Measuring and Calculating
... Elements in the same family have the same valence e-config, and thus similar properties When moving down a group the distance (# of energy levels) between the nucleus and the valence e’s increases causing the attraction between them to decrease, so atomic radius increases down a group while the ...
... Elements in the same family have the same valence e-config, and thus similar properties When moving down a group the distance (# of energy levels) between the nucleus and the valence e’s increases causing the attraction between them to decrease, so atomic radius increases down a group while the ...
CHM_101_ASSIGNMENT_COPY_1_2
... solid NaOH to a buffer solution that consists of 0.15M sodium acetate and 0.15M acetic acid solution, if we assume that there is no change in volume (Ka = 1.8 x 10-5). 2. (a) The rate constant of a first order reaction is 2.5 ×10 -6/s and the initial concentration is 0.1moldm-3, what is the initial ...
... solid NaOH to a buffer solution that consists of 0.15M sodium acetate and 0.15M acetic acid solution, if we assume that there is no change in volume (Ka = 1.8 x 10-5). 2. (a) The rate constant of a first order reaction is 2.5 ×10 -6/s and the initial concentration is 0.1moldm-3, what is the initial ...
oxidation number
... Bonding and Molecules Most stable atoms have eight valence electrons. When an atom has 8 valence electrons, it is said to have an octet of electrons. ...
... Bonding and Molecules Most stable atoms have eight valence electrons. When an atom has 8 valence electrons, it is said to have an octet of electrons. ...
Periodic Properties of the Elements Effective Nuclear Charge, Zeff
... increasing ATOMIC NUMBER. The properties of the elements tend to repeat, are periodic, from row to row. ...
... increasing ATOMIC NUMBER. The properties of the elements tend to repeat, are periodic, from row to row. ...
Advanced Chemistry Midterm
... 35. A substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by a chemical change is called a(n) a. compound b. mixture c. element d. crystal 36. Which of the following statements is part of Dalton’s atomic theory of matter? a. all atoms are identical b. all atoms of a given element are identica ...
... 35. A substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by a chemical change is called a(n) a. compound b. mixture c. element d. crystal 36. Which of the following statements is part of Dalton’s atomic theory of matter? a. all atoms are identical b. all atoms of a given element are identica ...
CHM_101_TUTORIAL_QUESTIONS_1
... Factors affecting the ionization energy. 1. Atomic size: In small atoms electrons remains closer to nucleus and they feel more nuclear attraction. So more ionization energy is required to remove electron from small atoms. While in big sized atoms, valence electrons are away from nucleus , so they ex ...
... Factors affecting the ionization energy. 1. Atomic size: In small atoms electrons remains closer to nucleus and they feel more nuclear attraction. So more ionization energy is required to remove electron from small atoms. While in big sized atoms, valence electrons are away from nucleus , so they ex ...
Document
... 18) What are two types of energy transfer that can occur between a system and its surroundings? Define each and give an example for each. Endothermic Process—Absorbs Energy; A cold pack Exothermic Process—Releases Energy; A fire 19) What is a physical property? Give 5 examples. A quality or conditio ...
... 18) What are two types of energy transfer that can occur between a system and its surroundings? Define each and give an example for each. Endothermic Process—Absorbs Energy; A cold pack Exothermic Process—Releases Energy; A fire 19) What is a physical property? Give 5 examples. A quality or conditio ...
8.3 Metals - UNSW Chemistry
... Rutherford later proposed that some atomic nuclei might contain neutral particles. However the neutron was not discovered until 1932 by Chadwick. Problems with the Rutherford “Nuclear” Model of the Atom There were two main problems with the Nuclear Atomic model proposed by Rutherford: – the electron ...
... Rutherford later proposed that some atomic nuclei might contain neutral particles. However the neutron was not discovered until 1932 by Chadwick. Problems with the Rutherford “Nuclear” Model of the Atom There were two main problems with the Nuclear Atomic model proposed by Rutherford: – the electron ...
section_2_review_set
... 1. What is the claim to fame for the proton? determines the element 2. What is the claim to fame for the electron? creates the chemical bonds 3. What is the claim to fame for the neutron? stabilizes the nucleus 4. What is the mass of each of the following particles?: proton 1; neutron 1; electron 0. ...
... 1. What is the claim to fame for the proton? determines the element 2. What is the claim to fame for the electron? creates the chemical bonds 3. What is the claim to fame for the neutron? stabilizes the nucleus 4. What is the mass of each of the following particles?: proton 1; neutron 1; electron 0. ...
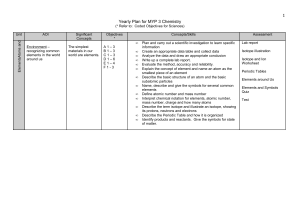
Yearly Plan for MYP 1 Science
... Explain the concept of element and name an atom as the smallest piece of an element Describe the basic structure of an atom and the basic subatomic particles Name, describe and give the symbols for several common elements Define atomic number and mass number Interpret chemical notation for elements, ...
... Explain the concept of element and name an atom as the smallest piece of an element Describe the basic structure of an atom and the basic subatomic particles Name, describe and give the symbols for several common elements Define atomic number and mass number Interpret chemical notation for elements, ...
final exam review packet
... C- Periodic Table-2302. I can locate metals, non-metals and metalloids on the periodic table. C- Periodic Table-2303. I can list properties of metals, non metals and metalloids. C- Periodic Table-2305. I can determine the charge of a main block (representative) ion. C- Periodic Table-2306. I can det ...
... C- Periodic Table-2302. I can locate metals, non-metals and metalloids on the periodic table. C- Periodic Table-2303. I can list properties of metals, non metals and metalloids. C- Periodic Table-2305. I can determine the charge of a main block (representative) ion. C- Periodic Table-2306. I can det ...
The chemical elements are fundamental building materials of matter
... • Mass number: total mass of a single atom (p+ + n10 = total mass (amu)) • Isotopes: Due to varying number neutrons atoms of the same element can vary in mass and therefore weight. • Average atomic mass: • Average mass (amu) of each atom naturally occurring on earth. • This number also correlates to ...
... • Mass number: total mass of a single atom (p+ + n10 = total mass (amu)) • Isotopes: Due to varying number neutrons atoms of the same element can vary in mass and therefore weight. • Average atomic mass: • Average mass (amu) of each atom naturally occurring on earth. • This number also correlates to ...
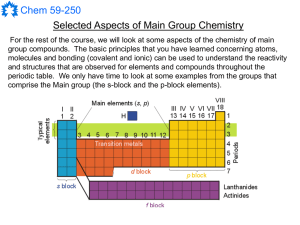
Main Group Notes 1
... Group 1: M(s) + HOR M+ + (OR)- + ½ H2(g) Group 2: M(s) + 2 HOR M+2 + 2 (OR)- + H2(g) These reactions make metal alkoxides that are very useful for the synthesis of other products using metathesis reactions. Metathesis indicates that the reagents exchange ligands with one another. Such reactions ...
... Group 1: M(s) + HOR M+ + (OR)- + ½ H2(g) Group 2: M(s) + 2 HOR M+2 + 2 (OR)- + H2(g) These reactions make metal alkoxides that are very useful for the synthesis of other products using metathesis reactions. Metathesis indicates that the reagents exchange ligands with one another. Such reactions ...
File
... 94. During which phase changes is energy released? A. condensation B. freezing C. both A and B D. neither A nor B 95. What happens during a phase change? A. Energy is added and temperature increases B. Energy is taken away and temperature decreases C. Energy is added or removed and temperature stay ...
... 94. During which phase changes is energy released? A. condensation B. freezing C. both A and B D. neither A nor B 95. What happens during a phase change? A. Energy is added and temperature increases B. Energy is taken away and temperature decreases C. Energy is added or removed and temperature stay ...
Here
... a. e- equally shared resulting in a balanced distribution of charge b. e-neg < 0.3 c. H2 C. Basic Definitions 1. Molecule – a neutral group of atoms held together by covalent bonds 2. Chemical Formula – indicates the relative numbers of each kind of atom in a chemical compound by using atomic symbol ...
... a. e- equally shared resulting in a balanced distribution of charge b. e-neg < 0.3 c. H2 C. Basic Definitions 1. Molecule – a neutral group of atoms held together by covalent bonds 2. Chemical Formula – indicates the relative numbers of each kind of atom in a chemical compound by using atomic symbol ...
C1 Revision Fundamental ideas adapted CS
... Complete the following using the periodic table to help: H2O: ........... atoms of h.......................... .......... atoms of o....................... ...
... Complete the following using the periodic table to help: H2O: ........... atoms of h.......................... .......... atoms of o....................... ...
HW / Unit 2
... 5. Why do the elements show a decrease in size as one proceeds across a period? Why do the elements show an increase in size as one proceeds down a group? 6. Place the following atoms in order of increasing size: S, Rb, K, C, O, Al, P 7. What happens to the size of an atom when it loses an electron? ...
... 5. Why do the elements show a decrease in size as one proceeds across a period? Why do the elements show an increase in size as one proceeds down a group? 6. Place the following atoms in order of increasing size: S, Rb, K, C, O, Al, P 7. What happens to the size of an atom when it loses an electron? ...
Use the following to answer questions 1-14:
... 49. Using your knowledge of compounds, their formulas, and how they bond, determine the formulas of the missing products in the following chemical equations. (6 marks) a) Sn + AgNO3 _______________________ + _______________________ b) CrI3 + NaOH _______________________ + _______________________ ...
... 49. Using your knowledge of compounds, their formulas, and how they bond, determine the formulas of the missing products in the following chemical equations. (6 marks) a) Sn + AgNO3 _______________________ + _______________________ b) CrI3 + NaOH _______________________ + _______________________ ...
2nd Semester Chemistry Terms - Glancy 4TH PERIOD PHYSICAL
... 47. Chemical bond- the force of attraction between two atoms that holds them together 48. Chemical change- a change in which the atoms of one or more substances are rearranged into one or more new substances 49. Chemical reaction- synonymous with chemical change 50. Elemental formula- a notation tha ...
... 47. Chemical bond- the force of attraction between two atoms that holds them together 48. Chemical change- a change in which the atoms of one or more substances are rearranged into one or more new substances 49. Chemical reaction- synonymous with chemical change 50. Elemental formula- a notation tha ...
Summer Resources - mvhs
... When a compound containing C,H and O undergoes combustion, it forms CO2 and H2O. Then from the mass of CO2 and H2O, we can calculate the mass of C and Hand then find the mass of O by subtracting the sum of masses of C and H from total g present of that substance. From the mass of C,H and O, we can c ...
... When a compound containing C,H and O undergoes combustion, it forms CO2 and H2O. Then from the mass of CO2 and H2O, we can calculate the mass of C and Hand then find the mass of O by subtracting the sum of masses of C and H from total g present of that substance. From the mass of C,H and O, we can c ...
The ocean is a mixture.
... form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. The family of noble gases includes helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon. All the noble gases are found in small amounts in the earth's ...
... form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. The family of noble gases includes helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon. All the noble gases are found in small amounts in the earth's ...
Fall Exam 3
... Orbital energies increase in the order 3s < 3p < 3d because orbital penetration decreases in the order 3s > 3p > 3d. Orbital energies increase in the order 3s < 3p < 3d because the Schrödinger equation predicts that orbital energy depends only on the angular momentum quantum number, l. Orbital energ ...
... Orbital energies increase in the order 3s < 3p < 3d because orbital penetration decreases in the order 3s > 3p > 3d. Orbital energies increase in the order 3s < 3p < 3d because the Schrödinger equation predicts that orbital energy depends only on the angular momentum quantum number, l. Orbital energ ...
Electronegativity

Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity number, the more an element or compound attracts electrons towards it. The term ""electronegativity"" was introduced by Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1811,though the concept was known even before that and was studied by many chemists including Avogadro.In spite of its long history, an accurate scale of electronegativity had to wait till 1932, when Linus Pauling proposed an electronegativity scale, which depends on bond energies, as a development of valence bond theory. It has been shown to correlate with a number of other chemical properties. Electronegativity cannot be directly measured and must be calculated from other atomic or molecular properties. Several methods of calculation have been proposed, and although there may be small differences in the numerical values of the electronegativity, all methods show the same periodic trends between elements. The most commonly used method of calculation is that originally proposed by Linus Pauling. This gives a dimensionless quantity, commonly referred to as the Pauling scale, on a relative scale running from around 0.7 to 3.98 (hydrogen = 2.20). When other methods of calculation are used, it is conventional (although not obligatory) to quote the results on a scale that covers the same range of numerical values: this is known as an electronegativity in Pauling units. As it is usually calculated, electronegativity is not a property of an atom alone, but rather a property of an atom in a molecule. Properties of a free atom include ionization energy and electron affinity. It is to be expected that the electronegativity of an element will vary with its chemical environment, but it is usually considered to be a transferable property, that is to say that similar values will be valid in a variety of situations.On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more ""pull"" it will have on electrons) and the number/location of other electrons present in the atomic shells (the more electrons an atom has, the farther from the nucleus the valence electrons will be, and as a result the less positive charge they will experience—both because of their increased distance from the nucleus, and because the other electrons in the lower energy core orbitals will act to shield the valence electrons from the positively charged nucleus).The opposite of electronegativity is electropositivity: a measure of an element's ability to donate electrons.Caesium is the least electronegative element in the periodic table (=0.79), while fluorine is most electronegative (=3.98). (Francium and caesium were originally assigned both assigned 0.7; caesium's value was later refined to 0.79, but no experimental data allows a similar refinement for francium. However, francium's ionization energy is known to be slightly higher than caesium's, in accordance with the relativistic stabilization of the 7s orbital, and this in turn implies that caesium is in fact more electronegative than francium.)