Chapter 3: The Basics of Classical Mechanics
... time and thus the Hamiltonian is not the total energy of the system. However, if the Lagrangian is not an explicit function of time, the Hamiltonian is still a constant of the motion. One standard way of proceeding with a classical mechanics problem is to find the Lagrangian by determining the poten ...
... time and thus the Hamiltonian is not the total energy of the system. However, if the Lagrangian is not an explicit function of time, the Hamiltonian is still a constant of the motion. One standard way of proceeding with a classical mechanics problem is to find the Lagrangian by determining the poten ...
MATH 2800 Problem Set #9 1. A 24- pound weight is attached to the
... damping constant so that the subsequent motion is: a) overdamped, b) critically damped, c) damped. If the system starts at equilibrium with an initial downward velocity of 9 ft/s, find the equation of motion, and make a rough sketch of the graph for =15/4, =3, and = 5 . ...
... damping constant so that the subsequent motion is: a) overdamped, b) critically damped, c) damped. If the system starts at equilibrium with an initial downward velocity of 9 ft/s, find the equation of motion, and make a rough sketch of the graph for =15/4, =3, and = 5 . ...
physics_11_review_be.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
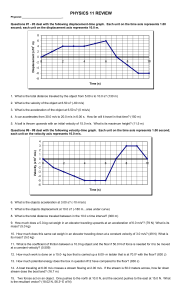
... 8. What is the total distance traveled between in the 10.0 s time interval? (300 m) 9. How much does a 5.0-kg cat weigh in an elevator traveling upwards at an acceleration of 6.0 m/s2? (79 N) What is its mass? (5.0 kg) 10. How much does this same cat weigh in an elevator traveling down at a constant ...
... 8. What is the total distance traveled between in the 10.0 s time interval? (300 m) 9. How much does a 5.0-kg cat weigh in an elevator traveling upwards at an acceleration of 6.0 m/s2? (79 N) What is its mass? (5.0 kg) 10. How much does this same cat weigh in an elevator traveling down at a constant ...
Langevin Equation
... To understand the Brownian motion more completely, we need to start from the basic physics, i.e. Newton’s law of motion. The most direct way of implementing this is to recognize that there is a stochastic component to the force on the particle, which we only know through a probabilistic description. ...
... To understand the Brownian motion more completely, we need to start from the basic physics, i.e. Newton’s law of motion. The most direct way of implementing this is to recognize that there is a stochastic component to the force on the particle, which we only know through a probabilistic description. ...