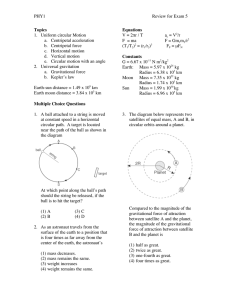
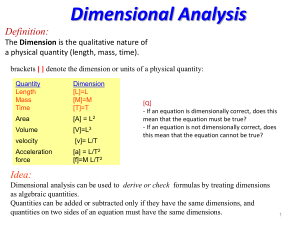
Hill Question
... •Speed: Scalar (magnitude) •Velocity: Vector (magnitude AND direction) •Unit is m/s • s and v often interchanged ….. ...
... •Speed: Scalar (magnitude) •Velocity: Vector (magnitude AND direction) •Unit is m/s • s and v often interchanged ….. ...
Chapter 4 Rotating Coordinate Systems and the Equations of Motion
... where Utangent is the tangential velocity of the surface. In the 19th century, during the period of the original formulation of the Navier Stokes equations, the validity of this condition was in doubt. Experimental verification was uncertain and Stokes himself, who felt the no slip condition was the ...
... where Utangent is the tangential velocity of the surface. In the 19th century, during the period of the original formulation of the Navier Stokes equations, the validity of this condition was in doubt. Experimental verification was uncertain and Stokes himself, who felt the no slip condition was the ...
Physics 312
... semicircular cross section of radius R = 5 m, as shown in the figure. I hold a frictionless skateboard on the side of the trough pointing down toward the bottom and release it. Discuss the subsequent motion using Newton’s second law. In particular, if I release the board just a short way from the bo ...
... semicircular cross section of radius R = 5 m, as shown in the figure. I hold a frictionless skateboard on the side of the trough pointing down toward the bottom and release it. Discuss the subsequent motion using Newton’s second law. In particular, if I release the board just a short way from the bo ...
Introduction to Circular Motion
... and as always units are important. The mass, m, must be in kg, the velocity, v, must be in m/s, and the radius, r, must be in meters. We will restrict the motion of the object to that of a horizontal circle, i.e. a circle parallel to the ground as on a merry-go-round. What may not be intuitively obv ...
... and as always units are important. The mass, m, must be in kg, the velocity, v, must be in m/s, and the radius, r, must be in meters. We will restrict the motion of the object to that of a horizontal circle, i.e. a circle parallel to the ground as on a merry-go-round. What may not be intuitively obv ...
Proper particle mechanics
... This paper shows how to formulate conventional relativistic mechanics without referring to observers or coordinates. To emphasize the distinctive features of this formulation, it will be called “proper mechanics.” The common expression “relativistic mechanics” will be avoided here because, by the mo ...
... This paper shows how to formulate conventional relativistic mechanics without referring to observers or coordinates. To emphasize the distinctive features of this formulation, it will be called “proper mechanics.” The common expression “relativistic mechanics” will be avoided here because, by the mo ...
Unit Review
... 17) A .015 kg marble moving to the right at .225 m/s makes an elastic head on collision with a .03 kg shooter marble moving to the left at .18 m/s. After the collision, the smaller marble moves to the left at .315 m/s. What is the velocity of the .03 kg marble after the collision. Since this is an e ...
... 17) A .015 kg marble moving to the right at .225 m/s makes an elastic head on collision with a .03 kg shooter marble moving to the left at .18 m/s. After the collision, the smaller marble moves to the left at .315 m/s. What is the velocity of the .03 kg marble after the collision. Since this is an e ...
Name Class Date Applying Coordinate Geometry Geometry
... Plan a coordinate proof to show that the diagonals of a square are congruent. Draw and label a square on a coordinate grid. In square ABCD, AB = BC = CD = DA. Draw in the diagonals, AC and BD . Prove that AC = BD. Use the Distance Formula. CA = (0 a)2 + (a 0)2 = a 2 + a 2 = 2a 2 BD = (a 0)2 + ...
... Plan a coordinate proof to show that the diagonals of a square are congruent. Draw and label a square on a coordinate grid. In square ABCD, AB = BC = CD = DA. Draw in the diagonals, AC and BD . Prove that AC = BD. Use the Distance Formula. CA = (0 a)2 + (a 0)2 = a 2 + a 2 = 2a 2 BD = (a 0)2 + ...
Chapter 4
... where Utangent is the tangential velocity of the surface. In the 19th century, during the period of the original formulation of the Navier Stokes equations, the validity of this condition was in doubt. Experimental verification was uncertain and Stokes himself, who felt the no slip condition was the ...
... where Utangent is the tangential velocity of the surface. In the 19th century, during the period of the original formulation of the Navier Stokes equations, the validity of this condition was in doubt. Experimental verification was uncertain and Stokes himself, who felt the no slip condition was the ...