Brucellosis - Developing Anaesthesia
... Brucellosis is a systemic disease with acute or insidious onset. ...
... Brucellosis is a systemic disease with acute or insidious onset. ...
Identification of a new monosaccharide in Mycobacterium
... Recently, we discovered an unusual sugar residue attached to the mannosyl caps of LAM. High resolution NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry studies revealed that this novel monosaccharide was a 5-methylthio-pentofuranoside, which was partially oxidised to the sulfoxide. However, it was not possibl ...
... Recently, we discovered an unusual sugar residue attached to the mannosyl caps of LAM. High resolution NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry studies revealed that this novel monosaccharide was a 5-methylthio-pentofuranoside, which was partially oxidised to the sulfoxide. However, it was not possibl ...
Hand Foot and Mouth Disease
... Meningitis, which causes fever, headache, stiff neck, and/or back pain ...
... Meningitis, which causes fever, headache, stiff neck, and/or back pain ...
Document
... On appearance of bacteria an organism answers a local and general reaction. The local reaction of tissues is expressed foremost, by the change of circulation of blood of neural-reflector nature. Arterial hyperemia develops, and then venous stasis with formation of edema, pain, local increase of temp ...
... On appearance of bacteria an organism answers a local and general reaction. The local reaction of tissues is expressed foremost, by the change of circulation of blood of neural-reflector nature. Arterial hyperemia develops, and then venous stasis with formation of edema, pain, local increase of temp ...
infectious diseases
... • jaundice (JAWN dis), or yellowing of the skin. • Hepatitis A is transmitted in human wastes and in contaminated water and food. • Hepatitis B can be transmitted in blood, during sexual contact, or during tattooing or body piercing. • Hepatitis C can be transmitted in blood, during sexual contact, ...
... • jaundice (JAWN dis), or yellowing of the skin. • Hepatitis A is transmitted in human wastes and in contaminated water and food. • Hepatitis B can be transmitted in blood, during sexual contact, or during tattooing or body piercing. • Hepatitis C can be transmitted in blood, during sexual contact, ...
Slide 1
... • jaundice (JAWN dis), or yellowing of the skin. • Hepatitis A is transmitted in human wastes and in contaminated water and food. • Hepatitis B can be transmitted in blood, during sexual contact, or during tattooing or body piercing. • Hepatitis C can be transmitted in blood, during sexual contact, ...
... • jaundice (JAWN dis), or yellowing of the skin. • Hepatitis A is transmitted in human wastes and in contaminated water and food. • Hepatitis B can be transmitted in blood, during sexual contact, or during tattooing or body piercing. • Hepatitis C can be transmitted in blood, during sexual contact, ...
Ch.13 Part II
... Persistence of Microbes and Pathologic Conditions • Apparent recovery of host does not always mean the microbe has been removed • Latency – after the initial symptoms in certain chronic diseases, the microbe can periodically become active and produce a recurrent disease; person may or may not shed ...
... Persistence of Microbes and Pathologic Conditions • Apparent recovery of host does not always mean the microbe has been removed • Latency – after the initial symptoms in certain chronic diseases, the microbe can periodically become active and produce a recurrent disease; person may or may not shed ...
Common Infectious Diseases
... impossible to avoid them. • Although the young and the elderly are most susceptible to infectious diseases, we are all capable of being infected. • Our best defense against pathogens is to avoid behaviors that increase our chances of becoming infected. ...
... impossible to avoid them. • Although the young and the elderly are most susceptible to infectious diseases, we are all capable of being infected. • Our best defense against pathogens is to avoid behaviors that increase our chances of becoming infected. ...
Current Threats to Public Health
... hands are visibly soiled, use soap and water to wash them instead of an alcohol-based hand sanitizer. Saccharomyces boulardii (a yeast found in lychee fruit) is the only probiotic worldwide known to diminish levels of C. difficile in the body (OptiBac Probiotics). ...
... hands are visibly soiled, use soap and water to wash them instead of an alcohol-based hand sanitizer. Saccharomyces boulardii (a yeast found in lychee fruit) is the only probiotic worldwide known to diminish levels of C. difficile in the body (OptiBac Probiotics). ...
REVIEW Molecular evolution of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
... world’s deadliest infectious diseases. The WHO reports that TB kills 5000 people a day, and between two and three million people annually, 98% of whom live in the developing world (http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/ fs104/en/). Approximately one-third of the world’s population is infected wi ...
... world’s deadliest infectious diseases. The WHO reports that TB kills 5000 people a day, and between two and three million people annually, 98% of whom live in the developing world (http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/ fs104/en/). Approximately one-third of the world’s population is infected wi ...
References
... mycobacteria inside macrophages. Trends Microbiol, 2002. 10: p. 142-146. Jayachandran, R., Sundaramurthy, V., Combaluzier, B., Mueller, P., Korf, H., Huygen, K., Miyazaki, T., Albrecht, I., Massner, J., Pieters, J., Survival of mycobacteria in macrophages is mediated by coronin 1-dependent activatio ...
... mycobacteria inside macrophages. Trends Microbiol, 2002. 10: p. 142-146. Jayachandran, R., Sundaramurthy, V., Combaluzier, B., Mueller, P., Korf, H., Huygen, K., Miyazaki, T., Albrecht, I., Massner, J., Pieters, J., Survival of mycobacteria in macrophages is mediated by coronin 1-dependent activatio ...
Set 7 Antibiotics - IUP Personal Websites
... infectious • Teriary-disease invades entire body including bones and brain Syphilis is called the Great Imitator because its symptoms resemble those of other diseases ...
... infectious • Teriary-disease invades entire body including bones and brain Syphilis is called the Great Imitator because its symptoms resemble those of other diseases ...
Acute HIV infection
... Passing through the placenta from an infected, pregnant mother to the unborn baby Breastfeeding (rarely) After someone is infected with HIV, blood tests can detect antibodies to the virus, even if they never had any symptoms of their infection. This is called HIV seroconversion (converting from HIV ...
... Passing through the placenta from an infected, pregnant mother to the unborn baby Breastfeeding (rarely) After someone is infected with HIV, blood tests can detect antibodies to the virus, even if they never had any symptoms of their infection. This is called HIV seroconversion (converting from HIV ...
Chapter 1: The Microbial World and You
... that mainly infects lungs but may spread to other parts of body. • Leading killer of world’s infectious diseases: • 3 million die worldwide every year. • Over 1 million killed in U.S. between 1930-49. ...
... that mainly infects lungs but may spread to other parts of body. • Leading killer of world’s infectious diseases: • 3 million die worldwide every year. • Over 1 million killed in U.S. between 1930-49. ...
Communicable diseases: epidemiology surveillance and response
... • Communicable diseases occur as a result of the interaction between: • The Infectious Agent • The Transmission Process • The Host • The Environment. ...
... • Communicable diseases occur as a result of the interaction between: • The Infectious Agent • The Transmission Process • The Host • The Environment. ...
Event Program - Institute for Public Health
... and Tropical Diseases, focuses on the host responses to TB vaccination. She is currently developing a biological/functional assay to determine if blood samples from vaccinated subjects can better control the growth of live mycobacteria in vitro. Through her work she has collaborated with colleagues ...
... and Tropical Diseases, focuses on the host responses to TB vaccination. She is currently developing a biological/functional assay to determine if blood samples from vaccinated subjects can better control the growth of live mycobacteria in vitro. Through her work she has collaborated with colleagues ...
HIV Information - Aureus Medical
... The symptoms of HIV infection are the symptoms of the diseases that attack the body because of a weakened The epidemic's impact on our nation's health was immune system. Most of the following symptoms are not highlighted during 1995, when the cumulative number of specific to HIV infection: fever tha ...
... The symptoms of HIV infection are the symptoms of the diseases that attack the body because of a weakened The epidemic's impact on our nation's health was immune system. Most of the following symptoms are not highlighted during 1995, when the cumulative number of specific to HIV infection: fever tha ...
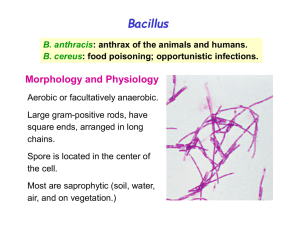
B. anthracis
... hours. The papule rapidly changes into a vesicle, then a pustule, and finally a necrotic eschar. The infection may disseminate, giving rise to septicemia. Inhalation anthrax (wool-sorters’ disease): long incubation time (2 months or more). Mediastinitis (enlargement of mediastinal lymph nodes), seps ...
... hours. The papule rapidly changes into a vesicle, then a pustule, and finally a necrotic eschar. The infection may disseminate, giving rise to septicemia. Inhalation anthrax (wool-sorters’ disease): long incubation time (2 months or more). Mediastinitis (enlargement of mediastinal lymph nodes), seps ...
Diagnosis & treatment of tuberculosis in HIV co-infected patients Review Article
... quantify the number of peripheral blood mononuclear cells producing IFN- γ in response to tuberculosisspecific antigen stimulation (ESAT-6 and CFP10). Both assays give objective results, with sensitivity (as measured in patients with active tuberculosis) comparable to that of the tuberculin skin tes ...
... quantify the number of peripheral blood mononuclear cells producing IFN- γ in response to tuberculosisspecific antigen stimulation (ESAT-6 and CFP10). Both assays give objective results, with sensitivity (as measured in patients with active tuberculosis) comparable to that of the tuberculin skin tes ...
A Review of Zoonotic Tuberculosis at the Human-Livestock
... ▫ Systematic Literature Review ▫ Preliminary Field Data ...
... ▫ Systematic Literature Review ▫ Preliminary Field Data ...
Genital warts
... • Men who are infected may be asymptomatic or may have nongonococcal urethritis. • Women who are infected may have no or minimal symptoms. ...
... • Men who are infected may be asymptomatic or may have nongonococcal urethritis. • Women who are infected may have no or minimal symptoms. ...
ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE A Growing Threat
... ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE ... A Growing Threat Two main pathogens (germs) - bacteria and viruses - cause most infections. Since penicillin was made available to the public in the 1940's, antibiotics have been the cornerstone of infectious disease control and treatment. Antibiotics can only cure illnesse ...
... ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE ... A Growing Threat Two main pathogens (germs) - bacteria and viruses - cause most infections. Since penicillin was made available to the public in the 1940's, antibiotics have been the cornerstone of infectious disease control and treatment. Antibiotics can only cure illnesse ...
THE IMPACT OF TRANSMISSIBLE DISEASE ON THE
... diseases known to humans. Causative organism- M.tuberculosis Transmission by inhalation of infective droplets expelled through cough by an infectious patient with active pulmonary disease. Mostly affects lungs But can virtually affect every organ system in the body. TB is able to produce acute to la ...
... diseases known to humans. Causative organism- M.tuberculosis Transmission by inhalation of infective droplets expelled through cough by an infectious patient with active pulmonary disease. Mostly affects lungs But can virtually affect every organ system in the body. TB is able to produce acute to la ...
The regulation of an organism`s internal environment is to maintain
... Students know disease disrupts the equilibrium that exists in a healthy organism. E/S Homeostasis, or the regulation of an organism’s internal environment is necessary to maintain conditions suitable for life. The internal equilibrium of the body is the ultimate gauge of its proper function. Homeost ...
... Students know disease disrupts the equilibrium that exists in a healthy organism. E/S Homeostasis, or the regulation of an organism’s internal environment is necessary to maintain conditions suitable for life. The internal equilibrium of the body is the ultimate gauge of its proper function. Homeost ...
Tuberculosis

Tuberculosis, MTB, or TB (short for tubercle bacillus), in the past also called phthisis, phthisis pulmonalis, or consumption, is a widespread, infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis typically attacks the lungs, but can also affect other parts of the body. It is spread through the air when people who have an active TB infection cough, sneeze, or otherwise transmit respiratory fluids through the air. Most infections do not have symptoms, known as latent tuberculosis. About one in ten latent infections eventually progresses to active disease which, if left untreated, kills more than 50% of those so infected.The classic symptoms of active TB infection are a chronic cough with blood-tinged sputum, fever, night sweats, and weight loss (the last of these giving rise to the formerly common term for the disease, ""consumption""). Infection of other organs causes a wide range of symptoms. Diagnosis of active TB relies on radiology (commonly chest X-rays), as well as microscopic examination and microbiological culture of body fluids. Diagnosis of latent TB relies on the tuberculin skin test (TST) and/or blood tests. Treatment is difficult and requires administration of multiple antibiotics over a long period of time. Household, workplace and social contacts are also screened and treated if necessary. Antibiotic resistance is a growing problem in multiple drug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) infections. Prevention relies on early detection and treatment of cases and on screening programs and vaccination with the bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccine.One-third of the world's population is thought to have been infected with M. tuberculosis, and new infections occur in about 1% of the population each year. In 2007, an estimated 13.7 million chronic cases were active globally, while in 2013, an estimated 9 million new cases occurred. In 2013 there were between 1.3 and 1.5 million associated deaths, most of which occurred in developing countries. The total number of tuberculosis cases has been decreasing since 2006, and new cases have decreased since 2002. The rate of tuberculosis in different areas varies across the globe; about 80% of the population in many Asian and African countries tests positive in tuberculin tests, while only 5–10% of the United States population tests positive. More people in the developing world contract tuberculosis because of a poor immune system, largely due to high rates of HIV infection and the corresponding development of AIDS.