Econ 492: Comparative Financial Crises
... • Prices in those markets may be determined by cash in the market • The resulting “fire sale prices” may be quite low • Banks have to mark assets held in their trading book to market. At the end of the quarter, these losses will show up in the calculation of profits/losses and thus affect the bank’s ...
... • Prices in those markets may be determined by cash in the market • The resulting “fire sale prices” may be quite low • Banks have to mark assets held in their trading book to market. At the end of the quarter, these losses will show up in the calculation of profits/losses and thus affect the bank’s ...
Chapter 5: Money is for Lunatics
... pay each other with deposits at Bank of Canada lender of last resort — making loans to banks to preserve stability of financial system banker to government — managing government accounts, foreign currency reserves, national debt conducting monetary policy — changing money supply and interest r ...
... pay each other with deposits at Bank of Canada lender of last resort — making loans to banks to preserve stability of financial system banker to government — managing government accounts, foreign currency reserves, national debt conducting monetary policy — changing money supply and interest r ...
Lecture 16 Chapter 22
... Transactions Demand for Money • Higher i => higher opportunity cost of holding money => the less money individuals and businesses will hold for a given level of transactions => higher velocity of money. • High inflation countries, the opportunity cost of holding money is high. • M and V are increas ...
... Transactions Demand for Money • Higher i => higher opportunity cost of holding money => the less money individuals and businesses will hold for a given level of transactions => higher velocity of money. • High inflation countries, the opportunity cost of holding money is high. • M and V are increas ...
What Should Banks Do? - Levy Economics Institute of Bard College
... equities or debt into portfolios using markets. They typically rely on fee income rather than interest. In normal circumstances they would not hold these assets directly, but if markets became disorderly they could get stuck with assets they cannot sell (at prices they have promised) and thus would ...
... equities or debt into portfolios using markets. They typically rely on fee income rather than interest. In normal circumstances they would not hold these assets directly, but if markets became disorderly they could get stuck with assets they cannot sell (at prices they have promised) and thus would ...
Discount Rate
... Economic growth is made possible through increased productivity of labour and capital. For example: Productivity can be increased by training the labour and applying new technologies to the capital. ...
... Economic growth is made possible through increased productivity of labour and capital. For example: Productivity can be increased by training the labour and applying new technologies to the capital. ...
A money Demand Function with Output Uncertainty, Monetary
... the mid-1970s received wide attention. ...
... the mid-1970s received wide attention. ...
Pricing Bank Stocks: The Contribution of Bank Examinations
... role for market discipline in the banking industry. In contrast, Morgan (1998) finds evidence that banks may be more opaque than non-banking institutions. He tests for differences in the ability of outside monitors to judge risk at banks compared with other types of firms by examining how often a di ...
... role for market discipline in the banking industry. In contrast, Morgan (1998) finds evidence that banks may be more opaque than non-banking institutions. He tests for differences in the ability of outside monitors to judge risk at banks compared with other types of firms by examining how often a di ...
Monetary Policy
... deregulation and financial innovations (paying interest on savings accounts and money market mutual funds) made M1 a less relevant measure and the Fed relied more on M2. During the 1990’s the relationship between M2 and economic growth started to break down. July 1993, Greenspan told Congress th ...
... deregulation and financial innovations (paying interest on savings accounts and money market mutual funds) made M1 a less relevant measure and the Fed relied more on M2. During the 1990’s the relationship between M2 and economic growth started to break down. July 1993, Greenspan told Congress th ...
Solutions
... that the real interest rate rises; this is re‡ected in a higher MP curve. When the real interest rate rises, investment and real output decline leading to a negative output gap; this is re‡ected in a movement along the IS curve. In this case, we see that a change in the nominal interest rate impacts ...
... that the real interest rate rises; this is re‡ected in a higher MP curve. When the real interest rate rises, investment and real output decline leading to a negative output gap; this is re‡ected in a movement along the IS curve. In this case, we see that a change in the nominal interest rate impacts ...
cbk newsletter - Central Bank of Kenya
... its last meeting. The meeting reviewed the outcomes of various measures that had been taken by the Bank to contain inflation and reduce volatilities of the exchange rate . After its deliberations, the Committee decided to raise the Central Bank Rate (CBR) by 400 basis points to 11.0 percent. In addi ...
... its last meeting. The meeting reviewed the outcomes of various measures that had been taken by the Bank to contain inflation and reduce volatilities of the exchange rate . After its deliberations, the Committee decided to raise the Central Bank Rate (CBR) by 400 basis points to 11.0 percent. In addi ...
Bank runs: A comparison between two English liquidity crises
... A failing bank may be very costly for taxpayers: for example, during the bankruptcy of IceSave of 2008, the Dutch government paid more than 140 million euro. Although, if contained, a single bank run is just a minor event for the overall health of a nation’s economy. Instead, a bank panic, or even ...
... A failing bank may be very costly for taxpayers: for example, during the bankruptcy of IceSave of 2008, the Dutch government paid more than 140 million euro. Although, if contained, a single bank run is just a minor event for the overall health of a nation’s economy. Instead, a bank panic, or even ...
Chapter 13 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • In 1960, U.S. tried to prevent dollars from leaving the country by increasing costs for foreigners to borrow dollars in the U.S. • In the early 1970s, domestic interest rate controls and high inflation made domestic deposits less attractive than eurodollar deposits. ...
... • In 1960, U.S. tried to prevent dollars from leaving the country by increasing costs for foreigners to borrow dollars in the U.S. • In the early 1970s, domestic interest rate controls and high inflation made domestic deposits less attractive than eurodollar deposits. ...
Deflation: Definition - Mr. Stobbs' Virtual Economics
... The Great Deflation: 1873 - 1896 Also called the “Great Sag” and “the Great Depression” After the Civil War, the government tries to restore normality by returning to the gold standard (parity) Other countries around the world also adopt the gold standard World prices of goods, materials an ...
... The Great Deflation: 1873 - 1896 Also called the “Great Sag” and “the Great Depression” After the Civil War, the government tries to restore normality by returning to the gold standard (parity) Other countries around the world also adopt the gold standard World prices of goods, materials an ...
View/Open
... cannot control money supply, since it is considered to be exogenous, and they are incapable of stimulating economic growth or curbing inflation. Inflation, to structuralists, is imported and to say it is a monetary phenomenon caused by money supply expansion is tautological . They argue that for the ...
... cannot control money supply, since it is considered to be exogenous, and they are incapable of stimulating economic growth or curbing inflation. Inflation, to structuralists, is imported and to say it is a monetary phenomenon caused by money supply expansion is tautological . They argue that for the ...
PDF - Mercatus Center
... A 2005 study found that “the benefits of transparency for bank stability outweigh its costs” and that “banks that disclose more information are less at risk of falling into crisis.”23 Requirements that banking entities make regular, detailed disclosures to the public would help prevent crises and th ...
... A 2005 study found that “the benefits of transparency for bank stability outweigh its costs” and that “banks that disclose more information are less at risk of falling into crisis.”23 Requirements that banking entities make regular, detailed disclosures to the public would help prevent crises and th ...
im02
... not have intrinsic value (it does not in today’s economies); it need only be generally acceptable as a means of payment. Though in the past countries such as the United States have used commodity-backed money (e.g., money backed by gold), this is no longer the case. The central bank (the Federal Res ...
... not have intrinsic value (it does not in today’s economies); it need only be generally acceptable as a means of payment. Though in the past countries such as the United States have used commodity-backed money (e.g., money backed by gold), this is no longer the case. The central bank (the Federal Res ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from the... of Economic Research Volume Title: Currency Crises
... economy will eventually go back to where it started (before the capital inflow episode). The paper argues that this could be an important coordinating factor to shift expectations from a good to a bad equilibrium. Output collapse will be addressed in the context of self-fulfilling prophesies. The pa ...
... economy will eventually go back to where it started (before the capital inflow episode). The paper argues that this could be an important coordinating factor to shift expectations from a good to a bad equilibrium. Output collapse will be addressed in the context of self-fulfilling prophesies. The pa ...
lecture4_2008old
... A: No. Our banking system is called fractional reserve banking. Bankers understand that it is not necessary to keep 100 percent of a depositors money on hand at all times. As a result, bankers take some of your money and loan it out to other people. ...
... A: No. Our banking system is called fractional reserve banking. Bankers understand that it is not necessary to keep 100 percent of a depositors money on hand at all times. As a result, bankers take some of your money and loan it out to other people. ...
Recent developments in the sterling overnight
... Remunerating all reserves at Bank Rate provides a ‘floor’ to market interbank overnight interest rates because it means that individual banks with reserves accounts have no incentive to lend reserves in the market at a rate below that at which reserves are remunerated by the Bank. If money market ra ...
... Remunerating all reserves at Bank Rate provides a ‘floor’ to market interbank overnight interest rates because it means that individual banks with reserves accounts have no incentive to lend reserves in the market at a rate below that at which reserves are remunerated by the Bank. If money market ra ...
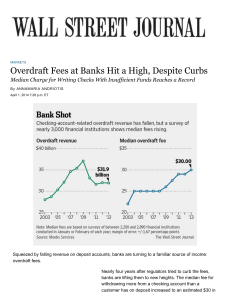
Overdraft fees at banks make a comeback, hitting a record.
... law included an amendment that went into effect in 2011 lowering a debit-card fee large financial institutions charge ...
... law included an amendment that went into effect in 2011 lowering a debit-card fee large financial institutions charge ...
Banks, Bonds, and the Liquidity Effect
... to the unexpected injection of reserves into the banking system. This precommitment can be conceptualized (and modeled) as an “information friction” under which households do not take into account this unexpected increase in bank reserves when choosing their deposit positions. A lack of response in ...
... to the unexpected injection of reserves into the banking system. This precommitment can be conceptualized (and modeled) as an “information friction” under which households do not take into account this unexpected increase in bank reserves when choosing their deposit positions. A lack of response in ...
M&B-Ch.3
... In a barter economy, transaction costs are high because people have to satisfy a “double coincidence of wants”; i.e., they have to find someone who not only has a good or service they want but also wants the good or service they have to offer. It is very difficult to find another individual who has ...
... In a barter economy, transaction costs are high because people have to satisfy a “double coincidence of wants”; i.e., they have to find someone who not only has a good or service they want but also wants the good or service they have to offer. It is very difficult to find another individual who has ...