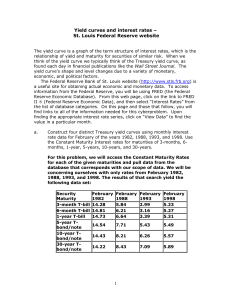
The Scary Debate Over Secular Stagnation Hiccup…
... reins could guard against both the inflationary dysfunctions of the 1970s and the depressionprone dysfunctions of the 1930s. Live and learn. The consensus has become that quantitative easing works, but only weakly. Reliance on monetary policy as an adequate tool for macroeconomic management thus ...
... reins could guard against both the inflationary dysfunctions of the 1970s and the depressionprone dysfunctions of the 1930s. Live and learn. The consensus has become that quantitative easing works, but only weakly. Reliance on monetary policy as an adequate tool for macroeconomic management thus ...
Monetary Policy Instruments for Developing
... financial sector may alter the equilibrium relation between money, prices and output in ways that are hard to predict and may lead to an increase in the volatility of this relationship (see Goodhart (1989) and Lindsey and Wallich). Accelerating inflation in many industrial countries in the 1960s and ...
... financial sector may alter the equilibrium relation between money, prices and output in ways that are hard to predict and may lead to an increase in the volatility of this relationship (see Goodhart (1989) and Lindsey and Wallich). Accelerating inflation in many industrial countries in the 1960s and ...
The Backing of the Currency and Economic Stability
... monetary life (Woods, “Great Gold Robbery”). A month after its passage, Roosevelt issued Executive Order 6102, which required private individuals to surrender their gold holdings to the government in exchange for paper notes, which had historically been redeemable in gold (Woods, “Great Gold Robbery ...
... monetary life (Woods, “Great Gold Robbery”). A month after its passage, Roosevelt issued Executive Order 6102, which required private individuals to surrender their gold holdings to the government in exchange for paper notes, which had historically been redeemable in gold (Woods, “Great Gold Robbery ...
Management`s primary goal is to maximize stockholder
... Once again, expectations theory and liquidity preference theory could be used to help explain the difference. This answer focuses on expectations theory. In 1993, short-term interest rates declined to levels not seen in decades, possibly indicating very low expected short-term inflation. While actua ...
... Once again, expectations theory and liquidity preference theory could be used to help explain the difference. This answer focuses on expectations theory. In 1993, short-term interest rates declined to levels not seen in decades, possibly indicating very low expected short-term inflation. While actua ...
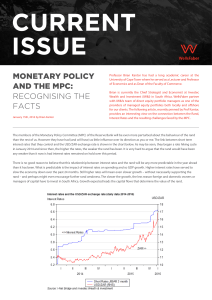
Monetary policy and the Mpc: Recognising the facts
... rand and vice versa as usual. But the rand has not behaved as usual since President Jacob Zuma intervened so dramatically in SA’s fiscal affairs last month. Without such intervention, the rand, given global risk appetites, would have been much closer to 14 to the US dollar than 17. Zuma’s actions ca ...
... rand and vice versa as usual. But the rand has not behaved as usual since President Jacob Zuma intervened so dramatically in SA’s fiscal affairs last month. Without such intervention, the rand, given global risk appetites, would have been much closer to 14 to the US dollar than 17. Zuma’s actions ca ...
Speech by Martin Weale at the University of Nottingham, Tuesday 8
... The second mechanism proposed is that asset purchases provide a signal that short-term rates are expected to remain low for longer than might otherwise be the case (Bhattarai, Eggertson and Gafarov, 2015). Policy committees would not buy assets if they thought that Bank Rate increases were likely to ...
... The second mechanism proposed is that asset purchases provide a signal that short-term rates are expected to remain low for longer than might otherwise be the case (Bhattarai, Eggertson and Gafarov, 2015). Policy committees would not buy assets if they thought that Bank Rate increases were likely to ...
The Heisei Recession: An Overview Koichi Hamada, Yale University
... sometimes foreign, have been in heated debates over the causes of the Heisei Recession as well as over the remedies for coming out of the recession. Are the causes chronic due to the declining growth potential of the Japanese economy or cyclical due to the lack of demand? Should the remedies be sou ...
... sometimes foreign, have been in heated debates over the causes of the Heisei Recession as well as over the remedies for coming out of the recession. Are the causes chronic due to the declining growth potential of the Japanese economy or cyclical due to the lack of demand? Should the remedies be sou ...
Rutgers Model United Nations 2007
... lent is going to as well as what development projects are being implemented with that money. This will ensure that the capital being borrowed is being used for appropriate measures and projects. Furthermore, these financial institutions should consider lending to specific programs and aid effort org ...
... lent is going to as well as what development projects are being implemented with that money. This will ensure that the capital being borrowed is being used for appropriate measures and projects. Furthermore, these financial institutions should consider lending to specific programs and aid effort org ...
the press release
... the impact of monetary normalization on debt service payments of the private sector in the eurozone. In contrast to the public sector (and big companies), the majority of smaller companies and households cannot shield themselves against rising rates by issuing long-term debt, locking in current ultr ...
... the impact of monetary normalization on debt service payments of the private sector in the eurozone. In contrast to the public sector (and big companies), the majority of smaller companies and households cannot shield themselves against rising rates by issuing long-term debt, locking in current ultr ...
01-03-2016
... China stocks rise on stimulus ignoring factory slowdown, while Japanese stocks fall as stronger yen; Oil slips from 7-week high; 10yr TY reaches 1.71%: Most Chinese stocks advanced after the central bank’s move to cut the amount of cash lenders must hold in reserve and a strengthening yuan countered ...
... China stocks rise on stimulus ignoring factory slowdown, while Japanese stocks fall as stronger yen; Oil slips from 7-week high; 10yr TY reaches 1.71%: Most Chinese stocks advanced after the central bank’s move to cut the amount of cash lenders must hold in reserve and a strengthening yuan countered ...
MetInvest Gratuity April 2017
... Month gone by – A snapshot Emerging market (EM) equities rallied for the third consecutive month, with India outperforming the broader EM pack. Fixed income market also ran up sharply amid strong foreign capital inflows and appreciating currency. Expectations of continued reform momentum and passage ...
... Month gone by – A snapshot Emerging market (EM) equities rallied for the third consecutive month, with India outperforming the broader EM pack. Fixed income market also ran up sharply amid strong foreign capital inflows and appreciating currency. Expectations of continued reform momentum and passage ...
chapter overview
... 2. Loans to commercial banks (Note: again commercial banks term is used even though the chapter analysis also applies to other thrift institutions.) B. The liability side of the balance sheet contains three major items. 1. Reserves of banks held as deposits at Federal Reserve Banks 2. U.S. Treasury ...
... 2. Loans to commercial banks (Note: again commercial banks term is used even though the chapter analysis also applies to other thrift institutions.) B. The liability side of the balance sheet contains three major items. 1. Reserves of banks held as deposits at Federal Reserve Banks 2. U.S. Treasury ...
CHAPTER OVERVIEW
... 2. Loans to commercial banks (Note: again commercial banks term is used even though the chapter analysis also applies to other thrift institutions.) B. The liability side of the balance sheet contains three major items. 1. Reserves of banks held as deposits at Federal Reserve Banks 2. U.S. Treasury ...
... 2. Loans to commercial banks (Note: again commercial banks term is used even though the chapter analysis also applies to other thrift institutions.) B. The liability side of the balance sheet contains three major items. 1. Reserves of banks held as deposits at Federal Reserve Banks 2. U.S. Treasury ...
increase
... •Serve as a financial intermediary between savings and investments; •Assist the process of money circulation, connect lenders to borrowers, in other words, “create money”. Money in the economy is represented not only by Federal Reserve notes (a.k.a. dollar bills) but also by loans made and taken out ...
... •Serve as a financial intermediary between savings and investments; •Assist the process of money circulation, connect lenders to borrowers, in other words, “create money”. Money in the economy is represented not only by Federal Reserve notes (a.k.a. dollar bills) but also by loans made and taken out ...
China`s Monetary Policy: 1998 - 2002
... Note: The inflation rate in 1998 is based on retail price, others, the consumer price index. Target value of M2 growth rate is adjusted to 14% in mid-2002. ...
... Note: The inflation rate in 1998 is based on retail price, others, the consumer price index. Target value of M2 growth rate is adjusted to 14% in mid-2002. ...
Asset-based Reserve Requirements: Reasserting
... assets. In this instance, causation runs from the composition of assets to the liability side of the balance sheet, making risk-based equity requirements an asset-to-liability link. Margin requirements are another non-bank form of LBRR, applying to stock market investors. They require that agents bu ...
... assets. In this instance, causation runs from the composition of assets to the liability side of the balance sheet, making risk-based equity requirements an asset-to-liability link. Margin requirements are another non-bank form of LBRR, applying to stock market investors. They require that agents bu ...
CRS Report for Congress
... deflation (a general decline in prices over time) and persistently stagnant growth. Although the United States has not experienced deflation since the Great Depression, the Japanese economy has now suffered from deflation for several years. These analysts argue that Japan cannot escape deflation bec ...
... deflation (a general decline in prices over time) and persistently stagnant growth. Although the United States has not experienced deflation since the Great Depression, the Japanese economy has now suffered from deflation for several years. These analysts argue that Japan cannot escape deflation bec ...
quantitative easing - Sheboygan Economic Club
... “The answer is straightforward: The Bank of Japan can buy government bonds on the open market, paying for them with either currency or deposits at the Bank of Japan, what economists call highpowered money.” “There is no limit to the extent to which the Bank of Japan can increase the money supply if ...
... “The answer is straightforward: The Bank of Japan can buy government bonds on the open market, paying for them with either currency or deposits at the Bank of Japan, what economists call highpowered money.” “There is no limit to the extent to which the Bank of Japan can increase the money supply if ...
Asset-Backed Commercial Paper
... Generally securitisation is used as a funding instrument by companies for three main reasons: it offers lower-cost funding compared with than traditional bank loan or bond financing; it is a mechanism by which assets such as corporate loans or mortgages can be removed from the balance sheet, thus im ...
... Generally securitisation is used as a funding instrument by companies for three main reasons: it offers lower-cost funding compared with than traditional bank loan or bond financing; it is a mechanism by which assets such as corporate loans or mortgages can be removed from the balance sheet, thus im ...
The Asynchronous Monetary Stances of Advanced Economies and
... (FED). The US economy has begun to show signs of recovery and the FED is expected to normalise interest rates in the years ahead. In the midst of sluggish growth, prospects of deflation, and near zero policy rates, the European Central Bank (ECB) has embarked on a QE quest of its own in order to sti ...
... (FED). The US economy has begun to show signs of recovery and the FED is expected to normalise interest rates in the years ahead. In the midst of sluggish growth, prospects of deflation, and near zero policy rates, the European Central Bank (ECB) has embarked on a QE quest of its own in order to sti ...
MACROECONOMIC STUDY REVIEW SHEET Bond prices move in
... 69. Savings, Taxes and Imports are considered _____________ while Investments, Government Purchases, Transfer Payments and Exports are considered ______________. 70. ___________ ____________ are not included in GDP because they do not represent a 2-sided transaction (i.e. – there is not an exchange ...
... 69. Savings, Taxes and Imports are considered _____________ while Investments, Government Purchases, Transfer Payments and Exports are considered ______________. 70. ___________ ____________ are not included in GDP because they do not represent a 2-sided transaction (i.e. – there is not an exchange ...
Session 6 Inflation - University of Reading
... wages and other incomes, this should not be a problem for consumers! But there are several reasons why inflation is a problem for people and for the economy: 1. Wages and pensions often rise by less than the CPI, and/or lag behind inflation, so that real incomes (nominal incomes minus inflation) fal ...
... wages and other incomes, this should not be a problem for consumers! But there are several reasons why inflation is a problem for people and for the economy: 1. Wages and pensions often rise by less than the CPI, and/or lag behind inflation, so that real incomes (nominal incomes minus inflation) fal ...
Economics 5310: Applications of IS
... The IS curve becomes flatter, i.e. more sensitive to a change in the interest rate. Now a lower interest rate not only leads to more domestic investment, but it adds to net exports, increasing domestic spending in the goods market. 3. Is monetary policy more or less effective in changing real output ...
... The IS curve becomes flatter, i.e. more sensitive to a change in the interest rate. Now a lower interest rate not only leads to more domestic investment, but it adds to net exports, increasing domestic spending in the goods market. 3. Is monetary policy more or less effective in changing real output ...
PDF - Department of Economics
... unobservable natural rate of interest (Amadeo, 1989). Inflationary pressures where an indication of a bank rate that was too low with respect to the natural one, and vice versa in deflationary situations.12 It is only in this case, when one has combined the idea of endogenous money, with the view t ...
... unobservable natural rate of interest (Amadeo, 1989). Inflationary pressures where an indication of a bank rate that was too low with respect to the natural one, and vice versa in deflationary situations.12 It is only in this case, when one has combined the idea of endogenous money, with the view t ...