Chapter 11 Clickers
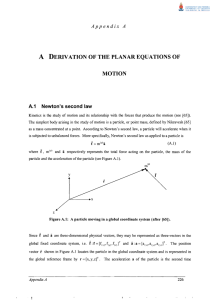
... both ends. The radius of the cylinder is r. At what angular speed must the this cylinder rotate to have the same total kinetic energy that it would have if it were moving horizontally with a speed v without rotation? v2 a) 2r ...
... both ends. The radius of the cylinder is r. At what angular speed must the this cylinder rotate to have the same total kinetic energy that it would have if it were moving horizontally with a speed v without rotation? v2 a) 2r ...
Acceleration and free fall
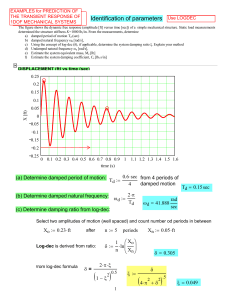
... both the strength of the spring and the amount of friction. If there is too much friction in relation to the strength of the spring, the door takes too long to close, but if there is too little, the door will oscillate. For an optimal design, we get motion of the form x = cte−bt , where x is the pos ...
... both the strength of the spring and the amount of friction. If there is too much friction in relation to the strength of the spring, the door takes too long to close, but if there is too little, the door will oscillate. For an optimal design, we get motion of the form x = cte−bt , where x is the pos ...
lecture1437132938
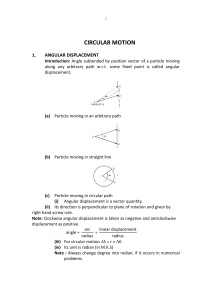
... B will rotate about a , if ABC is greater than 1800 in any case, and b will rotate about c if DBC is more than 1800 in any case. Different mechanisms obtained by fixing different links of this kind of chain will be as follows (known as inversion). 1. If any of the adjacent links of link d i.e. a o ...
... B will rotate about a , if ABC is greater than 1800 in any case, and b will rotate about c if DBC is more than 1800 in any case. Different mechanisms obtained by fixing different links of this kind of chain will be as follows (known as inversion). 1. If any of the adjacent links of link d i.e. a o ...