Introduction to Statistics: Formula Sheet
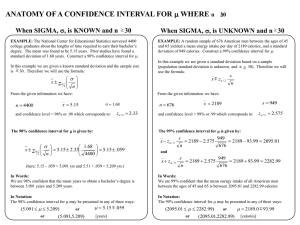
... Confidence interval for the population average (p. 437) is obtained by going the right number of SEs either way from the average of the draws. The confidence level is read off the normal curve. For example, a 95%-confidence interval for the population average is: sample average ± 2 SEs Should only b ...
... Confidence interval for the population average (p. 437) is obtained by going the right number of SEs either way from the average of the draws. The confidence level is read off the normal curve. For example, a 95%-confidence interval for the population average is: sample average ± 2 SEs Should only b ...
Final Exam Questions
... Part I. For the following questions, state either True or False. (1point each =6 points total). 1. A study of 4000 Dell PC customers listed among other variables, the age of the customer. The youngest customer was 14 years old and the oldest customer was 84 years old. If you wish to develop a freque ...
... Part I. For the following questions, state either True or False. (1point each =6 points total). 1. A study of 4000 Dell PC customers listed among other variables, the age of the customer. The youngest customer was 14 years old and the oldest customer was 84 years old. If you wish to develop a freque ...
Slides
... P10 • Load S = i=1 Xi where Xi is the weight of the i’th person. P10 P10 • E [S] = E [ i=1 Xi ] = i=1 E [Xi ] = 10 × 80 = 800 • By Markov inequality, P(S ≥ 1000) ≤ E [S]/1000 = 800/1000 = 0.8 • Note that we need only information about the mean – no need for ...
... P10 • Load S = i=1 Xi where Xi is the weight of the i’th person. P10 P10 • E [S] = E [ i=1 Xi ] = i=1 E [Xi ] = 10 × 80 = 800 • By Markov inequality, P(S ≥ 1000) ≤ E [S]/1000 = 800/1000 = 0.8 • Note that we need only information about the mean – no need for ...
Module 8 - Royal Statistical Society
... standard deviation of stress scores. The estimated standard deviations and the total numbers of employees in the offices are shown below. Office number ...
... standard deviation of stress scores. The estimated standard deviations and the total numbers of employees in the offices are shown below. Office number ...
Product Integration
... just scalar valued functions. The concept now really comes into its own, because when we multiply a sequence of matrices together the result will generally depend on the order in which the matrices are taken. Even in the continuous case there will not be a simple exponential formula expressing the r ...
... just scalar valued functions. The concept now really comes into its own, because when we multiply a sequence of matrices together the result will generally depend on the order in which the matrices are taken. Even in the continuous case there will not be a simple exponential formula expressing the r ...
Confidence Intervals
... population proportion is between ...”. This statement of confidence is correctly interpreted by going back to the idea of a sampling distribution. What this statement means is ***** If we could take all possible samples of size n, calculate the confidence interval in the formula above for each and e ...
... population proportion is between ...”. This statement of confidence is correctly interpreted by going back to the idea of a sampling distribution. What this statement means is ***** If we could take all possible samples of size n, calculate the confidence interval in the formula above for each and e ...
Comparison of Estimation Methods for Frechet Distribution with
... As the shape parameter α is assumed to be known, the ML estimator of β is obtained by solving the following equation ...
... As the shape parameter α is assumed to be known, the ML estimator of β is obtained by solving the following equation ...
Review for Exam 3 - El Camino College
... In a recent survey of 4276 randomly selected households showed that 94% of them had telephones. Using these results, construct a 99% confidence interval estimate of the true proportion of households with telephones. Problem 16 The music industry must adjust to the growing practice of consumers downl ...
... In a recent survey of 4276 randomly selected households showed that 94% of them had telephones. Using these results, construct a 99% confidence interval estimate of the true proportion of households with telephones. Problem 16 The music industry must adjust to the growing practice of consumers downl ...
403: Quantitative Business Analysis for Decision Making
... Assumptions and Sample Size for Estimation of the mean The population should be normally (at least close to) distributed. If skew, then median is an appropriate measure of the center than the mean. To estimate mean with a specified margin of error (m.e.), take a random sample of size n z 2 2 n ...
... Assumptions and Sample Size for Estimation of the mean The population should be normally (at least close to) distributed. If skew, then median is an appropriate measure of the center than the mean. To estimate mean with a specified margin of error (m.e.), take a random sample of size n z 2 2 n ...
test one sample questions.
... (c) Find the mean of the distribution. (d) Find the standard deviation of the distribution. 8. (a) How many election outcomes are there if a club of 14 elects five officers? Give an appropriate formula, and actual number. (b) How many ways are there to select a committee of five people in the club o ...
... (c) Find the mean of the distribution. (d) Find the standard deviation of the distribution. 8. (a) How many election outcomes are there if a club of 14 elects five officers? Give an appropriate formula, and actual number. (b) How many ways are there to select a committee of five people in the club o ...
German tank problem

In the statistical theory of estimation, the problem of estimating the maximum of a discrete uniform distribution from sampling without replacement is known in English as the German tank problem, due to its application in World War II to the estimation of the number of German tanks.The analyses illustrate the difference between frequentist inference and Bayesian inference.Estimating the population maximum based on a single sample yields divergent results, while the estimation based on multiple samples is an instructive practical estimation question whose answer is simple but not obvious.