Net ionic equation
... The forces holding an ionic compound together are the strong electrical attraction that exists between cations and anions. It is therefore somewhat surprising that ionic compounds will dissolve in water. The reason some ionic compounds will dissolve in water is because the water molecules have a par ...
... The forces holding an ionic compound together are the strong electrical attraction that exists between cations and anions. It is therefore somewhat surprising that ionic compounds will dissolve in water. The reason some ionic compounds will dissolve in water is because the water molecules have a par ...
Chemistry - Kendriya Vidyalaya Raigarh
... higher charge of the atoms. COVALENCY:The number of electrons which an atom contributes towards mutual sharing during the formation of a chemical bond called its covalency in that compound. SINGLE COVALENT BOND: A covalent bond formed by the mutual sharing of one pair of electrons is called a single ...
... higher charge of the atoms. COVALENCY:The number of electrons which an atom contributes towards mutual sharing during the formation of a chemical bond called its covalency in that compound. SINGLE COVALENT BOND: A covalent bond formed by the mutual sharing of one pair of electrons is called a single ...
Chemistry
... Use electronegativity values to determine whether a compound is ionic, polar or nonpolar covalent. d. Illustrate neutral atoms and ions using electron dot notation. e. Illustrate ionic and covalent bonds utilizing electron dot notation. f. Use appropriate materials to build adequate models of simple ...
... Use electronegativity values to determine whether a compound is ionic, polar or nonpolar covalent. d. Illustrate neutral atoms and ions using electron dot notation. e. Illustrate ionic and covalent bonds utilizing electron dot notation. f. Use appropriate materials to build adequate models of simple ...
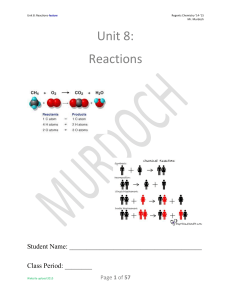
Unit 8: Reactions
... When you write 2 Cl, that states there are TWO atoms of chlorine. When you write Cl2, that states there is ONE molecule of diatomic (2 atoms) chlorine. Diatomic molecules of (Br2, I2, N2, Cl2, H2, O2, & F2) exist whenever these elements are not in a compound with another element. In NaCl, there ...
... When you write 2 Cl, that states there are TWO atoms of chlorine. When you write Cl2, that states there is ONE molecule of diatomic (2 atoms) chlorine. Diatomic molecules of (Br2, I2, N2, Cl2, H2, O2, & F2) exist whenever these elements are not in a compound with another element. In NaCl, there ...
9.1 REDOX Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction
... copper and tin during the Bronze Age, 4500 BCE to 1200 BCE Copper & tin occur naturally, but this was the 1st evidence for the use of heat to reduce metallic ores, like iron oxides Evidence of iron oxides are found in India dating 1800 BCE, start of Iron Age ...
... copper and tin during the Bronze Age, 4500 BCE to 1200 BCE Copper & tin occur naturally, but this was the 1st evidence for the use of heat to reduce metallic ores, like iron oxides Evidence of iron oxides are found in India dating 1800 BCE, start of Iron Age ...
analisis farmasi analisis farmasi anorganik -
... The ability of an aqueous solution to resist changes in pH upon the The ability of an aqueous solution to resist changes in pH upon the addition of acid or base is termed the buffering capability of the solution. The ability of a natural water body to resist a decrease in pH is very important due ...
... The ability of an aqueous solution to resist changes in pH upon the The ability of an aqueous solution to resist changes in pH upon the addition of acid or base is termed the buffering capability of the solution. The ability of a natural water body to resist a decrease in pH is very important due ...
KHOA: HÓA HỌC - CCS - Trường Đại học Sư phạm Hà Nội
... Elements are made up of tiny particles called atoms. Atoms are the smallest particles of an element that have the chemical properties of that element. Each element contains only one type of atoms. The atoms of one element are not the same as the atoms of another element. Most of the elements exist a ...
... Elements are made up of tiny particles called atoms. Atoms are the smallest particles of an element that have the chemical properties of that element. Each element contains only one type of atoms. The atoms of one element are not the same as the atoms of another element. Most of the elements exist a ...
Two-Electron Reduction of a Vanadium(V) Nitride by CO to Release
... achieved by treatment of metal complexes with azide sources and is fostered by N2 extrusion.1 The analogous transformation involving isocyanate and production of CO is less well documented. A previous study by Fickes et al. showed that the 1e reduction of a niobium(IV) isocyanate complex (OCN)Nb(N[t ...
... achieved by treatment of metal complexes with azide sources and is fostered by N2 extrusion.1 The analogous transformation involving isocyanate and production of CO is less well documented. A previous study by Fickes et al. showed that the 1e reduction of a niobium(IV) isocyanate complex (OCN)Nb(N[t ...
elements of chemistry unit
... ELECTRONEGATIVITY An element’s ability to attract electrons is its electronegativity. In general, the halogens and group 16 atoms have the highest electronegativity. The metals on the left side of the periodic table tend to donate electrons to the high electronegative elements. ...
... ELECTRONEGATIVITY An element’s ability to attract electrons is its electronegativity. In general, the halogens and group 16 atoms have the highest electronegativity. The metals on the left side of the periodic table tend to donate electrons to the high electronegative elements. ...
Calculations on the equations reaction
... valences this element can have in compounds? Write the formula of highest oxide of this element. 2. An element has serial number 19 define: а) charge of nucleus atom b) number of electrons c) number of neutrons and protons. Write electronic formula of element. What valences this element can have in ...
... valences this element can have in compounds? Write the formula of highest oxide of this element. 2. An element has serial number 19 define: а) charge of nucleus atom b) number of electrons c) number of neutrons and protons. Write electronic formula of element. What valences this element can have in ...
organic problems - St. Olaf College
... 17 The radical halogenation of 2-methylpropane gives two products: (CH3)2CHCH2X (minor) and (CH3)3CX (major) Chlorination gives a larger amount of the minor product than does bromination, Why? A) Bromine is more reactive than chlorine and is able to attack the less reactive 3º C-H. B) Bromine atoms ...
... 17 The radical halogenation of 2-methylpropane gives two products: (CH3)2CHCH2X (minor) and (CH3)3CX (major) Chlorination gives a larger amount of the minor product than does bromination, Why? A) Bromine is more reactive than chlorine and is able to attack the less reactive 3º C-H. B) Bromine atoms ...
COMPLEX IONS AND AMPHOTERISM
... An amphoteric substance is one that can behave as a Lewis acid and a Brønsted base. The best examples are found with metal hydroxides such as aluminum hydroxide [Al(OH)3] and zinc hydroxide [Zn(OH)2]. Insoluble aluminum hydroxide can be formed by the addition of hydroxide ion, OH-, to a soluble salt ...
... An amphoteric substance is one that can behave as a Lewis acid and a Brønsted base. The best examples are found with metal hydroxides such as aluminum hydroxide [Al(OH)3] and zinc hydroxide [Zn(OH)2]. Insoluble aluminum hydroxide can be formed by the addition of hydroxide ion, OH-, to a soluble salt ...
Part II
... Reacts with OH (daytime only), O3 (day and night) and NO3 (nighttime only). Calculate isoprene lifetime during daylight hours and during nighttime hours, assuming the following rate constants and concentrations: [OH] = 106 molecule cm-3, 12-hr daylight; k(OH+Isoprene) = 1 x 10-10 cm3 molecule-1 s-1 ...
... Reacts with OH (daytime only), O3 (day and night) and NO3 (nighttime only). Calculate isoprene lifetime during daylight hours and during nighttime hours, assuming the following rate constants and concentrations: [OH] = 106 molecule cm-3, 12-hr daylight; k(OH+Isoprene) = 1 x 10-10 cm3 molecule-1 s-1 ...
CHAPTER 2 ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS Questions
... a. Dinitrogen monoxide is correct. N and O are both nonmetals, resulting in a covalent compound. We need to use the covalent rules of nomenclature. The other two names are for ionic compounds. b. Copper(I) oxide is correct. With a metal in a compound, we have an ionic compound. Because copper, like ...
... a. Dinitrogen monoxide is correct. N and O are both nonmetals, resulting in a covalent compound. We need to use the covalent rules of nomenclature. The other two names are for ionic compounds. b. Copper(I) oxide is correct. With a metal in a compound, we have an ionic compound. Because copper, like ...
CHAPTER 2 ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS Questions
... a. Dinitrogen monoxide is correct. N and O are both nonmetals, resulting in a covalent compound. We need to use the covalent rules of nomenclature. The other two names are for ionic compounds. b. Copper(I) oxide is correct. With a metal in a compound, we have an ionic compound. Because copper, like ...
... a. Dinitrogen monoxide is correct. N and O are both nonmetals, resulting in a covalent compound. We need to use the covalent rules of nomenclature. The other two names are for ionic compounds. b. Copper(I) oxide is correct. With a metal in a compound, we have an ionic compound. Because copper, like ...
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry
... petroleum (a mixture of thousands of substances, mainly hydrocarbons that were formed from the decomposition of plants and animals). Although alkanes are not very reactive, they do burn. As discussed in Section 9.3, combustion of alkanes such as C3H8 (propane, home heating and cooking), C4H10 (butan ...
... petroleum (a mixture of thousands of substances, mainly hydrocarbons that were formed from the decomposition of plants and animals). Although alkanes are not very reactive, they do burn. As discussed in Section 9.3, combustion of alkanes such as C3H8 (propane, home heating and cooking), C4H10 (butan ...
Inorganic chemistry

Inorganic chemistry deals with the synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds (carbon based compounds, usually containing C-H bonds), which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, and there is much overlap, most importantly in the sub-discipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry–including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medicine, fuel, and agriculture.