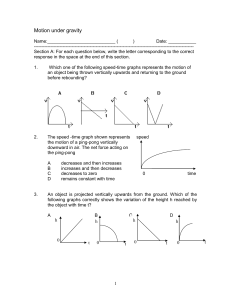
Quiz on Motion under gravity
... The acceleration of the object decreases as the object rises up; The acceleration is positive for the upward motion and negative for the downward motion; At maximum height, the velocity of the object is zero; If air resistance is negligible, the time for the upward motion is equal to the time for th ...
... The acceleration of the object decreases as the object rises up; The acceleration is positive for the upward motion and negative for the downward motion; At maximum height, the velocity of the object is zero; If air resistance is negligible, the time for the upward motion is equal to the time for th ...
PDF (English
... this video, we'll provide you with the tools to explain why hurricanes rotate the way that they do. This video is part of the Representations video series. Information can be represented in words, through mathematical symbols, graphically, or in 3-D models. Representations are used to develop a deep ...
... this video, we'll provide you with the tools to explain why hurricanes rotate the way that they do. This video is part of the Representations video series. Information can be represented in words, through mathematical symbols, graphically, or in 3-D models. Representations are used to develop a deep ...
Name Student ID
... Name ______________________________ Student ID ______________________ Score ________ Last First II) Long answer (25 points) Show all of your work to receive full credit. Suppose Block 1 with a mass of m1 and Block 2 with a mass of m2 are on a rough level surface. The blocks are connected by a massl ...
... Name ______________________________ Student ID ______________________ Score ________ Last First II) Long answer (25 points) Show all of your work to receive full credit. Suppose Block 1 with a mass of m1 and Block 2 with a mass of m2 are on a rough level surface. The blocks are connected by a massl ...
4-1_to_4-3 - mrhsluniewskiscience
... Inertial frames of reference • There are several ways to describe an inertial frame. Here are a few descriptions: – An inertial frame of reference is a frame of reference with constant velocity. – An inertial frame of reference is a non-accelerating frame of reference. – An inertial frame of refere ...
... Inertial frames of reference • There are several ways to describe an inertial frame. Here are a few descriptions: – An inertial frame of reference is a frame of reference with constant velocity. – An inertial frame of reference is a non-accelerating frame of reference. – An inertial frame of refere ...
Test 1 Sample
... a. has the same magnitude as the weight of the box. b. is greater than the weight of the box. c. has the same magnitude as the total force that resists the motion. d. is greater than the total force that resists the motion of the box. 5. A sprinter runs 13 meters from rest in 4.2 seconds in a straig ...
... a. has the same magnitude as the weight of the box. b. is greater than the weight of the box. c. has the same magnitude as the total force that resists the motion. d. is greater than the total force that resists the motion of the box. 5. A sprinter runs 13 meters from rest in 4.2 seconds in a straig ...
Common Core Geometry
... the order of the composite transformations often changes the result. In addition we look at transformations working backwards. Given a pre-image and an image determine the composite transformations that have taken place between them. ...
... the order of the composite transformations often changes the result. In addition we look at transformations working backwards. Given a pre-image and an image determine the composite transformations that have taken place between them. ...
Midterm Solutions
... 9. A rifle bullet with mass 8.00 g strikes and embeds itself in a block with a mass of 0.992 kg that rests on a frictionless, horizontal surface and is attached to a coil spring. The impact compresses the spring 15.0 cm. Calibration of the spring shows that a force of 0.750 N is required to compress ...
... 9. A rifle bullet with mass 8.00 g strikes and embeds itself in a block with a mass of 0.992 kg that rests on a frictionless, horizontal surface and is attached to a coil spring. The impact compresses the spring 15.0 cm. Calibration of the spring shows that a force of 0.750 N is required to compress ...
Acceleration
... constant, it is changing direction, and therefore changing its velocity. If the velocity changes, it is accelerating. ...
... constant, it is changing direction, and therefore changing its velocity. If the velocity changes, it is accelerating. ...
Lecture Notes for Section 11.3
... Big idea: Vector-valued functions can be used to efficiently describe the position, velocity, and acceleration of an object moving through space. Big skill: You should be able to compute the velocity, acceleration, and force vectors for an object given its position vector function, or derive its pos ...
... Big idea: Vector-valued functions can be used to efficiently describe the position, velocity, and acceleration of an object moving through space. Big skill: You should be able to compute the velocity, acceleration, and force vectors for an object given its position vector function, or derive its pos ...
pps
... • Web content to the course All the slides I use and examples we make in class will be made available on the web, every Wednesday before class – Navigate to www.nucastro.ph.tum.de – Click “Lehre” “Experimental physics in English I” ...
... • Web content to the course All the slides I use and examples we make in class will be made available on the web, every Wednesday before class – Navigate to www.nucastro.ph.tum.de – Click “Lehre” “Experimental physics in English I” ...