Carboxylic Acids - BSAK Chemistry weebly
... Esters from Acyl Chlorides • If you add an acyl chloride to an alcohol, you get a vigorous (even violent) reaction at room temperature producing an ester and misty fumes of hydrogen chloride. • Add the liquid ethanoyl chloride to ethanol, you get a burst of hydrogen chloride produced together with ...
... Esters from Acyl Chlorides • If you add an acyl chloride to an alcohol, you get a vigorous (even violent) reaction at room temperature producing an ester and misty fumes of hydrogen chloride. • Add the liquid ethanoyl chloride to ethanol, you get a burst of hydrogen chloride produced together with ...
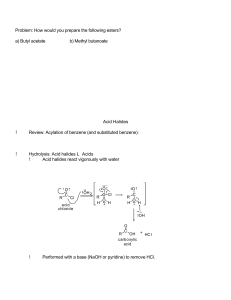
Problem: How would you prepare the following esters? a) Butyl
... The aldehyde intermediate can be isolated by using a gentler reducing agent such as lithium tri-tert-butoxyaluminum hydride. O CCl 1. LiAlH(OC)CH3) 3, ether ...
... The aldehyde intermediate can be isolated by using a gentler reducing agent such as lithium tri-tert-butoxyaluminum hydride. O CCl 1. LiAlH(OC)CH3) 3, ether ...
nucleophile (亲核试剂)
... Restrictions on the Use of Grignard Reagents Grignard reagents are very powerful nucleophiles and bases. They react as if they were carbanions. Grignard reagents cannot be made from halides which contain acidic groups or electrophilic sites elsewhere in the molecule. ...
... Restrictions on the Use of Grignard Reagents Grignard reagents are very powerful nucleophiles and bases. They react as if they were carbanions. Grignard reagents cannot be made from halides which contain acidic groups or electrophilic sites elsewhere in the molecule. ...
Study guide/lecture topics
... are indicated clearly by chapter and page numbers where necessary. Topics NOT from Clayden are listed in italics. PLTL topics are in CAPS. This document will be updated throughout the term. The goals of this course are: - to achieve an advanced understanding of the reactivity of organic molecules - ...
... are indicated clearly by chapter and page numbers where necessary. Topics NOT from Clayden are listed in italics. PLTL topics are in CAPS. This document will be updated throughout the term. The goals of this course are: - to achieve an advanced understanding of the reactivity of organic molecules - ...
INTRODUCING ALCOHOLS
... Alcohols are compounds in which one or more hydrogen atoms in an alkane have been replaced by an -OH group. The different kinds of alcohols Alcohols fall into different classes depending on how the -OH group is positioned on the chain of carbon atoms. There are some chemical differences between the ...
... Alcohols are compounds in which one or more hydrogen atoms in an alkane have been replaced by an -OH group. The different kinds of alcohols Alcohols fall into different classes depending on how the -OH group is positioned on the chain of carbon atoms. There are some chemical differences between the ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... carbonyl and both hydrogens come from the nitrogen. When we consider the mechanism for this reaction, we need to carefully consider the following factors: 1. Charge balance and conservation: Since the reaction takes place in acidic solution, we cannot have isolated negative charges. Molecules can ei ...
... carbonyl and both hydrogens come from the nitrogen. When we consider the mechanism for this reaction, we need to carefully consider the following factors: 1. Charge balance and conservation: Since the reaction takes place in acidic solution, we cannot have isolated negative charges. Molecules can ei ...
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
... The most useful reagents for reducing aldehydes and ketones are the metal hydride reagents.The two most common metal hydride reagents are sodium borohydride (NaBH4) and lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4). These reagents contain a polar metal-hydrogen bond that serves as a source of the nucleophile hy ...
... The most useful reagents for reducing aldehydes and ketones are the metal hydride reagents.The two most common metal hydride reagents are sodium borohydride (NaBH4) and lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4). These reagents contain a polar metal-hydrogen bond that serves as a source of the nucleophile hy ...
Carboxylic Acids - BSAK Chemistry weebly
... • Acyl chlorides: These contain a -COCl group, e.g. ethanoyl chloride, CH3COCl, or benzoyl chloride, C6H5COCl • Alkyl chlorides: These have a chlorine attached to a carbon chain, e.g. chloroethane, C2H5Cl • Aryl chlorides: These have a chlorine attached directly to a benzene ring, e.g. chlorobenzen ...
... • Acyl chlorides: These contain a -COCl group, e.g. ethanoyl chloride, CH3COCl, or benzoyl chloride, C6H5COCl • Alkyl chlorides: These have a chlorine attached to a carbon chain, e.g. chloroethane, C2H5Cl • Aryl chlorides: These have a chlorine attached directly to a benzene ring, e.g. chlorobenzen ...
Ethers, Sulfides, Epoxides
... We are breaking the CN bond; bond order goes from 3 to 0. Probably stepwise. Chemically speaking: the nitrogen of the nitrile is basic (lone pair) and can be protonated. This makes it a better electrophile (cf. carbonyl). Multiple bond can undergo addition (cf. carbonyl) reducing bond order. Goal: B ...
... We are breaking the CN bond; bond order goes from 3 to 0. Probably stepwise. Chemically speaking: the nitrogen of the nitrile is basic (lone pair) and can be protonated. This makes it a better electrophile (cf. carbonyl). Multiple bond can undergo addition (cf. carbonyl) reducing bond order. Goal: B ...
Organic Compounds Containing C, H and O
... Ans. a) Alcohols boils at higher temperature than hydrocarbons and ethers of comparable molecular masses because of inter molecular H-bonding is present in alcohol but not in hydrocarbons and ethers ...
... Ans. a) Alcohols boils at higher temperature than hydrocarbons and ethers of comparable molecular masses because of inter molecular H-bonding is present in alcohol but not in hydrocarbons and ethers ...
Compounds
... different types of elements that make up a compound. Sugar has the chemical formula C6H12O6. Using the periodic table it is clear that sugar is made up of the elements carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). ...
... different types of elements that make up a compound. Sugar has the chemical formula C6H12O6. Using the periodic table it is clear that sugar is made up of the elements carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). ...
Here is the Original File - University of New Hampshire
... 1. W.R.G. Baeyens, S.G. Schulman, Y. Zhao; Chemiluminescence-Based Detection: Principles and Analytical Applications in Flowing Streams and in Immunoassays. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 1998, 17(6-7), (941-953) 2. Jaworek. Christine, Lacobucci. Sarah; Wittig Reaction: The Synth ...
... 1. W.R.G. Baeyens, S.G. Schulman, Y. Zhao; Chemiluminescence-Based Detection: Principles and Analytical Applications in Flowing Streams and in Immunoassays. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 1998, 17(6-7), (941-953) 2. Jaworek. Christine, Lacobucci. Sarah; Wittig Reaction: The Synth ...
The Synthesis of trans-9-(2
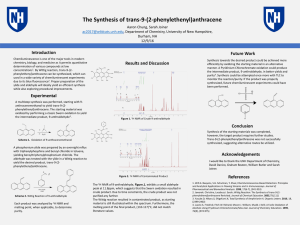
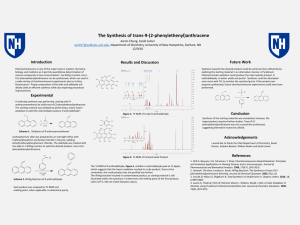
... Chemiluminescence is one of the major tools in modern chemistry, biology, and medicine as it permits quantitative determination of various compounds at low concentrations1. By Wittig reaction, trans9-(2-phenylethenyl)anthracene can be synthesized, which can used in a wide variety of chemiluminescent ...
... Chemiluminescence is one of the major tools in modern chemistry, biology, and medicine as it permits quantitative determination of various compounds at low concentrations1. By Wittig reaction, trans9-(2-phenylethenyl)anthracene can be synthesized, which can used in a wide variety of chemiluminescent ...
OrganicChemistryforAPlecture2010StudentVersioncompatibility
... • Alkenes exhibit not only structural isomerism but geometric (cis-trans) isomerism as well. In geometric isomers the bonds are the same, but the molecules have different geometries. Geometric isomerism is possible in alkenes because rotation about the C=C double bond is restricted. ...
... • Alkenes exhibit not only structural isomerism but geometric (cis-trans) isomerism as well. In geometric isomers the bonds are the same, but the molecules have different geometries. Geometric isomerism is possible in alkenes because rotation about the C=C double bond is restricted. ...
Organic Chemistry = the study of carbon and most carbon compounds
... • Alkenes exhibit not only structural isomerism but geometric (cis-trans) isomerism as well. In geometric isomers the bonds are the same, but the molecules have different geometries. Geometric isomerism is possible in alkenes because rotation about the C=C double bond is restricted. ...
... • Alkenes exhibit not only structural isomerism but geometric (cis-trans) isomerism as well. In geometric isomers the bonds are the same, but the molecules have different geometries. Geometric isomerism is possible in alkenes because rotation about the C=C double bond is restricted. ...
Lecture 21 Enzyme mechanisms
... adjacent phosphorous atom. In the concerted way His 119 acts as an acid by protonating the oxygen atom of the leaving group which promotes the bond scission between phosphorous and 5ʹ oxygen. As a result of this step a 2ʹ,3ʹ-cyclic intermediate is formed. 2. In the second step, actually reverse of t ...
... adjacent phosphorous atom. In the concerted way His 119 acts as an acid by protonating the oxygen atom of the leaving group which promotes the bond scission between phosphorous and 5ʹ oxygen. As a result of this step a 2ʹ,3ʹ-cyclic intermediate is formed. 2. In the second step, actually reverse of t ...
Alcohols - City University of New York
... 1. Nucleophilic substitution on tertiary halides invokes the carbocation but nucleophilic substitution on primary RX avoids the carbocation by requiring the nucleophile to become involved immediately. 2. The E2 reaction requires the strong base to become involved immediately. ...
... 1. Nucleophilic substitution on tertiary halides invokes the carbocation but nucleophilic substitution on primary RX avoids the carbocation by requiring the nucleophile to become involved immediately. 2. The E2 reaction requires the strong base to become involved immediately. ...
Exam 2-Answer Key
... two pi bonds and a sigma bond, each formed by a lateral overlap of two p orbitals. a sigma bond formed by overlap of two s orbitals and two pi bonds, each formed by lateral overlap of two p orbitals. a sigma bond formed by end-on overlap of two sp" orbitals and a pi bond formed by lateral overlap of ...
... two pi bonds and a sigma bond, each formed by a lateral overlap of two p orbitals. a sigma bond formed by overlap of two s orbitals and two pi bonds, each formed by lateral overlap of two p orbitals. a sigma bond formed by end-on overlap of two sp" orbitals and a pi bond formed by lateral overlap of ...
Alcohols/Wade: Reactions
... 10. Compound A is an optically active alcohol. Treatment with chromic acid converts A to a ketone B. In a separate reaction A is treated with PBr3, converting A to C. Compound D is purified and reacted with magnesium and ether. Compound B is added to the resulting solution of the Grignard reagent. ...
... 10. Compound A is an optically active alcohol. Treatment with chromic acid converts A to a ketone B. In a separate reaction A is treated with PBr3, converting A to C. Compound D is purified and reacted with magnesium and ether. Compound B is added to the resulting solution of the Grignard reagent. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... approach. State whether the reaction is feasible by thermal or photochemical means. 13. Predict the products in the following pericyclic reactions and explain the mechanism with proper stereochemistry. a) hv 4+2 addition b) H Sigmatropic reaction 120 C ...
... approach. State whether the reaction is feasible by thermal or photochemical means. 13. Predict the products in the following pericyclic reactions and explain the mechanism with proper stereochemistry. a) hv 4+2 addition b) H Sigmatropic reaction 120 C ...
Haloalkane

The haloalkanes (also known, as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and commercial names. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes which contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula ″RX″ where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I).Haloalkanes have been known for centuries. Chloroethane was produced synthetically in the 15th century. The systematic synthesis of such compounds developed in the 19th century in step with the development of organic chemistry and the understanding of the structure of alkanes. Methods were developed for the selective formation of C-halogen bonds. Especially versatile methods included the addition of halogens to alkenes, hydrohalogenation of alkenes, and the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides. These methods are so reliable and so easily implemented that haloalkanes became cheaply available for use in industrial chemistry because the halide could be further replaced by other functional groups.While most haloalkanes are human-produced, non-artificial-source haloalkanes do occur on Earth, mostly through enzyme-mediated synthesis by bacteria, fungi, and especially sea macroalgae (seaweeds). More than 1600 halogenated organics have been identified, with bromoalkanes being the most common haloalkanes. Brominated organics in biology range from biologically produced methyl bromide to non-alkane aromatics and unsaturates (indoles, terpenes, acetogenins, and phenols). Halogenated alkanes in land plants are more rare, but do occur, as for example the fluoroacetate produced as a toxin by at least 40 species of known plants. Specific dehalogenase enzymes in bacteria which remove halogens from haloalkanes, are also known.