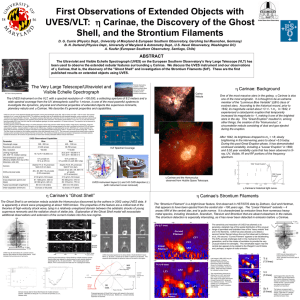
The Swansong of Stars Orbiting Massive Black Holes
... The signal is expected to be weak. To detect it, it is necessary to know in advance the shape of the wave trains, and to do that, it is necessary to know the eccentricity of the inspiral orbits. High eccentricity can change the nature of the signal drastically. The eccentricity also determines how m ...
... The signal is expected to be weak. To detect it, it is necessary to know in advance the shape of the wave trains, and to do that, it is necessary to know the eccentricity of the inspiral orbits. High eccentricity can change the nature of the signal drastically. The eccentricity also determines how m ...
No Slide Title
... • We learn about stars by studying energy. – Stars produce a full range of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy X-rays to low-energy radio waves. – Scientists use optical telescopes to study visible light and radio telescopes to study radio waves emitted from astronomical objects. – Earth’s a ...
... • We learn about stars by studying energy. – Stars produce a full range of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy X-rays to low-energy radio waves. – Scientists use optical telescopes to study visible light and radio telescopes to study radio waves emitted from astronomical objects. – Earth’s a ...
spie_poster1 - UMD Physics
... evolved stars. According to the historical record, prior to 1842, its magnitude varied about +3 +/- 1 mv. In 1842, it experienced a cataclysmic eruption that temporarily increased its magnitude to -1, making it one of the brightest stars in the sky. This “Great Eruption” resulted in, among other thi ...
... evolved stars. According to the historical record, prior to 1842, its magnitude varied about +3 +/- 1 mv. In 1842, it experienced a cataclysmic eruption that temporarily increased its magnitude to -1, making it one of the brightest stars in the sky. This “Great Eruption” resulted in, among other thi ...
ISM and star formation
... Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are forming too, but make few UV photons. Why "H II Region? H I: Hydrogen atom H II: Ionized Hydrogen ...
... Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are forming too, but make few UV photons. Why "H II Region? H I: Hydrogen atom H II: Ionized Hydrogen ...
PDF 630 kB - Prague Relativistic Astrophysics
... up as the SNIa. Then Harvey Richer pre- Scott Ransom, therefore we can mention sented the results of careful analysis of directly the contribution of Jeff Newman, HST observations of the faintest stars in who presented results of the DEEP2 proja globular cluster NGC 6397. NGC 6397 ect. DEEP2 is a re ...
... up as the SNIa. Then Harvey Richer pre- Scott Ransom, therefore we can mention sented the results of careful analysis of directly the contribution of Jeff Newman, HST observations of the faintest stars in who presented results of the DEEP2 proja globular cluster NGC 6397. NGC 6397 ect. DEEP2 is a re ...
Constellations Reading
... Generally, there is little resemblance between the star pattern and the fully illustrated object or figure that represents the constellation. For example, consider the Northern Hemisphere’s winter constellation Orion the Hunter. The star pattern on which it is based — four bright stars at the corne ...
... Generally, there is little resemblance between the star pattern and the fully illustrated object or figure that represents the constellation. For example, consider the Northern Hemisphere’s winter constellation Orion the Hunter. The star pattern on which it is based — four bright stars at the corne ...
Document
... Galactic Distances • How do we know the distance to stars and clusters in our galaxy? • Stellar parallax: – Parallax of nearby stars relative to background stars. – Good out to ~500 pc. ...
... Galactic Distances • How do we know the distance to stars and clusters in our galaxy? • Stellar parallax: – Parallax of nearby stars relative to background stars. – Good out to ~500 pc. ...
How Big Is Our Universe? - Harvard
... The Sun is so far away that it would take the Space Shuttle seven months to fly there. That’s why the Sun, which is one hundred times the diameter of the Earth, looks so small! Three hundred years ago, astronomer Edmund Halley found a way to measure the distance to the Sun and to the planet Venus. K ...
... The Sun is so far away that it would take the Space Shuttle seven months to fly there. That’s why the Sun, which is one hundred times the diameter of the Earth, looks so small! Three hundred years ago, astronomer Edmund Halley found a way to measure the distance to the Sun and to the planet Venus. K ...
WHERE DO ELEMENTS COME FROM?
... Milky Way – Center contains massive black hole (>106 solar mass) 10,000 light years to the middle, 100,000 light years across ...
... Milky Way – Center contains massive black hole (>106 solar mass) 10,000 light years to the middle, 100,000 light years across ...
ppt
... • AstroGrid (and other VO projects) will supply the middleware, but have no remit (and no funding) to update the archives themselves. • Serious data mining research will require serious processing power near the data stores (e.g. an Astronomical Data Warehouse). ...
... • AstroGrid (and other VO projects) will supply the middleware, but have no remit (and no funding) to update the archives themselves. • Serious data mining research will require serious processing power near the data stores (e.g. an Astronomical Data Warehouse). ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... The Mass of the Galaxy • Can be determined using Kepler’s 3rd Law – Solar System: the orbital velocities of planets determined by mass of Sun – Galaxy: orbital velocities of stars are determined by total mass of the galaxy contained within that star’s orbit ...
... The Mass of the Galaxy • Can be determined using Kepler’s 3rd Law – Solar System: the orbital velocities of planets determined by mass of Sun – Galaxy: orbital velocities of stars are determined by total mass of the galaxy contained within that star’s orbit ...
Merit Badge College 2017 Astronomy
... Then explain how to safely observe the Sun, objects near the Sun, and the Moon. 2. Explain what light pollution is and how it and air pollution affect astronomy. 3. With the aid of diagrams (or real telescopes if available), do each of the following: a. Explain why binoculars and telescopes ar ...
... Then explain how to safely observe the Sun, objects near the Sun, and the Moon. 2. Explain what light pollution is and how it and air pollution affect astronomy. 3. With the aid of diagrams (or real telescopes if available), do each of the following: a. Explain why binoculars and telescopes ar ...
Chapter 2: The Sky
... Stars are divided into six classes: brightest stars are first-class stars, fainter stars are second-class and so on until the sixth class of stars is reached ...
... Stars are divided into six classes: brightest stars are first-class stars, fainter stars are second-class and so on until the sixth class of stars is reached ...
lecture11
... concentrated in a rather narrow range of wavelengths. The spectrum of a star’s light is approximately a black body spectrum. In fact, the spectrum of a star at the photosphere, before the light passes through the atmosphere of the star, is a nearly PERFECT black body one ...
... concentrated in a rather narrow range of wavelengths. The spectrum of a star’s light is approximately a black body spectrum. In fact, the spectrum of a star at the photosphere, before the light passes through the atmosphere of the star, is a nearly PERFECT black body one ...
Star project
... have their own gravity and have a fixed position in space. • They are extremely burning hot. • The nearest star to us is the sun. • They are made up of mainly hydrogen and helium, but have a little bit of other elements like oxygen and carbon as well. ...
... have their own gravity and have a fixed position in space. • They are extremely burning hot. • The nearest star to us is the sun. • They are made up of mainly hydrogen and helium, but have a little bit of other elements like oxygen and carbon as well. ...
LETTERS A giant planet orbiting the ‘extreme horizontal
... planets have now been detected. Most of them orbit mainsequence stars similar to our Sun, although a few planets orbiting red giant stars have been recently found3. When the hydrogen in their cores runs out, main-sequence stars undergo an expansion into red-giant stars. This expansion can modify the ...
... planets have now been detected. Most of them orbit mainsequence stars similar to our Sun, although a few planets orbiting red giant stars have been recently found3. When the hydrogen in their cores runs out, main-sequence stars undergo an expansion into red-giant stars. This expansion can modify the ...
PHYS 2410 General Astronomy Homework 8
... 14. The material that accretes onto a neutron star or black hole is expected to emit x-rays because ...
... 14. The material that accretes onto a neutron star or black hole is expected to emit x-rays because ...
Great Migrations & other natural history tales
... attempt at stardom As seen in the simulation of molecular cloud fragmentation, brown dwarfs (smallest objects simulated as white points) form in large numbers, and are mostly dispersed throughout the Galaxy afterwards. Sometimes, they are found as orbital companions to stars (not frequently, hence t ...
... attempt at stardom As seen in the simulation of molecular cloud fragmentation, brown dwarfs (smallest objects simulated as white points) form in large numbers, and are mostly dispersed throughout the Galaxy afterwards. Sometimes, they are found as orbital companions to stars (not frequently, hence t ...
Phobos
... This star is the famous Castor, the horseman. There is some idea that either this star or Pollux has changed in brightness over the past few hundred years because Castor is no longer the brighter of the two. Instead it is now ranked as the 23rd brightest star in the sky or perhaps we should say brig ...
... This star is the famous Castor, the horseman. There is some idea that either this star or Pollux has changed in brightness over the past few hundred years because Castor is no longer the brighter of the two. Instead it is now ranked as the 23rd brightest star in the sky or perhaps we should say brig ...
InternetArchive_ManagingBornDigitalData
... It has data on every part of the sky In every measured spectral band: optical, x-ray, radio.. As deep as the best instruments (2 years ago). It is up when you are up. The “seeing” is always great (no working at night, no clouds no moons no..). – It’s a smart telescope: links objects and data to lite ...
... It has data on every part of the sky In every measured spectral band: optical, x-ray, radio.. As deep as the best instruments (2 years ago). It is up when you are up. The “seeing” is always great (no working at night, no clouds no moons no..). – It’s a smart telescope: links objects and data to lite ...
May / June 2009 - Astroadventures.net
... Distribute the targets throughout the sky so that one or more would always be visible, even in partly cloudy skies. The pages are divided by season, with 7 stars listed per page. Polaris is included in the Autumn. From Gainesville, each star rises at least 30 degrees above the horizon at some point ...
... Distribute the targets throughout the sky so that one or more would always be visible, even in partly cloudy skies. The pages are divided by season, with 7 stars listed per page. Polaris is included in the Autumn. From Gainesville, each star rises at least 30 degrees above the horizon at some point ...
Two-Gyro Performance, Scheduling and Acquisitions
... – This problem was identified by the OTA SEs in some follow-on analysis of the previous problem’s test results. However, the cause of this problem is different. – Problem only occurs with Target-ReAcq style Acqs/ReAcqs where both PASS and the onboard ReAcq process are effectively accounting for a po ...
... – This problem was identified by the OTA SEs in some follow-on analysis of the previous problem’s test results. However, the cause of this problem is different. – Problem only occurs with Target-ReAcq style Acqs/ReAcqs where both PASS and the onboard ReAcq process are effectively accounting for a po ...
AN INTRODUCTION TO ASTRONOMY Dr. Uri Griv Department of Physics, Ben-Gurion University
... the basis of a geometric progression rather than an arithmetic progression • The modern magnitude classification: a difference of 5 magnitudes to equal exactly a factor of 100 in apparent brightness • If m1 and m2 are the apparent magnitudes with apparent brightness f1 and f1 m2 − m1 = 2.5 log10 (f1 ...
... the basis of a geometric progression rather than an arithmetic progression • The modern magnitude classification: a difference of 5 magnitudes to equal exactly a factor of 100 in apparent brightness • If m1 and m2 are the apparent magnitudes with apparent brightness f1 and f1 m2 − m1 = 2.5 log10 (f1 ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.