8.3 Metals - UNSW Chemistry
... ♦ identify where metals, non-metals and semi-metals are to be found in the periodic table ♦ identify where the most reactive metals and non-metals are to be found in the periodic table. The relatively unreactive nature of the group 18 (the noble gases) elements would also be assumed to have been bro ...
... ♦ identify where metals, non-metals and semi-metals are to be found in the periodic table ♦ identify where the most reactive metals and non-metals are to be found in the periodic table. The relatively unreactive nature of the group 18 (the noble gases) elements would also be assumed to have been bro ...
Sulfate Complexation of Trivalent Lanthanides Proben by
... that are usually taken into account are the ones selected by the NEA-TDB critical reviews (Thermochemical Data Base project of the Nuclear Energy Agency OECD):9,10 log β1° = 3.85±0.03 and log K2° = 1.5±0.7 have been selected by Silva et al. in 1995 from experimental data determined by using solvent ...
... that are usually taken into account are the ones selected by the NEA-TDB critical reviews (Thermochemical Data Base project of the Nuclear Energy Agency OECD):9,10 log β1° = 3.85±0.03 and log K2° = 1.5±0.7 have been selected by Silva et al. in 1995 from experimental data determined by using solvent ...
Lecture 12 –Octahedral Substitution Reactions
... either associative (A) or dissociative (D) mechanisms. Show that you understand these terms by drawing diagrams or writing equations to show the reaction mechanism for each of the following reactions: (i) [PtCl4]2- + NH3 ...
... either associative (A) or dissociative (D) mechanisms. Show that you understand these terms by drawing diagrams or writing equations to show the reaction mechanism for each of the following reactions: (i) [PtCl4]2- + NH3 ...
Chemistry of the d
... e.g.: i) all Co(III) Complexes are diamagnetic; except [CoF6]3-, [CoF3(H2O)3] ii) Cr(III) in Oh: 3 unpaired e−; Cr(II) in Oh: predicted: 2e−, exp.: 4 unpaired e− 2) Ni(II) planar vs. octahedral is supposed to introduce change from covalent to ionic e.g.: [Ni(en)2]2+ 2NH3 Æ [Ni(NH3)2(en)2] 3) Two Ato ...
... e.g.: i) all Co(III) Complexes are diamagnetic; except [CoF6]3-, [CoF3(H2O)3] ii) Cr(III) in Oh: 3 unpaired e−; Cr(II) in Oh: predicted: 2e−, exp.: 4 unpaired e− 2) Ni(II) planar vs. octahedral is supposed to introduce change from covalent to ionic e.g.: [Ni(en)2]2+ 2NH3 Æ [Ni(NH3)2(en)2] 3) Two Ato ...
here
... We choose the best structure based upon two ideas: i) Electroneutrality Principle: Electrons are distributed in such a way that the charges on the atoms are as close to zero as possible. ii) Electronegativity: If there is a negative charge, it should be placed on the most electronegative atom. Draw ...
... We choose the best structure based upon two ideas: i) Electroneutrality Principle: Electrons are distributed in such a way that the charges on the atoms are as close to zero as possible. ii) Electronegativity: If there is a negative charge, it should be placed on the most electronegative atom. Draw ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... cleaner chemical synthetic process. Photosensitivity of the synthesized complexes has been studied. A series of photochemical experiments has been performed to investigate the role of these complexes in photo-oxygenation reactions. Study of photolysis of these complexes suggests the involvement of s ...
... cleaner chemical synthetic process. Photosensitivity of the synthesized complexes has been studied. A series of photochemical experiments has been performed to investigate the role of these complexes in photo-oxygenation reactions. Study of photolysis of these complexes suggests the involvement of s ...
Small Molecule Activation Using Transfer Hydrogenation Catalysts
... increases the breadth of possible substrates. Although the organic transformations performed by these catalysts have been studied for some time, little is known about their coordination chemistry.3 ...
... increases the breadth of possible substrates. Although the organic transformations performed by these catalysts have been studied for some time, little is known about their coordination chemistry.3 ...
Taking advantage of luminescent lanthanide ions
... Electric dipole selection rules forbid such transitions but these rules are relaxed by several mechanisms. An important one is the coupling with vibrational states, where a molecular vibration temporarily changes the geometric arrangement around the metal ion and, therefore, its symmetry. Other mech ...
... Electric dipole selection rules forbid such transitions but these rules are relaxed by several mechanisms. An important one is the coupling with vibrational states, where a molecular vibration temporarily changes the geometric arrangement around the metal ion and, therefore, its symmetry. Other mech ...
Chemistry Revision Guide - Mr Cartlidge`s Science Blog
... mole of something has the same mass in grams (molar mass, Mm) as its formula mass. E.g.: the Mr of water is 18.02 so the Mm of is 18.02g; the Mr of decane is 142.34 so the Mm is 142.34g. Importantly this means that 18.02 g of water and 142.34g decane contains the same number of molecules. ...
... mole of something has the same mass in grams (molar mass, Mm) as its formula mass. E.g.: the Mr of water is 18.02 so the Mm of is 18.02g; the Mr of decane is 142.34 so the Mm is 142.34g. Importantly this means that 18.02 g of water and 142.34g decane contains the same number of molecules. ...
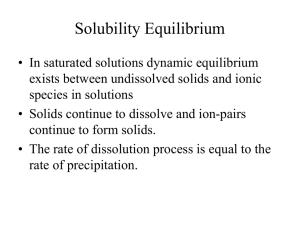
Chapter 16 Solubility Equilibrium
... • Consider the following equilibrium: Mg(OH)2(s) ⇌ Mg2+(aq) + 2 OH-(aq); • Increasing the pH means increasing [OH-] and equilibrium will shift to the left, causing some of Mg(OH)2 to precipitate out. • If the pH is lowered, [OH-] decreases and equilibrium shifts to the right, causing solid Mg(OH)2 t ...
... • Consider the following equilibrium: Mg(OH)2(s) ⇌ Mg2+(aq) + 2 OH-(aq); • Increasing the pH means increasing [OH-] and equilibrium will shift to the left, causing some of Mg(OH)2 to precipitate out. • If the pH is lowered, [OH-] decreases and equilibrium shifts to the right, causing solid Mg(OH)2 t ...
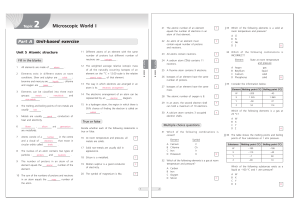
Topic 2 Microscopic World I
... (1) All metalloids are solids. (2) Gallium is a metalloid. (3) Metalloids cannot conduct electricity at room temperature. ...
... (1) All metalloids are solids. (2) Gallium is a metalloid. (3) Metalloids cannot conduct electricity at room temperature. ...
Main Group Metallocenes - Macdonald Research Group
... Cp) groups, however I will use the term to describe any compounds containing a “metal” that is bonded to the π-cloud of a cyclopentadienyl (or similar) substituent. I will use the term for convenience because: (a) some of the important p-block elements are not metals (b) many of the main group compo ...
... Cp) groups, however I will use the term to describe any compounds containing a “metal” that is bonded to the π-cloud of a cyclopentadienyl (or similar) substituent. I will use the term for convenience because: (a) some of the important p-block elements are not metals (b) many of the main group compo ...
P-block Cyclopentadienyl Compounds
... Cp) groups, however I will use the term to describe any compounds containing a “metal” that is bonded to the p-cloud of a cyclopentadienyl (or similar) substituent. I will use the term for convenience because: (a) some of the important p-block elements are not metals (b) many of the main group compo ...
... Cp) groups, however I will use the term to describe any compounds containing a “metal” that is bonded to the p-cloud of a cyclopentadienyl (or similar) substituent. I will use the term for convenience because: (a) some of the important p-block elements are not metals (b) many of the main group compo ...
Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solution 4.1 Aqueous Solutions
... • Neutralization reaction - reaction between acid and base to produce a salt and water • Salt - ionic compound w/ cation besides H+ • acid + base d salt + water HBr(aq) + KOH(aq) d KBr(aq) + H2O(l) net: H+(aq) + OH-(aq) d H2O(l) ...
... • Neutralization reaction - reaction between acid and base to produce a salt and water • Salt - ionic compound w/ cation besides H+ • acid + base d salt + water HBr(aq) + KOH(aq) d KBr(aq) + H2O(l) net: H+(aq) + OH-(aq) d H2O(l) ...
Naming Covalently Bonded Molecules
... when valence electrons are shared, not transferred Molecule – product of a covalent bond Usually occurs between nonmetals and elements that are close to each other on the periodic table ...
... when valence electrons are shared, not transferred Molecule – product of a covalent bond Usually occurs between nonmetals and elements that are close to each other on the periodic table ...
Electrochemistry
... Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers (In order of priority): 1. The oxidation number of any pure element is _________. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is __________ to its charge. 3. The ______ of the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero if ____________, or equal to the ___________ if ...
... Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers (In order of priority): 1. The oxidation number of any pure element is _________. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is __________ to its charge. 3. The ______ of the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero if ____________, or equal to the ___________ if ...
Theoretical Study in [C2 H4 –Tl]
... significance near the equilibrium bond lengths. This is obtained when some from the subsystems presents an electronic configuration of the type s2, the one that is inert. In contrast, one could think about a closed-shell organometallic hypothetical complex between an olefinic -system (L) and transitio ...
... significance near the equilibrium bond lengths. This is obtained when some from the subsystems presents an electronic configuration of the type s2, the one that is inert. In contrast, one could think about a closed-shell organometallic hypothetical complex between an olefinic -system (L) and transitio ...
Quantum Chemistry Predicts Multiply Bonded Diuranium
... electrons was eight for the U4+ 2 unit and six for U2 . More details of the choice of active orbitals will be given when the different molecules are discussed. A basis set of the atomic natural orbital type was used. It has been developed especially for relativistic calculations with the DKH Hamilto ...
... electrons was eight for the U4+ 2 unit and six for U2 . More details of the choice of active orbitals will be given when the different molecules are discussed. A basis set of the atomic natural orbital type was used. It has been developed especially for relativistic calculations with the DKH Hamilto ...
Coordination complex

In chemistry, a coordination complex or metal complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the coordination centre, and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those of transition metals, are coordination complexes.


















![Theoretical Study in [C2 H4 –Tl]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002722361_1-eb696f17258f2d22bec64ad25583944b-300x300.png)
