Integrated Physics and Chemistry
... reflection, refraction and resonance within various materials Recognize what factors affect the speed of sound; Relate loudness and pitch to properties of sound waves; Describe the function of the ear; Explain how sonar and ultrasound imaging work Describe the physics of cell phones; Describe the im ...
... reflection, refraction and resonance within various materials Recognize what factors affect the speed of sound; Relate loudness and pitch to properties of sound waves; Describe the function of the ear; Explain how sonar and ultrasound imaging work Describe the physics of cell phones; Describe the im ...
Chemistry Essentials For Dummies
... Nice Properties You’ve Got There ......................................... 13 Energy Types ............................................................................ 14 Kinetic energy ................................................................ 14 Potential energy ............................. ...
... Nice Properties You’ve Got There ......................................... 13 Energy Types ............................................................................ 14 Kinetic energy ................................................................ 14 Potential energy ............................. ...
4) What is the term for the procedure of collecting data and recording
... What is the subatomic particle having a negligible mass and a negative charge? A) electron B) neutron C) proton D) quark E) none of the above What is the term for the shorthand description of the arrangement of electrons by sublevels according to increasing energy? A) atomic notation B) atomic numbe ...
... What is the subatomic particle having a negligible mass and a negative charge? A) electron B) neutron C) proton D) quark E) none of the above What is the term for the shorthand description of the arrangement of electrons by sublevels according to increasing energy? A) atomic notation B) atomic numbe ...
Auger cascade processes in xenon and krypton studied by electron
... Humankind has been concerned with the structure of matter for thousands of years, and the term atomos, ”uncuttable”, dates back to around 450 BCE (coined by Democritus). However, the scientific studies of atoms did not begin until the 19th century. Atoms were thought of as indivisible units, until in ...
... Humankind has been concerned with the structure of matter for thousands of years, and the term atomos, ”uncuttable”, dates back to around 450 BCE (coined by Democritus). However, the scientific studies of atoms did not begin until the 19th century. Atoms were thought of as indivisible units, until in ...
Holt Modern Chemistry Workbook
... because the sum of the partial charges on either end of the bond is zero. A molecular compound is any chemical compound whose simplest units are molecules. In other words, a single molecule of any molecular compound is an individual unit that is capable of existing on its own. A molecule may contain ...
... because the sum of the partial charges on either end of the bond is zero. A molecular compound is any chemical compound whose simplest units are molecules. In other words, a single molecule of any molecular compound is an individual unit that is capable of existing on its own. A molecule may contain ...
Chapter 1 exercises - Cognella Titles Store
... contributor to the wide-ranging endeavor known as “natural philosophy.” In fact, with the quantitative description of gaseous behavior, chemistry had begun its fateful trek down the road pioneered by physics with its use of powerful mathematical techniques. Further, because chemistry had long stood ...
... contributor to the wide-ranging endeavor known as “natural philosophy.” In fact, with the quantitative description of gaseous behavior, chemistry had begun its fateful trek down the road pioneered by physics with its use of powerful mathematical techniques. Further, because chemistry had long stood ...
Chemistry 101L
... will be making. Remember to include room for multiple trials and average values, if appropriate. If appropriate, have room for classmates’ data. Now organize your list into things that are similar or data that should be compared. Tables columns/rows do not have to be listed in the same order that th ...
... will be making. Remember to include room for multiple trials and average values, if appropriate. If appropriate, have room for classmates’ data. Now organize your list into things that are similar or data that should be compared. Tables columns/rows do not have to be listed in the same order that th ...
Stability of Few-Charge Systems in Quantum Mechanics
... charge or four electrons plus two-positive charges. The stability studies presented in this paper clearly show that such systems are not stable if only the pairwise Coulomb (or Coulomb like) interaction is included and their existence is therefore due to some other binding mechanism, e.g., confinemen ...
... charge or four electrons plus two-positive charges. The stability studies presented in this paper clearly show that such systems are not stable if only the pairwise Coulomb (or Coulomb like) interaction is included and their existence is therefore due to some other binding mechanism, e.g., confinemen ...
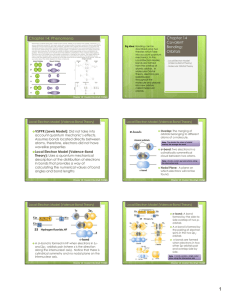
Chapter 14: Phenomena Chapter 14 Covalent Bonding: Orbitals
... Phenomena: Scientists knew that in order to form a bond, orbitals on two atoms must overlap. However, px, py, and pz orbitals are located 90˚ from each other and compounds like CH4 (which would form bonds using their p orbitals) do not have bond angles of 90˚. Therefore, scientists had to explain th ...
... Phenomena: Scientists knew that in order to form a bond, orbitals on two atoms must overlap. However, px, py, and pz orbitals are located 90˚ from each other and compounds like CH4 (which would form bonds using their p orbitals) do not have bond angles of 90˚. Therefore, scientists had to explain th ...
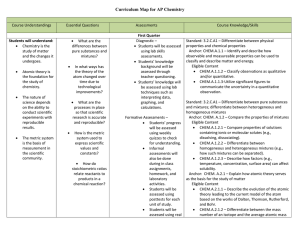
AP Chemistry Curriculum Map - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Anchor: CHEM.B.1.2 – Apply the mole concept to the composition of matter. Eligible Content CHEM.B.1.2.1 – Determine the empirical and molecular formulas of compounds. CHEM.B.1.2.3 – Relate the percent composition and mass of each element present in a compound. Standard: 3.2.C.A2 – Predict chemi ...
... Anchor: CHEM.B.1.2 – Apply the mole concept to the composition of matter. Eligible Content CHEM.B.1.2.1 – Determine the empirical and molecular formulas of compounds. CHEM.B.1.2.3 – Relate the percent composition and mass of each element present in a compound. Standard: 3.2.C.A2 – Predict chemi ...
When wood, paper, and wax are burned, they ap
... In this chapter we will use what we have learned about chemical structure and formulas in studying the mass relationships of atoms and molecules. These relationships in turn will help us to explain the composition of compounds and the ways in which the composition changes. The mass of an atom is rel ...
... In this chapter we will use what we have learned about chemical structure and formulas in studying the mass relationships of atoms and molecules. These relationships in turn will help us to explain the composition of compounds and the ways in which the composition changes. The mass of an atom is rel ...
W. Ketterle
... ultimate control over the motion and position of atoms limited only by Heisenberg’s uncertainty relation; (2) to generate a coherent sample of atoms all occupying the same quantum state (this was subsequently used to realize an atom laser, a device which generates coherent matter waves); and (3) to ...
... ultimate control over the motion and position of atoms limited only by Heisenberg’s uncertainty relation; (2) to generate a coherent sample of atoms all occupying the same quantum state (this was subsequently used to realize an atom laser, a device which generates coherent matter waves); and (3) to ...
To do List
... He concluded that the atom had a small, compact, positively-charged nucleus surrounded by electrons based on his gold-foil experiment. ...
... He concluded that the atom had a small, compact, positively-charged nucleus surrounded by electrons based on his gold-foil experiment. ...
Introduction: The 2p x-ray absorption spectrum of NiO
... Theoretical background of the origin of Multiplet effects The single particle description of x-ray absorption works well for all K edges and a range of dedicated computer codes exist to calculate the x-ray absorption cross section. The review of John Rehr in this issue deals with the latest developm ...
... Theoretical background of the origin of Multiplet effects The single particle description of x-ray absorption works well for all K edges and a range of dedicated computer codes exist to calculate the x-ray absorption cross section. The review of John Rehr in this issue deals with the latest developm ...
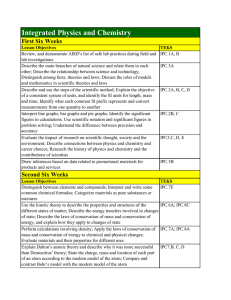
Quarter 1
... 5. Ernest Rutherford performed an experiment in which he shot alpha particles through a thin layer of gold foil. He predicted that the alpha particles would travel straight through the gold atoms, as shown below ...
... 5. Ernest Rutherford performed an experiment in which he shot alpha particles through a thin layer of gold foil. He predicted that the alpha particles would travel straight through the gold atoms, as shown below ...