Jeopardy - Cloudfront.net
... brightness measured if it were at a distance of 10 parsecs (Uses + and – values) ...
... brightness measured if it were at a distance of 10 parsecs (Uses + and – values) ...
Experimental Low Earth Orbit Surveillance Stereoscope
... - in short The combined tasks of the detection, characterization, correlation, and orbit determination of space objects describe the scope of ”space object surveillance”. For the most part, detector technology is sufficiently advanced to build the kind of capability required for satisfactory identif ...
... - in short The combined tasks of the detection, characterization, correlation, and orbit determination of space objects describe the scope of ”space object surveillance”. For the most part, detector technology is sufficiently advanced to build the kind of capability required for satisfactory identif ...
Time - Academic Computer Center
... • In reality because the Earth rotates on its axis from West to East the Sun, Moon and stars all appear to move from East to West. • The Sun appears to rise in the East and set in the West because the Earth spins. • The Moon however also orbits the Earth traveling from West to East but it takes much ...
... • In reality because the Earth rotates on its axis from West to East the Sun, Moon and stars all appear to move from East to West. • The Sun appears to rise in the East and set in the West because the Earth spins. • The Moon however also orbits the Earth traveling from West to East but it takes much ...
3A8d
... of occasional instances of galaxies merging at the present time. In each case explain why the same observations are not as readily understood in the traditional formation/evolution model, which proposed that the formation of galaxies was largely completed in single rapid collapse events more than 10 ...
... of occasional instances of galaxies merging at the present time. In each case explain why the same observations are not as readily understood in the traditional formation/evolution model, which proposed that the formation of galaxies was largely completed in single rapid collapse events more than 10 ...
Stars
... Larger and hotter stars are brighter than smaller and cooler stars. Brighter stars send out more light energy. How bright a star looks to us also depends on how far away it is. ...
... Larger and hotter stars are brighter than smaller and cooler stars. Brighter stars send out more light energy. How bright a star looks to us also depends on how far away it is. ...
The Science of Life in the Universe (Chap 2
... Given that we discover a civilization around other stars, let’s examine the closest that such a civilization could be from the Earth. The nearest star is 4.3 light years distant from Earth. This means that a two-way conversation would take at least 8.6 years, since no information can travel faster ...
... Given that we discover a civilization around other stars, let’s examine the closest that such a civilization could be from the Earth. The nearest star is 4.3 light years distant from Earth. This means that a two-way conversation would take at least 8.6 years, since no information can travel faster ...
The Science of Life in the Universe (Chap 2
... Given that we discover a civilization around other stars, let’s examine the closest that such a civilization could be from the Earth. The nearest star is 4.3 light years distant from Earth. This means that a two-way conversation would take at least 8.6 years, since no information can travel faster ...
... Given that we discover a civilization around other stars, let’s examine the closest that such a civilization could be from the Earth. The nearest star is 4.3 light years distant from Earth. This means that a two-way conversation would take at least 8.6 years, since no information can travel faster ...
Hubble Deep Field Image
... dust Could not contain very bright objects or anything that emitted too much infrared, x-ray, or UV In addition, field could never be occulted by the Earth or Moon. ...
... dust Could not contain very bright objects or anything that emitted too much infrared, x-ray, or UV In addition, field could never be occulted by the Earth or Moon. ...
stars
... huge explosion. • This huge explosion was known as The Big Bang. • Scientist believe that this huge explosion gave birth to the stars and planets ...
... huge explosion. • This huge explosion was known as The Big Bang. • Scientist believe that this huge explosion gave birth to the stars and planets ...
Fun Sun Facts! Facts and Figures • Diameter: 865,000 miles (109
... transmit a single frequency of light, the hydrogen alpha line at 6562.8 angstroms, visible in the red part of the spectrum. • This frequency is a primary emission source for the Sun, and many of the Sun’s features – such as sunspots, prominences and granulations – are visible in the Halpha frequency ...
... transmit a single frequency of light, the hydrogen alpha line at 6562.8 angstroms, visible in the red part of the spectrum. • This frequency is a primary emission source for the Sun, and many of the Sun’s features – such as sunspots, prominences and granulations – are visible in the Halpha frequency ...
Why do excited at - UC Berkeley Astronomy w
... (c) for the mantle, R = 6400km, V = 9.7 × 1011 km3 (where we calculated the volume at radius 6400km and then subtracted the volume within the radius = 3500km) and the fraction of total volume is f = 83.6%. (d) for the crust we calculated volumes at R=6450 km and R =6400 km and subtracted them to get ...
... (c) for the mantle, R = 6400km, V = 9.7 × 1011 km3 (where we calculated the volume at radius 6400km and then subtracted the volume within the radius = 3500km) and the fraction of total volume is f = 83.6%. (d) for the crust we calculated volumes at R=6450 km and R =6400 km and subtracted them to get ...
What is your real star sign - teacher notes
... thought that the Earth was the centre of the Universe and that the things that appeared in the night sky were to do with supernatural beings that could affect their everyday life. They thought there must be a connection between where the celestial objects were in the sky and what would happen in the ...
... thought that the Earth was the centre of the Universe and that the things that appeared in the night sky were to do with supernatural beings that could affect their everyday life. They thought there must be a connection between where the celestial objects were in the sky and what would happen in the ...
First Light for May, 2001 - South Bay Astronomical Society
... I’d anticipated. Too windy for doing any photography, I set the scope up for visual observing. A huge cloud had formed over the mountains to the north which must have been influenced by spiral winds rising over the mountains. It made a really striking shape and by sunset, lit by the red light, it al ...
... I’d anticipated. Too windy for doing any photography, I set the scope up for visual observing. A huge cloud had formed over the mountains to the north which must have been influenced by spiral winds rising over the mountains. It made a really striking shape and by sunset, lit by the red light, it al ...
Chapter 8: Stars
... relationship between a stars’ surface temperature and its absolute magnitude. • The modern HR Diagram is shown below. ...
... relationship between a stars’ surface temperature and its absolute magnitude. • The modern HR Diagram is shown below. ...
notes
... Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) for ten consecutive days between December 18 and 28, 1995. 1,500 galaxies at various stages of evolution. Most of the galaxies are so faint (nearly 30th magnitude or about four-billion times fainter than can be seen by the human eye) they have never before b ...
... Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) for ten consecutive days between December 18 and 28, 1995. 1,500 galaxies at various stages of evolution. Most of the galaxies are so faint (nearly 30th magnitude or about four-billion times fainter than can be seen by the human eye) they have never before b ...
Stars
... • Stars begin as a large cloud of gas and dust called a nebula. • Gravity pulls the particles of gas and dust causing the nebula to shrink. • A contracting cloud of gas and dust with enough mass to form a star is called a protostar. (Proto means “earliest” in ...
... • Stars begin as a large cloud of gas and dust called a nebula. • Gravity pulls the particles of gas and dust causing the nebula to shrink. • A contracting cloud of gas and dust with enough mass to form a star is called a protostar. (Proto means “earliest” in ...
Computing for Space Science - Current practice and future challenges
... • GERB Ground Segment Processing System • Multi-national data processing system – Germany RAL Belgium RAL Users ...
... • GERB Ground Segment Processing System • Multi-national data processing system – Germany RAL Belgium RAL Users ...
Large telescopes and why we need them Transcript
... we can only work with the light it emits that happens to fall on Earth. How much we can interpret and understand about the Universe around us depends on how well we can collect and analyse that light. This talk is about the first part of that problem: how we improve the collection of light. The key ...
... we can only work with the light it emits that happens to fall on Earth. How much we can interpret and understand about the Universe around us depends on how well we can collect and analyse that light. This talk is about the first part of that problem: how we improve the collection of light. The key ...
distance to the centre of the Milky Way.
... Herschel (1790) Star Counts He used telescopes to see more stars (since this makes fainter ones visible), but was still just working ‘by eye’. He could not take photographs, for instance. ...
... Herschel (1790) Star Counts He used telescopes to see more stars (since this makes fainter ones visible), but was still just working ‘by eye’. He could not take photographs, for instance. ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • There is an uncertainty with every measurement reflect this in the number of digits used in quoted results • Do not count trailing or leading zeros ...
... • There is an uncertainty with every measurement reflect this in the number of digits used in quoted results • Do not count trailing or leading zeros ...
Astronomy and Space Science
... – the distance the of the light source from the observer (inverse square law) • E.g., if a 6th magnitude star located 100 pc from the Earth were moved to 10 pc from us, it would appear 100 times brighter, and become a 1st magnitude star. • To compare the luminosity between different stars, the absol ...
... – the distance the of the light source from the observer (inverse square law) • E.g., if a 6th magnitude star located 100 pc from the Earth were moved to 10 pc from us, it would appear 100 times brighter, and become a 1st magnitude star. • To compare the luminosity between different stars, the absol ...
SWFAS Sept 2016 Newsletter - Southwest Florida Astronomical
... study the outer Solar System, Voyager 1 launched 16 days after its twin, Voyager 2. Having operated for 38 years, 11 months and 19 days, the spacecraft still communicates with the Deep Space Network to receive routine commands and return data. At a distance of 135 AU (2.02×1010 km) from the Sun as o ...
... study the outer Solar System, Voyager 1 launched 16 days after its twin, Voyager 2. Having operated for 38 years, 11 months and 19 days, the spacecraft still communicates with the Deep Space Network to receive routine commands and return data. At a distance of 135 AU (2.02×1010 km) from the Sun as o ...
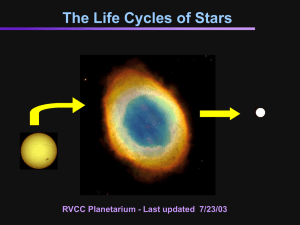
Life Cycles of Stars
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
2b. Which of Kepler`s laws did this illustrate? (State the law – don`t
... 2. Earth exerts a gravitational force on the Sun and the Sun exerts a gravitational force on Earth. a. Which exerts the larger force? Explain your choice. b. Which has the greater acceleration? Explain your choice. 3. Imagine another solar system with a star of the same mass as the Sun. In this sola ...
... 2. Earth exerts a gravitational force on the Sun and the Sun exerts a gravitational force on Earth. a. Which exerts the larger force? Explain your choice. b. Which has the greater acceleration? Explain your choice. 3. Imagine another solar system with a star of the same mass as the Sun. In this sola ...
To learn how the shape and period of... To learn how the shape of the orbit... Gravity, Orbits and Kepler’s Laws
... 2. Earth exerts a gravitational force on the Sun and the Sun exerts a gravitational force on Earth. a. Which exerts the larger force? Explain your choice. b. Which has the greater acceleration? Explain your choice. 3. Imagine another solar system with a star of the same mass as the Sun. In this sola ...
... 2. Earth exerts a gravitational force on the Sun and the Sun exerts a gravitational force on Earth. a. Which exerts the larger force? Explain your choice. b. Which has the greater acceleration? Explain your choice. 3. Imagine another solar system with a star of the same mass as the Sun. In this sola ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.