Astro-Tech`s AT6RC offers great imaging on a budget
... own for this test. It is important to note that Astro-Tech designed the AT6RC specifically for astrophotography using digital singlelens reflex (DSLR) cameras and other imagers with large chips. An observer can use it visually, but the real strength behind the RC design is its flat photographic fiel ...
... own for this test. It is important to note that Astro-Tech designed the AT6RC specifically for astrophotography using digital singlelens reflex (DSLR) cameras and other imagers with large chips. An observer can use it visually, but the real strength behind the RC design is its flat photographic fiel ...
Notes on Integral Field Spectroscopy (IFS/3D) Sebastián F. Sánchez / IA-UNAM
... FF IFU: Data Reduction (III) ...
... FF IFU: Data Reduction (III) ...
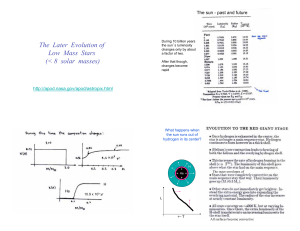
The Later Evolution of Low Mass Stars (< 8 solar masses)
... The C-O core is degenerate and transports its radiation by conduction. ...
... The C-O core is degenerate and transports its radiation by conduction. ...
ted_2012_power_of_design
... gassiest) kid on the block. A gas giant with a mass 2.5 times that of all other planets in our solar system combined, Jupiter is the third-brightest object in the night sky after the moon and Venus. Jupiter’s most prominent feature is the Great Red Spot, a storm larger than Earth that has possibly b ...
... gassiest) kid on the block. A gas giant with a mass 2.5 times that of all other planets in our solar system combined, Jupiter is the third-brightest object in the night sky after the moon and Venus. Jupiter’s most prominent feature is the Great Red Spot, a storm larger than Earth that has possibly b ...
High Mass Stars
... – From H-R diagram its luminosity is 100000 times greater than the Sun’s. – It therefore burns fuel (uses it’s mass) 100000 times faster than the Sun. – It has 25 times the mass of the Sun so its lifetime will be 25/100000 = 0.00025 times than the Sun’s lifetime = 2.5 million years. ...
... – From H-R diagram its luminosity is 100000 times greater than the Sun’s. – It therefore burns fuel (uses it’s mass) 100000 times faster than the Sun. – It has 25 times the mass of the Sun so its lifetime will be 25/100000 = 0.00025 times than the Sun’s lifetime = 2.5 million years. ...
telestar instruction manual
... The color of stars sometimes can tell you about the age of a star and the temperature that they burn at. Other stars to look for are multiple stars. Very often, you can find double (or binary) stars, stars that are very close together. These stars orbit each other. What do you notice about these sta ...
... The color of stars sometimes can tell you about the age of a star and the temperature that they burn at. Other stars to look for are multiple stars. Very often, you can find double (or binary) stars, stars that are very close together. These stars orbit each other. What do you notice about these sta ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... The central plane of the disc contains most of the Galaxy’s supply of cold, star-forming gas. This gas is extremely heavily polluted by eject a from stars: if it were compressed to the density of air (i.e., by a factor ~ 1021 ) one could see only a few cm through it because light is absorbed by part ...
... The central plane of the disc contains most of the Galaxy’s supply of cold, star-forming gas. This gas is extremely heavily polluted by eject a from stars: if it were compressed to the density of air (i.e., by a factor ~ 1021 ) one could see only a few cm through it because light is absorbed by part ...
PowerPoint
... Exploring (Earth-like) Exoplanets • RV search for new low-mass planets • Transit follow-up studies • Gravitational microlensing follow-up studies • Direct imaging studies ...
... Exploring (Earth-like) Exoplanets • RV search for new low-mass planets • Transit follow-up studies • Gravitational microlensing follow-up studies • Direct imaging studies ...
but restricted to nearby large stars
... 4,300 kelvin (slightly above the photosphere) to around 50,000 kelvin (near the corona). ...
... 4,300 kelvin (slightly above the photosphere) to around 50,000 kelvin (near the corona). ...
the stars
... magnitude versus spectral type and obtained the diagram. Today we can use the Virtual Observatory tools, so we do not need to perform astronomical observations during the night. We will observe in Stellarium the 25 brightest stars of the sky and then plot their spectral type versus absolute magnitud ...
... magnitude versus spectral type and obtained the diagram. Today we can use the Virtual Observatory tools, so we do not need to perform astronomical observations during the night. We will observe in Stellarium the 25 brightest stars of the sky and then plot their spectral type versus absolute magnitud ...
Synthetic color-magnitude diagrams: the ingredients
... two stellar masses and its luminosity depends on the mass ratio q=M2/M1 ü The equal-mass binaries form a sequence running almost parallel to the MS, and ~0.75mag brighter; ü When the masses of the two components are different, the binary will appear redder and brighter than the primary and popul ...
... two stellar masses and its luminosity depends on the mass ratio q=M2/M1 ü The equal-mass binaries form a sequence running almost parallel to the MS, and ~0.75mag brighter; ü When the masses of the two components are different, the binary will appear redder and brighter than the primary and popul ...
Lecture Eleven (Powerpoint format)
... In determining the position of our sun within our galaxy, astronomers were long confused by the fact that simply counting stars, we appear to be at the center of the Milky Way. The problem with this method is that it does not take into account the absorption and reddening of starlight by interve ...
... In determining the position of our sun within our galaxy, astronomers were long confused by the fact that simply counting stars, we appear to be at the center of the Milky Way. The problem with this method is that it does not take into account the absorption and reddening of starlight by interve ...
SST-GATE: An Innovative Telescope for the Very High
... a single gamma-ray, cannot be improved through increased exposure. This motivates the development of optical systems with very large primary mirrors, having diameters in the range of 10−30m. In addition, the optical systems of Cherenkov telescope must be composed of the minimal number of optical ele ...
... a single gamma-ray, cannot be improved through increased exposure. This motivates the development of optical systems with very large primary mirrors, having diameters in the range of 10−30m. In addition, the optical systems of Cherenkov telescope must be composed of the minimal number of optical ele ...
galctr
... For stars in close approach to Sgr A*, Br lines shifted by 1100-1500 km/s => can separate from local gas emission => consistent with OB star atmospheres ...
... For stars in close approach to Sgr A*, Br lines shifted by 1100-1500 km/s => can separate from local gas emission => consistent with OB star atmospheres ...
Thinking About Gravity
... 16. In a few sentences, what can you conclude about how the size of a planet and its distance from the Sun affects its orbit? The larger the Star is the more gravitational force it will exert, pulling planets towards it, the planets will orbit more quickly and be pulled more strongly giving a more e ...
... 16. In a few sentences, what can you conclude about how the size of a planet and its distance from the Sun affects its orbit? The larger the Star is the more gravitational force it will exert, pulling planets towards it, the planets will orbit more quickly and be pulled more strongly giving a more e ...
TE SC.4.E.5.4, 5.3, 5.2, 5.1
... Answer: The stars appear to move because of Earth’s rotation. Constellations or patterns of stars also change with the seasons because Earth is orbiting around the sun. 3. Why do constellations change with the seasons? Answer: The constellations have been in the same positions for thousands of years ...
... Answer: The stars appear to move because of Earth’s rotation. Constellations or patterns of stars also change with the seasons because Earth is orbiting around the sun. 3. Why do constellations change with the seasons? Answer: The constellations have been in the same positions for thousands of years ...
The Family of Stars
... The turn-off point from the Main Sequence. The minimum mass of stars at the lower end of the main sequence. ...
... The turn-off point from the Main Sequence. The minimum mass of stars at the lower end of the main sequence. ...
Define the following terms in the space provided
... horizon. When stars or other astronomical objects cross the meridian they are said to “transit” the meridian. 10) Sidereal Day A sidereal day is the period of time required for the celestial sphere to make on complete rotation on its axis. It is really the period of time the Earth requires completin ...
... horizon. When stars or other astronomical objects cross the meridian they are said to “transit” the meridian. 10) Sidereal Day A sidereal day is the period of time required for the celestial sphere to make on complete rotation on its axis. It is really the period of time the Earth requires completin ...
The Giant Magellan Telescope
... • Each M1 segment is used exactly twice. • Ideal PSFs are shown in second column. • A quarter wave of piston on either an edge or center segment will affect two of the three MTFs. • (N.B. MTFs are shown at much higher resolution than would actually need to be sampled.) ...
... • Each M1 segment is used exactly twice. • Ideal PSFs are shown in second column. • A quarter wave of piston on either an edge or center segment will affect two of the three MTFs. • (N.B. MTFs are shown at much higher resolution than would actually need to be sampled.) ...
FREE Sample Here
... 1. The moon appears larger when it rises than when it is high in the sky because A. You are closer to it when it rises (angular-size relation). B. You are farther from it when it rises (angular-size relation). C. It's an illusion from comparison to objects on the horizon. D. It's brighter when it ri ...
... 1. The moon appears larger when it rises than when it is high in the sky because A. You are closer to it when it rises (angular-size relation). B. You are farther from it when it rises (angular-size relation). C. It's an illusion from comparison to objects on the horizon. D. It's brighter when it ri ...
The woman who dissected the Sun
... theory with the theory of heat - thermodynamics. Collisions between atoms in a gas could also knock out electrons and the "Saha equation" predicted, for any temperature and density, what fraction of an element's atoms would be neutral, stripped of one electron, two electrons, and so on. The final st ...
... theory with the theory of heat - thermodynamics. Collisions between atoms in a gas could also knock out electrons and the "Saha equation" predicted, for any temperature and density, what fraction of an element's atoms would be neutral, stripped of one electron, two electrons, and so on. The final st ...
FREE Sample Here
... © 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part ...
... © 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part ...
Pluto and the Dwarf Planets
... • Strange object; located far out from the Sun with gas giants but small size and very elliptical and highly inclined orbit • Pluto is a mixture of ices and rocks • composition similar to satellites of giant planets • Could be captured Kuiper Belt Object (e.g. comet)? ...
... • Strange object; located far out from the Sun with gas giants but small size and very elliptical and highly inclined orbit • Pluto is a mixture of ices and rocks • composition similar to satellites of giant planets • Could be captured Kuiper Belt Object (e.g. comet)? ...
May - Rappahannock Astronomy Club
... samples, and two books he picked up at NEAF. Ben Ashley talked about upgrading equipment to get into astronomical imaging. He now has an Explore Scientific 127-mm apochromatic triplet refractor on an Atlas mount and a Kodak chip. Ben has had some success purchasing used equipment in like-new conditi ...
... samples, and two books he picked up at NEAF. Ben Ashley talked about upgrading equipment to get into astronomical imaging. He now has an Explore Scientific 127-mm apochromatic triplet refractor on an Atlas mount and a Kodak chip. Ben has had some success purchasing used equipment in like-new conditi ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.