Views on Atomic Stru..
... • Cathode rays are negatively charged fundamental particles of matter, now called electrons • An electron bears one fundamental unit of negative electric charge • A nucleus of an atom consists of protons and neutrons and contains practically all the mass of an atom • Mass spectrometry establishes at ...
... • Cathode rays are negatively charged fundamental particles of matter, now called electrons • An electron bears one fundamental unit of negative electric charge • A nucleus of an atom consists of protons and neutrons and contains practically all the mass of an atom • Mass spectrometry establishes at ...
L 35 Modern Physics [1] Modern Physics
... • According to classical physics, if the intensity of the light is strong enough, enough energy should be absorbed by the electrons to make them pop out • The wavelength of the light should not make a difference. ...
... • According to classical physics, if the intensity of the light is strong enough, enough energy should be absorbed by the electrons to make them pop out • The wavelength of the light should not make a difference. ...
Objective 3 Stations Student Sheet
... 1. How is the periodic table organized? 2. What family of elements has valence electrons at two energy levels? 3. What are the elements called that are between metals and nonmetals? 4. Which family of nonmetals has seven valence electrons? 5. What are some properties of noble gases? 6. What is anoth ...
... 1. How is the periodic table organized? 2. What family of elements has valence electrons at two energy levels? 3. What are the elements called that are between metals and nonmetals? 4. Which family of nonmetals has seven valence electrons? 5. What are some properties of noble gases? 6. What is anoth ...
Chemistry Electrons in Atoms Outline
... 1. we cannot tell the position and the momentum of an electron simultaneously (at the same time) 2. by observing an electron with light we actually change the electron’s position or its momentum C. Schrodinger Wave Equation 1. this equation describes mathematically the wave properties of electrons a ...
... 1. we cannot tell the position and the momentum of an electron simultaneously (at the same time) 2. by observing an electron with light we actually change the electron’s position or its momentum C. Schrodinger Wave Equation 1. this equation describes mathematically the wave properties of electrons a ...
Lecture 11
... It is worthwhile to conclude this Lecture with a few remarks. • The formula for the energy levels reproduces the Bohr spectrum, in agreement with the experimental data. The degeneracy of each level can only be obtained by the proper quantum-mechanical description that we have presented. • The Bohr r ...
... It is worthwhile to conclude this Lecture with a few remarks. • The formula for the energy levels reproduces the Bohr spectrum, in agreement with the experimental data. The degeneracy of each level can only be obtained by the proper quantum-mechanical description that we have presented. • The Bohr r ...
AP Atomic Structure Set 1
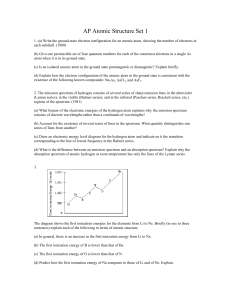
... (c) Is an isolated arsenic atom in the ground state paramagnetic or diamagnetic? Explain briefly. (d) Explain how the electron configuration of the arsenic atom in the ground state is consistent with the existence of the following known compounds: Na3As, AsCl3, and AsF5. 2. The emission spectrum of ...
... (c) Is an isolated arsenic atom in the ground state paramagnetic or diamagnetic? Explain briefly. (d) Explain how the electron configuration of the arsenic atom in the ground state is consistent with the existence of the following known compounds: Na3As, AsCl3, and AsF5. 2. The emission spectrum of ...
7.4 The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom
... – Assumes the quantization without explanation – Does not take into account Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle – Limited success only for the H atom ...
... – Assumes the quantization without explanation – Does not take into account Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle – Limited success only for the H atom ...
Chemistry Standards Checklist
... a. Trace the source on any large disparity between estimated and calculated answers to problems. b. Consider possible effects of measurement errors on calculations. ...
... a. Trace the source on any large disparity between estimated and calculated answers to problems. b. Consider possible effects of measurement errors on calculations. ...
quantum numbers - misshoughton.net
... The Bohr model of the atom was based on the line spectra of the Hydrogen atom. The model also incorporated the concept developed by Einstein regarding the particle behaviour of light during emission or absorption (photon or quanta of energy). Postulates: 1. Energy Levels an electron can only have ...
... The Bohr model of the atom was based on the line spectra of the Hydrogen atom. The model also incorporated the concept developed by Einstein regarding the particle behaviour of light during emission or absorption (photon or quanta of energy). Postulates: 1. Energy Levels an electron can only have ...
Semester 1 Study Guide – Chemistry
... meaning that only certain discrete energy levels are allowed. ...
... meaning that only certain discrete energy levels are allowed. ...
Early Modern Physics
... • Rutherford scattering can either be off a heavier object (nuclei) change in angle but little energy loss “multiple scattering” • or off light target (electrons) where can transfer energy but little angular change (energy loss due to ionization, also produces “delta rays” which are just more en ...
... • Rutherford scattering can either be off a heavier object (nuclei) change in angle but little energy loss “multiple scattering” • or off light target (electrons) where can transfer energy but little angular change (energy loss due to ionization, also produces “delta rays” which are just more en ...
Chapter 7 - Quantum Numbers, Orbitals, and Electron
... Orbital Energies and Electron Configurations of Multi-Electron Atoms For the H atom the orbital energy depends only on n, so all orbitals with the same value of n have the same energy. This is not true, however, for any other atom! The H atom orbitals may be used to approximate the orbitals for mult ...
... Orbital Energies and Electron Configurations of Multi-Electron Atoms For the H atom the orbital energy depends only on n, so all orbitals with the same value of n have the same energy. This is not true, however, for any other atom! The H atom orbitals may be used to approximate the orbitals for mult ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2013
... 1. Which idea of John Dalton is no longer considered part of the modern view of atoms? a. Atoms are extremely small. b. Atoms of the same element have identical masses. c. Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. d. Atoms of different elements can combine in different ratios to ...
... 1. Which idea of John Dalton is no longer considered part of the modern view of atoms? a. Atoms are extremely small. b. Atoms of the same element have identical masses. c. Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. d. Atoms of different elements can combine in different ratios to ...
- BUGS McGill
... 3. The virial theorem in a form in which: ET = -EK would apply to which of the following systems. Justify briefly. a) a particle in a 3D cubic box b) a Bohr atom c) a rotating diatomic molecule d) a hydrogen-like atom from the S-equation e) a harmonic oscillator f) planetary e.g. Earth/Sun systems ...
... 3. The virial theorem in a form in which: ET = -EK would apply to which of the following systems. Justify briefly. a) a particle in a 3D cubic box b) a Bohr atom c) a rotating diatomic molecule d) a hydrogen-like atom from the S-equation e) a harmonic oscillator f) planetary e.g. Earth/Sun systems ...

![L 35 Modern Physics [1] Modern Physics](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003926344_1-b779c05b753c6dc3972377c21f9bdcd3-300x300.png)