W. Pauli - Fisica Fundamental
... polarisation of the Zeeman components. It is, to be sure, not necessary according to this principle to assign in a definite stationary state to each electron an orbit uniquely determined in the sense of usual kinematics; however, it is necessary that the totality of the stationary states of an atom ...
... polarisation of the Zeeman components. It is, to be sure, not necessary according to this principle to assign in a definite stationary state to each electron an orbit uniquely determined in the sense of usual kinematics; however, it is necessary that the totality of the stationary states of an atom ...
As a result of activities in grades 9
... 1e Students know the nucleus of the atom is much smaller than the atom yet contains most of its mass. alchemy/air1d.htm#dalton 1f *Students know how to use the periodic table to identify the lanthanide, actinide, and transactinide elements and know that the transuranium elements were synthesized and ...
... 1e Students know the nucleus of the atom is much smaller than the atom yet contains most of its mass. alchemy/air1d.htm#dalton 1f *Students know how to use the periodic table to identify the lanthanide, actinide, and transactinide elements and know that the transuranium elements were synthesized and ...
ď - Google Sites
... combining these three points, it was possible to assign a value to any atom the term electronegativity is used to describe the relative ability of an atom to attract a pair of bonding electrons in its valence level (energy level) electronegativity is usually assigned on a developed scale – acc ...
... combining these three points, it was possible to assign a value to any atom the term electronegativity is used to describe the relative ability of an atom to attract a pair of bonding electrons in its valence level (energy level) electronegativity is usually assigned on a developed scale – acc ...
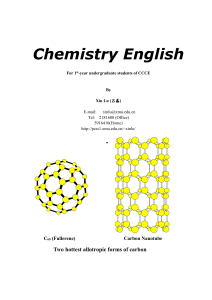
Chemistry English
... The atomic theory was presented by the British chemist John Dalton (1766-1844) in the early 1800s. It is one of the greatest advances in the history of chemistry. “Whether matter be atomic or not, this much is certain, that granting it to be atomic, it would appear as it now does.”(by Micheal Farada ...
... The atomic theory was presented by the British chemist John Dalton (1766-1844) in the early 1800s. It is one of the greatest advances in the history of chemistry. “Whether matter be atomic or not, this much is certain, that granting it to be atomic, it would appear as it now does.”(by Micheal Farada ...
Honors Chemistry / SAT II
... 2483. “The atom consists of a nucleus containing subatomic particles and electrons arranged in concentric shells around the nucleus.” This description most clearly fits the atomic theory proposed by (D) Thomson (A) Bohr (B) Rutherford (E) Avogadro (C) Dalton 2487. The maximum number of electrons pos ...
... 2483. “The atom consists of a nucleus containing subatomic particles and electrons arranged in concentric shells around the nucleus.” This description most clearly fits the atomic theory proposed by (D) Thomson (A) Bohr (B) Rutherford (E) Avogadro (C) Dalton 2487. The maximum number of electrons pos ...
total review package - Lighthouse Christian Academy
... substances stay in the flask. b. Small amounts of ink, pigments, etc. c. Spins quickly. Dense materials forced outward to the bottom of the test tube. 4. New chemical substances formed. Eg: Burning, photosynthesis, neutralization, etc. 5. a. Increase in temperature of the solid. b. Melting the solid ...
... substances stay in the flask. b. Small amounts of ink, pigments, etc. c. Spins quickly. Dense materials forced outward to the bottom of the test tube. 4. New chemical substances formed. Eg: Burning, photosynthesis, neutralization, etc. 5. a. Increase in temperature of the solid. b. Melting the solid ...
chemistry
... A beaker contains a liquid sample of a molecular substance. Both the beaker and the liquid are at 194 K. The graph below represents the relationship between temperature and time as the beaker and its contents are cooled for 12 minutes in a refrigerated chamber. Cooling Curve for a Substance ...
... A beaker contains a liquid sample of a molecular substance. Both the beaker and the liquid are at 194 K. The graph below represents the relationship between temperature and time as the beaker and its contents are cooled for 12 minutes in a refrigerated chamber. Cooling Curve for a Substance ...
Nature 425, (937
... This scheme can be generalized when more than two particles are placed next to each other, starting from a Mott insulating state of matter9,10. In such a Mott insulating state, atoms are localized to lattice sites, with a fixed number of atoms per site. For three particles for example, one can show ...
... This scheme can be generalized when more than two particles are placed next to each other, starting from a Mott insulating state of matter9,10. In such a Mott insulating state, atoms are localized to lattice sites, with a fixed number of atoms per site. For three particles for example, one can show ...
Brief presentation of the history of atomic physics
... The Bohr model Niels Bohr, 1885 (Copenhagen) – 1962 (Copenhagen) Bohr model of the atom (1913): Electrons in orbits around the nucleus. Only certain orbits with a fixed energy are allowed, and the electron looses energy only if it jumps between the orbits. The lost energy is emitted as light. ...
... The Bohr model Niels Bohr, 1885 (Copenhagen) – 1962 (Copenhagen) Bohr model of the atom (1913): Electrons in orbits around the nucleus. Only certain orbits with a fixed energy are allowed, and the electron looses energy only if it jumps between the orbits. The lost energy is emitted as light. ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... The first two quantum numbers (n and l) describe electrons that have different energies under normal circumstances in multi-electron atoms. The last two quantum numbers (ml , ms) describe electrons that have different energies only under special conditions, such as the presence of a strong magnetic ...
... The first two quantum numbers (n and l) describe electrons that have different energies under normal circumstances in multi-electron atoms. The last two quantum numbers (ml , ms) describe electrons that have different energies only under special conditions, such as the presence of a strong magnetic ...
Chap 3 - HCC Learning Web
... 19. If the equation Pb(NO3)2 + K2CrO4 PbCrO4 + KNO3 is balanced, which of the following quantity is correct? A)Pb(NO3)2, K2CrO4, PbCrO4 and 2 KNO3 B) 2 Pb(NO3)2, K2CrO4, PbCrO4 and KNO3 C) ½Pb(NO3)2, ½K2CrO4, ½PbCrO4 and KNO3 D)2Pb(NO3)2, 2K2CrO4, 2PbCrO4 and KNO3 Note: p.p. 102-105: example & pro ...
... 19. If the equation Pb(NO3)2 + K2CrO4 PbCrO4 + KNO3 is balanced, which of the following quantity is correct? A)Pb(NO3)2, K2CrO4, PbCrO4 and 2 KNO3 B) 2 Pb(NO3)2, K2CrO4, PbCrO4 and KNO3 C) ½Pb(NO3)2, ½K2CrO4, ½PbCrO4 and KNO3 D)2Pb(NO3)2, 2K2CrO4, 2PbCrO4 and KNO3 Note: p.p. 102-105: example & pro ...
From the Mendeleev periodic table to particle physics and back to
... during the 1960’s and 1970’s to describe interactions between particles. Let us mention the group SU(2)⊗U(1) for the weak and electromagnetic interactions, the group SU(3) for the strong interactions and the groups SU(5), SO(10) and E6 for a grand unified description of electroweak and strong intera ...
... during the 1960’s and 1970’s to describe interactions between particles. Let us mention the group SU(2)⊗U(1) for the weak and electromagnetic interactions, the group SU(3) for the strong interactions and the groups SU(5), SO(10) and E6 for a grand unified description of electroweak and strong intera ...
Zeeman effect – Studying magnetic fields in star
... • An experiment in 1896 showed that two of the lines of Na were broadened when a Na flame was placed between strong magnetic poles (Nature 1897, vol. 55, pg. 347) the 1902 Nobel Prize ...
... • An experiment in 1896 showed that two of the lines of Na were broadened when a Na flame was placed between strong magnetic poles (Nature 1897, vol. 55, pg. 347) the 1902 Nobel Prize ...