SOAR Telescope Photo Gallery
... center of mass. It is one of about 120 such clusters that are some of the very oldest objects in our own Galaxy, dating back to the galaxy’s formation some 13 billion years ago. n3603_final.jpg n3603_final.tiff NGC 3603 is the largest star-forming region in our own Milky Way Galaxy. The central port ...
... center of mass. It is one of about 120 such clusters that are some of the very oldest objects in our own Galaxy, dating back to the galaxy’s formation some 13 billion years ago. n3603_final.jpg n3603_final.tiff NGC 3603 is the largest star-forming region in our own Milky Way Galaxy. The central port ...
Astrophysics by Daniel Yang
... 1. Our understanding of celestial objects depends upon observations made from Earth or from space near the Earth - Discuss Galileo’s use of the telescope to identify features of the Moon Galileo was not the inventor of the telescope, but he built his own that was clear enough to observe the moon. He ...
... 1. Our understanding of celestial objects depends upon observations made from Earth or from space near the Earth - Discuss Galileo’s use of the telescope to identify features of the Moon Galileo was not the inventor of the telescope, but he built his own that was clear enough to observe the moon. He ...
Telescope
... continuously emitting sources; up to 10 times more sensitive for hour-scale emission; significantly more sensitive in the regime above 10 TeV; and possessing a sky coverage which is roughly an order of magnitude larger than existing instruments. Next Step: Bigger mirrors, even wider field-of-view, i ...
... continuously emitting sources; up to 10 times more sensitive for hour-scale emission; significantly more sensitive in the regime above 10 TeV; and possessing a sky coverage which is roughly an order of magnitude larger than existing instruments. Next Step: Bigger mirrors, even wider field-of-view, i ...
HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED
... in size to Jupiter. Planets of that size have proved easier to detect hundreds of light-years away. Most are not seen by direct imaging. They’re typically spotted indirectly by measuring the effect of their gravity on their parent ...
... in size to Jupiter. Planets of that size have proved easier to detect hundreds of light-years away. Most are not seen by direct imaging. They’re typically spotted indirectly by measuring the effect of their gravity on their parent ...
Dawn Spacecraft Will Go Asteroid
... and outer solar system. The inner solar system orbits (enlarged, at top) are, in order from the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Jupiter is part of the outer solar system. The outer solar system orbits are, in order: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. The Kuiper Belt, a realm of icy, ...
... and outer solar system. The inner solar system orbits (enlarged, at top) are, in order from the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Jupiter is part of the outer solar system. The outer solar system orbits are, in order: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. The Kuiper Belt, a realm of icy, ...
April 2005
... statehouse on I-270, the nucleus would be a soccer ball in Gov. Bob Taft’s office – Nuclei: made out of protons (el. positive) and neutrons (neutral) ...
... statehouse on I-270, the nucleus would be a soccer ball in Gov. Bob Taft’s office – Nuclei: made out of protons (el. positive) and neutrons (neutral) ...
Week 2 File
... parallax indicated that the stars were further away than had previously been imagined. He also tried to measure the parallax of a comet in 1577, but again failed (naked eye observa8ons allow angular ...
... parallax indicated that the stars were further away than had previously been imagined. He also tried to measure the parallax of a comet in 1577, but again failed (naked eye observa8ons allow angular ...
8 clusters stellar evo
... versus initial stellar mass Large stars live and die very quickly! 200 billion years! ...
... versus initial stellar mass Large stars live and die very quickly! 200 billion years! ...
Asteroids_comets_ooter belt
... They move among the stars, fastest when closest to the sun. (Why?) ...
... They move among the stars, fastest when closest to the sun. (Why?) ...
In the icy near-vacuum of interstellar space are seething
... other and how the galaxy as we know it is entirely a consequence of that balance and interplay." Astronomers have long known that there are huge, cloudlike collections of dust and gas swirling through the interstellar regions of a galaxy; they discovered these clouds as a result of the reddening eff ...
... other and how the galaxy as we know it is entirely a consequence of that balance and interplay." Astronomers have long known that there are huge, cloudlike collections of dust and gas swirling through the interstellar regions of a galaxy; they discovered these clouds as a result of the reddening eff ...
25 Study Guide
... • Color is a clue to a star’s temperature. • Binary stars can be used to determine stellar mass. • The nearest stars have the largest parallax angles, while those of distant stars are too small to measure. • Three factors control the apparent brightness of a star as seen from Earth: how big it is, h ...
... • Color is a clue to a star’s temperature. • Binary stars can be used to determine stellar mass. • The nearest stars have the largest parallax angles, while those of distant stars are too small to measure. • Three factors control the apparent brightness of a star as seen from Earth: how big it is, h ...
Lab Document - University of Iowa Astronomy and Astrophysics
... (8) Now let’s try and find a “Deep Sky” object using the Pocket Sky Atlas. We will look at the object M13 in the constellation of Hercules. Using the Star Wheel and SC1 chart, find Hercules. Both the Star Wheel and the SC1 indicate where M13 is located. The Pocket Sky Atlas has a more detailed map o ...
... (8) Now let’s try and find a “Deep Sky” object using the Pocket Sky Atlas. We will look at the object M13 in the constellation of Hercules. Using the Star Wheel and SC1 chart, find Hercules. Both the Star Wheel and the SC1 indicate where M13 is located. The Pocket Sky Atlas has a more detailed map o ...
absolute magnitude
... – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a smaller number, i.e. it is intrinsically brighter than it appears ...
... – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a smaller number, i.e. it is intrinsically brighter than it appears ...
Constellation
... Starry Night," Vincent van Gogh's famous painting, is renowned for its bold whorls of light sweeping across a raging night sky. Although this image of the heavens came only from the artist's restless imagination, a new picture from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope bears remarkable similarities to the v ...
... Starry Night," Vincent van Gogh's famous painting, is renowned for its bold whorls of light sweeping across a raging night sky. Although this image of the heavens came only from the artist's restless imagination, a new picture from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope bears remarkable similarities to the v ...
A-level Physics A Question paper Unit 5/W - Astrophysics
... ! The maximum mark for this paper is 40. This includes up to 2 marks for the Quality of Written Communication. ! The marks for questions are shown in brackets. ! A Data Sheet is provided on pages 3 and 4. You may wish to detach this perforated sheet at the start of the examination. ! You are expecte ...
... ! The maximum mark for this paper is 40. This includes up to 2 marks for the Quality of Written Communication. ! The marks for questions are shown in brackets. ! A Data Sheet is provided on pages 3 and 4. You may wish to detach this perforated sheet at the start of the examination. ! You are expecte ...
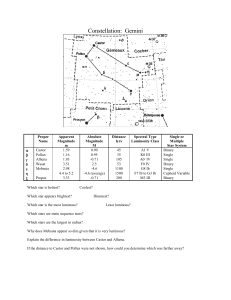
Gemini
... corresponds to a linear diameter of about 24 light years; its central density is about 6.21 stars per cubic parsec. Some authors have estimated a larger diameter of up to 46' (H. Shapley in 1930). With about 100 million years (WEBDA gives a value 95, the Sky Catalogue 2000.0 of 110 million years), i ...
... corresponds to a linear diameter of about 24 light years; its central density is about 6.21 stars per cubic parsec. Some authors have estimated a larger diameter of up to 46' (H. Shapley in 1930). With about 100 million years (WEBDA gives a value 95, the Sky Catalogue 2000.0 of 110 million years), i ...
high-resolution pdf file
... An idealized object that absorbs all radiation that hits it is called a black body. In equilibrium with its surroundings, it emits exactly as much radiation as it absorbs. Then it emits a spectrum as described in Figure 6-6 of (most editions of) the text. This black body or thermal radiation has the ...
... An idealized object that absorbs all radiation that hits it is called a black body. In equilibrium with its surroundings, it emits exactly as much radiation as it absorbs. Then it emits a spectrum as described in Figure 6-6 of (most editions of) the text. This black body or thermal radiation has the ...
Observers` Forum - British Astronomical Association
... which is impacting on the local medium. At the points of impact the bow shock generates Herbig−Haro (HH) objects as pairs on either side of the star. In the case of PV Cep three major pairs are clearly seen, with other knots of material present. There is circumstantial evidence that PV Cep is moving ...
... which is impacting on the local medium. At the points of impact the bow shock generates Herbig−Haro (HH) objects as pairs on either side of the star. In the case of PV Cep three major pairs are clearly seen, with other knots of material present. There is circumstantial evidence that PV Cep is moving ...
Return both exam and scantron sheet when you
... (c) the third Kepler’s law as formulated by Newton. 41. The Sun’s distance is 150,000,000 km. How long does it take a radar pulse sent from the Earth to travel to the Sun and back? The speed of light is 300,000 km/s. (a) 100 seconds. (b) 1000 seconds. (c) 10,000 seconds. (d) 100,000 seconds. 42. Wha ...
... (c) the third Kepler’s law as formulated by Newton. 41. The Sun’s distance is 150,000,000 km. How long does it take a radar pulse sent from the Earth to travel to the Sun and back? The speed of light is 300,000 km/s. (a) 100 seconds. (b) 1000 seconds. (c) 10,000 seconds. (d) 100,000 seconds. 42. Wha ...
Exercise 9
... star chart printed on a page, we often forget about the three-dimensional nature of the universe. In this exercise, you will construct (with welding rods and Styrofoam balls) a model of nearby space including many of the nearest stars. Of course, you will need information on where to place the stars ...
... star chart printed on a page, we often forget about the three-dimensional nature of the universe. In this exercise, you will construct (with welding rods and Styrofoam balls) a model of nearby space including many of the nearest stars. Of course, you will need information on where to place the stars ...
SBA_2 - Armagh Observatory
... faint stars and those with very broad lines, such as white dwarfs and rapidly rotating main sequence stars. Our revision of FORS1 data (Bagnulo et al. 2012) shows that a non-negligible fraction of the field detections obtained in the last few years is actually spurious. It is thus essential to under ...
... faint stars and those with very broad lines, such as white dwarfs and rapidly rotating main sequence stars. Our revision of FORS1 data (Bagnulo et al. 2012) shows that a non-negligible fraction of the field detections obtained in the last few years is actually spurious. It is thus essential to under ...
formation1
... the Galaxy once, then the O-star will only make it 1/250 the way around. • IF the circumference is 250,000 light years, then it will travel 250,000 ly/250. • Distance from the spot of origin is 1,000 light years. Then it dies. ...
... the Galaxy once, then the O-star will only make it 1/250 the way around. • IF the circumference is 250,000 light years, then it will travel 250,000 ly/250. • Distance from the spot of origin is 1,000 light years. Then it dies. ...
Science with multi-wavelength Archival Data
... information: data mining (increase obs. efficiency) + statistical identification (less need for spectra) • Good communication common language! Definition and adoption of VO standards and protocols within the ...
... information: data mining (increase obs. efficiency) + statistical identification (less need for spectra) • Good communication common language! Definition and adoption of VO standards and protocols within the ...
Bagnulo_2 - Armagh Observatory
... In stellar astronomy, a popular design for polarimeters is the one proposed by Appenzeller (1967). It comprises a retarder waveplate that may rotate at fixed positions in front of a beam splitter device such as a Wollaston prism. For linear polarization measurements, a halfwaveplate is employed and ...
... In stellar astronomy, a popular design for polarimeters is the one proposed by Appenzeller (1967). It comprises a retarder waveplate that may rotate at fixed positions in front of a beam splitter device such as a Wollaston prism. For linear polarization measurements, a halfwaveplate is employed and ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.