å¾è湿çå¦
... • Questions are all of the same value. • There is a penalty (1/4 off) for each incorrect answer, but no penalty if you do not answer. 7. Take care that you make firm, black pencil marks, just filling the oval. Be careful that any erasures are complete—make the ...
... • Questions are all of the same value. • There is a penalty (1/4 off) for each incorrect answer, but no penalty if you do not answer. 7. Take care that you make firm, black pencil marks, just filling the oval. Be careful that any erasures are complete—make the ...
SQA CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure
... Collision theory, based on the kinetic model of matter, provides an explanation for the effect that various factors have on the rate of chemical reactions in terms of the number of successful collisions which occur. Collision theory can be stated thus: • particles must collide to react. • not all co ...
... Collision theory, based on the kinetic model of matter, provides an explanation for the effect that various factors have on the rate of chemical reactions in terms of the number of successful collisions which occur. Collision theory can be stated thus: • particles must collide to react. • not all co ...
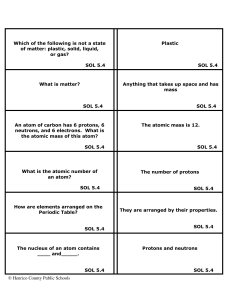
Matter Flashcards 5 - Henrico County Public Schools
... A molecule of an element is two or more atoms of the same kind of element joined together. A molecule of a compound is made of different kinds of elements joined together. SOL 5.4 A mixture is two or more substances joined physically. A compound is two or more substances joined ...
... A molecule of an element is two or more atoms of the same kind of element joined together. A molecule of a compound is made of different kinds of elements joined together. SOL 5.4 A mixture is two or more substances joined physically. A compound is two or more substances joined ...
Structure and transport properties of atomic chains and molecules
... continue to the ultimate limit [11]. At this length scale quantum effects such as conductance quantization, interference of electron waves, Coulomb blockade, and Kondo effects become dominant. This demonstrates that the current description of the semiconductor based electronic devices in terms of se ...
... continue to the ultimate limit [11]. At this length scale quantum effects such as conductance quantization, interference of electron waves, Coulomb blockade, and Kondo effects become dominant. This demonstrates that the current description of the semiconductor based electronic devices in terms of se ...
CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure
... Collisions and concentration Look at the illustrations showing the result of collisions between two different concentrations of hydrochloric acid and calcium carbonate, both after 10 seconds of reaction. The hydrochloric acid is represented as a large sphere and the calcium carbonate as a small sphe ...
... Collisions and concentration Look at the illustrations showing the result of collisions between two different concentrations of hydrochloric acid and calcium carbonate, both after 10 seconds of reaction. The hydrochloric acid is represented as a large sphere and the calcium carbonate as a small sphe ...
Chapter 5: Calculations and the Chemical Equation
... 3. The amounts (moles) of each substance used and each substance produced. The Numbers in a Chemical Equation: 1. Subscripts: The small numbers to the lower right of chemical symbols. Subscripts represent the number of atoms of each element in the molecule 2. Stoichiometric Coefficients: The large n ...
... 3. The amounts (moles) of each substance used and each substance produced. The Numbers in a Chemical Equation: 1. Subscripts: The small numbers to the lower right of chemical symbols. Subscripts represent the number of atoms of each element in the molecule 2. Stoichiometric Coefficients: The large n ...
Textbook sample chapter
... covalently bonded. Many of the formulae that you meet in this course have giant structures with ionic or covalent bonding. Sodium chloride has ionic bonding and consists of a large number of sodium ions and an equally large number of chloride ions held together in a lattice by electrostatic charges. ...
... covalently bonded. Many of the formulae that you meet in this course have giant structures with ionic or covalent bonding. Sodium chloride has ionic bonding and consists of a large number of sodium ions and an equally large number of chloride ions held together in a lattice by electrostatic charges. ...
Hybridization of atomic orbitals
... Atomic orbitals are (energy) states or wave forms of electrons in the atom. If we insist on the particle nature of electrons, then the probability of finding an electron in an atomic orbital is proportional to the square of the wavefunction. The values of the wavefunction can be either positive or n ...
... Atomic orbitals are (energy) states or wave forms of electrons in the atom. If we insist on the particle nature of electrons, then the probability of finding an electron in an atomic orbital is proportional to the square of the wavefunction. The values of the wavefunction can be either positive or n ...
DEMONSTRATION OF RYDBERG BLOCKADE AND A NEUTRAL
... lows quantum computers to perform parallel operations because all possible states can be represented during a calculation. This parallelism enables a quantum computer to solve certain problems far more efficiently than a classical computer. For example algorithms have been developed that allow impre ...
... lows quantum computers to perform parallel operations because all possible states can be represented during a calculation. This parallelism enables a quantum computer to solve certain problems far more efficiently than a classical computer. For example algorithms have been developed that allow impre ...
.
... dipole to be driven by the unperturbed incident field, but have to selfconsistently include the field emitted by the atom, and circulating in the cavity, into the total driving field. Thus for η > 1, the backaction of the cavity field generated by the oscillating atomic dipole on that same dipole is ...
... dipole to be driven by the unperturbed incident field, but have to selfconsistently include the field emitted by the atom, and circulating in the cavity, into the total driving field. Thus for η > 1, the backaction of the cavity field generated by the oscillating atomic dipole on that same dipole is ...
Empirical Formula, Molecular Formula, Percent Composition
... 1. The molecular formula indicates the types and number of atoms that make up a chemical compound. The chemical (molecular) formula is a multiple of a much simpler formula called the empirical formula. The empirical formula is simply the lowest reduced subscripts that make up a molecular formula. Fo ...
... 1. The molecular formula indicates the types and number of atoms that make up a chemical compound. The chemical (molecular) formula is a multiple of a much simpler formula called the empirical formula. The empirical formula is simply the lowest reduced subscripts that make up a molecular formula. Fo ...
The physics behind chemistry, and the Periodic Table
... Casimir forces between them. A good overview is given by Parsegian. 37 Secondly, just as an electric field can polarize a noble-gas atom, by virtual quantum mechanical excitations, the ’empty vacuum’ can be electrically polarized by creating virtual electron-positron pairs. This leads to the vacuum ...
... Casimir forces between them. A good overview is given by Parsegian. 37 Secondly, just as an electric field can polarize a noble-gas atom, by virtual quantum mechanical excitations, the ’empty vacuum’ can be electrically polarized by creating virtual electron-positron pairs. This leads to the vacuum ...
Interaction between Atomic Ensembles and Optical
... dipole to be driven by the unperturbed incident field, but have to selfconsistently include the field emitted by the atom, and circulating in the cavity, into the total driving field. Thus for η > 1, the backaction of the cavity field generated by the oscillating atomic dipole on that same dipole is ...
... dipole to be driven by the unperturbed incident field, but have to selfconsistently include the field emitted by the atom, and circulating in the cavity, into the total driving field. Thus for η > 1, the backaction of the cavity field generated by the oscillating atomic dipole on that same dipole is ...
A study of the electron structure of endohedrally confined atoms
... variable representation (PO-DVR) method [56–59]. In such a method, the Gaussian quadrature points are the eigenvalues of the position operator in a specific orthonormal basis function. Here a modification on the QMP is proposed transforming it in a self-consistent procedure to solve one-dimensional ...
... variable representation (PO-DVR) method [56–59]. In such a method, the Gaussian quadrature points are the eigenvalues of the position operator in a specific orthonormal basis function. Here a modification on the QMP is proposed transforming it in a self-consistent procedure to solve one-dimensional ...
spin squeezing and quantum entanglement in interaction
... first step is to choose a criterion to quantify it. Peres and Horodecki (Peres, 1996; Horodecki, 1997) found a criterion to evaluate the entanglement of mixed state. According to Peres et. al. when the partial transposition of its density matrix gives negative eigenvalues, the bipartite system is en ...
... first step is to choose a criterion to quantify it. Peres and Horodecki (Peres, 1996; Horodecki, 1997) found a criterion to evaluate the entanglement of mixed state. According to Peres et. al. when the partial transposition of its density matrix gives negative eigenvalues, the bipartite system is en ...