isomers is expected to be quite small. However, monosaccharides contain several asymmetric carbon atoms and therefore they show optical isomerism. Thus, aldohexoses have four asymmet ...
... Solution. Pentoses and hexoses are the most common in nature. Usually they have unbranched chains, so quantity of the isomers is expected to be quite small. However, monosaccharides contain several asymmetric carbon atoms and therefore they show optical isomerism. Thus, aldohexoses have four asymmet ...
Wolff–Kishner reduction

The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. Originally reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912, it has been applied to the total synthesis of scopadulcic acid B, aspidospermidine and dysidiolide.In general, the reaction mechanism first involves the in situ generation of a hydrazone by condensation of hydrazine with the ketone or aldehyde substrate. Sometimes it is however advantageous to use a pre-formed hydrazone as substrate (see modifications). The hydrazone is deprotonated by alkoxide base followed by a concerted, rate-determining step in which a diimide anion is formed. Collapse of this alkyldiimde with loss of N2 leads to formation of an alkylanion which can be protonated by solvent to give the desired product.Because the Wolff–Kishner reduction requires highly basic conditions, it is unsuitable for base-sensitive substrates. However, this method can be superior over the related Clemmensen reduction for acid-sensitive compounds such as pyrroles and for high-molecular weight compounds.