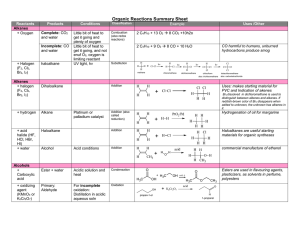
Organic Reactions Summary Sheet
... 2 C4H10 + 13 O2 8 CO2 +10h2o 2 C4H10 + 9 O2 8 CO + 10 H2O ...
... 2 C4H10 + 13 O2 8 CO2 +10h2o 2 C4H10 + 9 O2 8 CO + 10 H2O ...
Organic Compounds
... extremely soluble in water. The solubility decreases as the number of carbons increase to the strength of hydrogen bonds most alcohols have higher melting & boiling points than similar alkanes. Most alcohols are liquids at SATP ...
... extremely soluble in water. The solubility decreases as the number of carbons increase to the strength of hydrogen bonds most alcohols have higher melting & boiling points than similar alkanes. Most alcohols are liquids at SATP ...
WADE7Lecture10a
... The longest chain contains six carbon atoms, but it does not contain the carbon bonded to the hydroxyl group. The longest chain containing the carbon bonded to the —OH group is the one outlined by the green box, containing five carbon atoms. This chain is numbered from right to left in order to give ...
... The longest chain contains six carbon atoms, but it does not contain the carbon bonded to the hydroxyl group. The longest chain containing the carbon bonded to the —OH group is the one outlined by the green box, containing five carbon atoms. This chain is numbered from right to left in order to give ...
Chapter 10 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Alkanes
... groups followed by ether. Copyright © 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... groups followed by ether. Copyright © 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
23 • Organic Chemistry
... acid” ethyl acetate ethanoic acid (acetic acid + (acetic acid) ethyl alcohol) Reactions: Acids can be made by oxidizing aldehydes. Esters are formed (“esterification”) from a carboxylic acid & an alcohol. Water is removed (a “condensation” reaction). Esters often have pleasant, agreeable odors (e.g. ...
... acid” ethyl acetate ethanoic acid (acetic acid + (acetic acid) ethyl alcohol) Reactions: Acids can be made by oxidizing aldehydes. Esters are formed (“esterification”) from a carboxylic acid & an alcohol. Water is removed (a “condensation” reaction). Esters often have pleasant, agreeable odors (e.g. ...
F017006 - Fluorous Technologies
... F-PMB-OH is the fluorous equivalent of p-methoxybenzyl alcohol (PMB-OH) used in protecting alcohols in multi-step organic synthesis. Protection of an alcohol with F-PMB-OH and deprotection are achieved under traditional reaction conditions, with the advantage that products containing the F-PMB group ...
... F-PMB-OH is the fluorous equivalent of p-methoxybenzyl alcohol (PMB-OH) used in protecting alcohols in multi-step organic synthesis. Protection of an alcohol with F-PMB-OH and deprotection are achieved under traditional reaction conditions, with the advantage that products containing the F-PMB group ...
Nomenclature Summary
... 3. Identify substituents. If more than one substituent of the same kind is present, use the prefixes “di”, “tri”, “tetra”. 4. Locate the substituents by the number of the carbon to which they are attached. 5. Put substituents in alphabetical order (multiplier prefixes do not count). 6. Separate numb ...
... 3. Identify substituents. If more than one substituent of the same kind is present, use the prefixes “di”, “tri”, “tetra”. 4. Locate the substituents by the number of the carbon to which they are attached. 5. Put substituents in alphabetical order (multiplier prefixes do not count). 6. Separate numb ...
8. What are saturated hydrocarbons?
... Chapter 15 Organic Compounds and the Atomic Properties of Carbon The basis of this chapter is to understand how organic molecules are named and structured. Although organic chemistry is a vital part of chemistry, it is not a strong focus in the AP curriculum. There will only be a small number of que ...
... Chapter 15 Organic Compounds and the Atomic Properties of Carbon The basis of this chapter is to understand how organic molecules are named and structured. Although organic chemistry is a vital part of chemistry, it is not a strong focus in the AP curriculum. There will only be a small number of que ...
Toxic Chemicals
... Mp and bp in the determination of the compounds purities. Now let us look at another importance of them in identifyin An organic compounds. if you can be sure that the boiling point of a liquid alcohol is 132° (+,-) 2°C, you have narrowed the choice to only three or four possibilities from more than ...
... Mp and bp in the determination of the compounds purities. Now let us look at another importance of them in identifyin An organic compounds. if you can be sure that the boiling point of a liquid alcohol is 132° (+,-) 2°C, you have narrowed the choice to only three or four possibilities from more than ...
Organic Compounds
... or more hydrogen atoms replaced by another nonmetallic atom eg. bromomethane - CH3Br methanol - CH3OH ...
... or more hydrogen atoms replaced by another nonmetallic atom eg. bromomethane - CH3Br methanol - CH3OH ...
kinetic and thermodynamic studies of the oxidation of perfumery
... *E-mail: [email protected] ABSTRACT Oxidation is one of the most important industrial reactions as it yields useful products. Literature survey indicates the use of a variety of organic oxidants for the oxidation of alcohols to the corresponding carbonyl compounds but inorganic oxidants have rare ...
... *E-mail: [email protected] ABSTRACT Oxidation is one of the most important industrial reactions as it yields useful products. Literature survey indicates the use of a variety of organic oxidants for the oxidation of alcohols to the corresponding carbonyl compounds but inorganic oxidants have rare ...
review sheet
... text. The test will cover carbonyl compounds. The following textbook sections will NOT be covered on the exam: ...
... text. The test will cover carbonyl compounds. The following textbook sections will NOT be covered on the exam: ...
CHEMISTRY 1000
... Topic #9: Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Alcohols (more SN1 and SN2) Fall 2014 Dr. Susan Findlay ...
... Topic #9: Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Alcohols (more SN1 and SN2) Fall 2014 Dr. Susan Findlay ...
Organic Chemistry Chem 121: Topics
... Alkenes contain C, H atoms and single and double bonds. The simplest alkenes are H2C=CH2 (ethene) and CH3CH=CH2 (propene): • Their trivial names are ethylene and propylene. Alkenes are named in the same way as alkanes with the suffix -ene replacing the -ane in alkanes. The location of the doub ...
... Alkenes contain C, H atoms and single and double bonds. The simplest alkenes are H2C=CH2 (ethene) and CH3CH=CH2 (propene): • Their trivial names are ethylene and propylene. Alkenes are named in the same way as alkanes with the suffix -ene replacing the -ane in alkanes. The location of the doub ...
The reaction between bromine and alkenes is an example of a type
... building up designer molecules like drugs. Alkanes undergo a substitution reaction with halogens in the presence of light. For instance, in ultraviolet light, methane reacts with halogen molecules such as chlorine and bromine. ...
... building up designer molecules like drugs. Alkanes undergo a substitution reaction with halogens in the presence of light. For instance, in ultraviolet light, methane reacts with halogen molecules such as chlorine and bromine. ...
Regents Unit 15b: Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, & Esters
... • Contain –COOH group. • H is bonded to O. Hydrogen bonding occurs. Leads to increases in boiling point over corresponding alkane. • Also can form hydrogen bonds with water so the smaller acids are pretty soluble. ...
... • Contain –COOH group. • H is bonded to O. Hydrogen bonding occurs. Leads to increases in boiling point over corresponding alkane. • Also can form hydrogen bonds with water so the smaller acids are pretty soluble. ...
Assignment 4 Task 1a
... The ability of carbon to form extensive molecules made up of chains and branches and including ...
... The ability of carbon to form extensive molecules made up of chains and branches and including ...
Chapter 11 - Department of Chemistry and Physics
... The functional group in alcohols and phenols is the hydroxyl (-OH) group. Alcohols can be considered derivatives of hydrocarbons in which one or more H atoms have been replaced by -OH groups. Alcohols are considered neutral compounds because they are only very slightly acidic. Alcohols can b ...
... The functional group in alcohols and phenols is the hydroxyl (-OH) group. Alcohols can be considered derivatives of hydrocarbons in which one or more H atoms have been replaced by -OH groups. Alcohols are considered neutral compounds because they are only very slightly acidic. Alcohols can b ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.