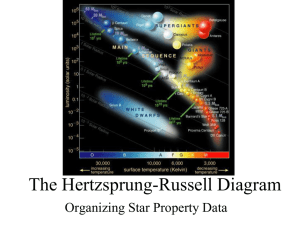
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
Characteristics of Main Sequence Stars
... nuclear reactions in high mass stars are generally confined to a very small region, much smaller than the size of the convective core. • As the stellar mass increases, so does the size of the convective core (due again to the large increase in ² with temperature). Supermassive stars with M ∼ 100M¯ w ...
... nuclear reactions in high mass stars are generally confined to a very small region, much smaller than the size of the convective core. • As the stellar mass increases, so does the size of the convective core (due again to the large increase in ² with temperature). Supermassive stars with M ∼ 100M¯ w ...
the life cycles of stars (5) - U3A Bendigo Courses / Activities
... The main sequence life burning hydrogen lasts only 100 million years instead of 10 billion for the sun. These are O and B type stars. Even before leaving the main sequence these stars emit material from their surface due to sheer radiation pressure. The strong light radiation carries gas with it. Ou ...
... The main sequence life burning hydrogen lasts only 100 million years instead of 10 billion for the sun. These are O and B type stars. Even before leaving the main sequence these stars emit material from their surface due to sheer radiation pressure. The strong light radiation carries gas with it. Ou ...
early greek astrophysics: the foundations of modern science and
... sowing the fields, some of which are kept even today in Greece and other countries, like the festivity of St. Demetrius, on October 26, a festivity which probably replaced the festivity of Demeter, the Goddess of Agriculture and the Cereals. It is worth mentioning that in ancient Egypt we encounter ...
... sowing the fields, some of which are kept even today in Greece and other countries, like the festivity of St. Demetrius, on October 26, a festivity which probably replaced the festivity of Demeter, the Goddess of Agriculture and the Cereals. It is worth mentioning that in ancient Egypt we encounter ...
Word document - Moray`s Astronomy Club, SIGMA
... Elgin as depicted on the map. From the hall it’s a short hop to our dark site at Easterton Airfield, which allows us to hold observing sessions immediately after meetings when conditions are suitable. We also have a number of Club telescopes available for members’ use. Observing sessions are also he ...
... Elgin as depicted on the map. From the hall it’s a short hop to our dark site at Easterton Airfield, which allows us to hold observing sessions immediately after meetings when conditions are suitable. We also have a number of Club telescopes available for members’ use. Observing sessions are also he ...
Word version of Episode 704
... External reference This activity is taken from Advancing Physics, chapter 12, 160O ...
... External reference This activity is taken from Advancing Physics, chapter 12, 160O ...
color-stellar mass diagram
... luminosity, mass, color, morphology, stellar population of galaxies are strongly related. analysis of such properties in the cosmic time started first with the study of the luminosity function but later included galaxy counts as function of the various parameters however, almost all these properties ...
... luminosity, mass, color, morphology, stellar population of galaxies are strongly related. analysis of such properties in the cosmic time started first with the study of the luminosity function but later included galaxy counts as function of the various parameters however, almost all these properties ...
A modern physics laboratory activity: Radio astronomical observations of recombination lines
... on. Many times the visible Balmer lines of hydrogen are measured in the modern physics laboratory if they were not measured in general physics. Perhaps the visible spectrum of deuterium is calculated and measured to show the effect of changing M. Observations of recombination lines provide another e ...
... on. Many times the visible Balmer lines of hydrogen are measured in the modern physics laboratory if they were not measured in general physics. Perhaps the visible spectrum of deuterium is calculated and measured to show the effect of changing M. Observations of recombination lines provide another e ...
Define the following terms in the space provided
... G) Would a star with a declination of +60 be circumpolar? Explain. A star with a declination of +60 be circumpolar. It would dip to 2° above the northern horizon. H) What would be altitude of the Celestial Equator looking south? The altitude of the Celestial Equator looking south would be 58°. I) ...
... G) Would a star with a declination of +60 be circumpolar? Explain. A star with a declination of +60 be circumpolar. It would dip to 2° above the northern horizon. H) What would be altitude of the Celestial Equator looking south? The altitude of the Celestial Equator looking south would be 58°. I) ...
The Classical Achromat
... So how does spherical aberration impair the image in a refractor? At low magnifications, little or no effects can be seen, but as you crank up the power an instrument displaying significant spherical aberration will be very hard to focus sharply. As a result, high power views of planets and the Moon ...
... So how does spherical aberration impair the image in a refractor? At low magnifications, little or no effects can be seen, but as you crank up the power an instrument displaying significant spherical aberration will be very hard to focus sharply. As a result, high power views of planets and the Moon ...
distant stars nearby star parallax angle The principle of geometrical
... Does the star Vega in Lyra appear exceptionally bright because it’s an intrinsically bright star, or simply because it’s unusually close by? What about Betelgeuse in Orion? If we didn’t know the distances to these stars, we wouldn’t know that Betelgeuse is a red giant star, with a much greater intri ...
... Does the star Vega in Lyra appear exceptionally bright because it’s an intrinsically bright star, or simply because it’s unusually close by? What about Betelgeuse in Orion? If we didn’t know the distances to these stars, we wouldn’t know that Betelgeuse is a red giant star, with a much greater intri ...
copyright 2002 scientific american, inc.
... Space Agency’s X-ray Multi-Mirror satellite found evidence of emission lines from silicon, sulfur, argon and other elements commonly released by supernovae. Although researchers still debate the matter, a growing school of thought holds that the same object can produce, in some cases, both a burst a ...
... Space Agency’s X-ray Multi-Mirror satellite found evidence of emission lines from silicon, sulfur, argon and other elements commonly released by supernovae. Although researchers still debate the matter, a growing school of thought holds that the same object can produce, in some cases, both a burst a ...
Seeds of a Tychonic Revolution: Telescopic Observations of the
... immense beyond reason – even infinite if the universe is infinite. The Earth, not the stars, must be what rotates daily. Mareo's systematic observations of the stars seem to be backing a Copernican (or Diggesian) world system – until he makes another discovery: A star that appears to be a single sta ...
... immense beyond reason – even infinite if the universe is infinite. The Earth, not the stars, must be what rotates daily. Mareo's systematic observations of the stars seem to be backing a Copernican (or Diggesian) world system – until he makes another discovery: A star that appears to be a single sta ...
PSC100 Summary Chapters 10 to Chapter 20
... hydrogen into helium. As long as this process continues, the star is said to be in its MAIN SEQUENCE LIFE TIME. This time that a star remains on the main sequence is determined by the mass of the star in a rather peculiar way. The more massive the star, the hotter the core and the faster the hydroge ...
... hydrogen into helium. As long as this process continues, the star is said to be in its MAIN SEQUENCE LIFE TIME. This time that a star remains on the main sequence is determined by the mass of the star in a rather peculiar way. The more massive the star, the hotter the core and the faster the hydroge ...
Chapter 20
... Astronomers have long speculated about the origin of our Solar System. They have noted regularities in the way the planets orbit the Sun and in the spacing of the planetary orbits. But until recently, astronomers have been limited to studying one planetary system: our own. In 1600, Giordano Bruno wa ...
... Astronomers have long speculated about the origin of our Solar System. They have noted regularities in the way the planets orbit the Sun and in the spacing of the planetary orbits. But until recently, astronomers have been limited to studying one planetary system: our own. In 1600, Giordano Bruno wa ...
The Solar System Interplanetary Matter and the Birth of the Planets
... The idea that the solar system was born from the collapse of a cloud of dust and gas for proposed by Immanuel Kant (1755) and by Pierre Simon Laplace (40 years later). During the first part of the 20th century, some proposed that the solar system was the result of a near collision of the Sun with an ...
... The idea that the solar system was born from the collapse of a cloud of dust and gas for proposed by Immanuel Kant (1755) and by Pierre Simon Laplace (40 years later). During the first part of the 20th century, some proposed that the solar system was the result of a near collision of the Sun with an ...
USING THE VISUAL METEOR DATA FORM
... Values will range from +3.0 to +7.5. Stellar magnitudes can be obtained from any star atlas. Values lower than +5.0 will rarely offer worthwhile viewing since most meteors are faint. Values higher than +6.5 are only available far from urban areas. A great majority of the data submitted to AMS has LM ...
... Values will range from +3.0 to +7.5. Stellar magnitudes can be obtained from any star atlas. Values lower than +5.0 will rarely offer worthwhile viewing since most meteors are faint. Values higher than +6.5 are only available far from urban areas. A great majority of the data submitted to AMS has LM ...
Slide 1
... Red Giant phase with inert He-core and outer H-burning shell; star expands and cools, but is brighter Climbs up the RG branch until He-flash in the core Core expands and cools; H-burning decreases; outer layers contract; luminosity decreases but temperature increases; star moves LEFT on the H-R diag ...
... Red Giant phase with inert He-core and outer H-burning shell; star expands and cools, but is brighter Climbs up the RG branch until He-flash in the core Core expands and cools; H-burning decreases; outer layers contract; luminosity decreases but temperature increases; star moves LEFT on the H-R diag ...
Lecture02: Astronomical Distance
... Astronomers study the Sun to learn the structure and evolution of stars and sun-earth connection (climate and space weather). ...
... Astronomers study the Sun to learn the structure and evolution of stars and sun-earth connection (climate and space weather). ...
STAR FORMATION (Ch. 19)
... pillars (emission nebulae), followed by circumstellar disks, and progressing to evolved massive stars in the young starburst cluster.To the upper right of center is the evolved blue supergiant called Sher 25. The star has a unique circumstellar ring of glowing gas that is a galactic twin to the famo ...
... pillars (emission nebulae), followed by circumstellar disks, and progressing to evolved massive stars in the young starburst cluster.To the upper right of center is the evolved blue supergiant called Sher 25. The star has a unique circumstellar ring of glowing gas that is a galactic twin to the famo ...
Patterns in the Night Sky
... the stars in a particular part of the sky (Figure 4). Some star maps show only those objects that can be seen with the unaided eye, while others show objects that can only be viewed using a telescope or other instrument. A star map can be used to recognize celestial objects in the sky, and to observ ...
... the stars in a particular part of the sky (Figure 4). Some star maps show only those objects that can be seen with the unaided eye, while others show objects that can only be viewed using a telescope or other instrument. A star map can be used to recognize celestial objects in the sky, and to observ ...
Answers to exam style questions
... got to be there. In this case a white dwarf is hot and dim – both properties which can be remotely measured. Answers related to their formation – such as the core of a much larger star – would not gain credit. Similarly restating the properties in the question – for example, ‘small’ – would not gain ...
... got to be there. In this case a white dwarf is hot and dim – both properties which can be remotely measured. Answers related to their formation – such as the core of a much larger star – would not gain credit. Similarly restating the properties in the question – for example, ‘small’ – would not gain ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.