Extending the application of the relativity principle: Some
... Using ~2!, and under the additional assumption of force invariance with change of inertial frame of reference, one can infer that Newton’s second law, ma5F, remains valid for all inertial observers. In regard to momentum and energy, IPC texts do not usually consider more than one observer.5 This is ...
... Using ~2!, and under the additional assumption of force invariance with change of inertial frame of reference, one can infer that Newton’s second law, ma5F, remains valid for all inertial observers. In regard to momentum and energy, IPC texts do not usually consider more than one observer.5 This is ...
Review Answers
... Draw free-body diagrams for the following problems. Be sure to draw all the forces with arrows that are of appropriate length to reflect the given descriptions. a) Object slides across a horizontal surface at constant speed without friction. Fn up; equal Fg down b) A sky diver falls downward through ...
... Draw free-body diagrams for the following problems. Be sure to draw all the forces with arrows that are of appropriate length to reflect the given descriptions. a) Object slides across a horizontal surface at constant speed without friction. Fn up; equal Fg down b) A sky diver falls downward through ...
Transformation of Internal Waves at the Bottom Ledge
... each of these wavenumbers we have performed runs for three values of the depth ratio h0 /h1 = {0.1, 1.0, 10.0}; this depth ratio characterises the relative thicknesses of fluid layer. Then, the calculations were performed for 20 differen values of the bottom layer thicknesses h2 /h1 varying from 0.0 ...
... each of these wavenumbers we have performed runs for three values of the depth ratio h0 /h1 = {0.1, 1.0, 10.0}; this depth ratio characterises the relative thicknesses of fluid layer. Then, the calculations were performed for 20 differen values of the bottom layer thicknesses h2 /h1 varying from 0.0 ...
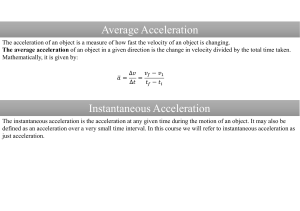
Average Acceleration Instantaneous Acceleration
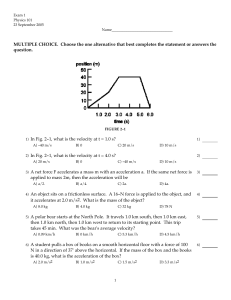
... 4. At least three of the kinematic variables should have values. Be sure to read the question carefully. There may be implied data like ‘an object is accelerated from rest’, in which case we may write u = 0. 5. Often a problem is divided into parts. For instance, a car may accelerate for a period of ...
... 4. At least three of the kinematic variables should have values. Be sure to read the question carefully. There may be implied data like ‘an object is accelerated from rest’, in which case we may write u = 0. 5. Often a problem is divided into parts. For instance, a car may accelerate for a period of ...
Ex 1 - SharpSchool
... in air. Force of gravity is the only force acting on it. it follows a curved path, called a trajectory, which is due to its horizontal and vertical velocity the horizontal distance the object travels is called the range characteristics of projectile motion: 1. the horizontal velocity is consta ...
... in air. Force of gravity is the only force acting on it. it follows a curved path, called a trajectory, which is due to its horizontal and vertical velocity the horizontal distance the object travels is called the range characteristics of projectile motion: 1. the horizontal velocity is consta ...
REGULATION 2013 ACADEMIC YEAR 2014
... 23. Find the angular velocity of a second hand of a clock? 24. What is relation b/w angular velocity and linear velocity? 25. Define linear velocity. 26. What is angular acceleration? 27. What is the relative motion? 28. What are motion curves? 29. A ball dropped from a height of 1.6 m on a floor re ...
... 23. Find the angular velocity of a second hand of a clock? 24. What is relation b/w angular velocity and linear velocity? 25. Define linear velocity. 26. What is angular acceleration? 27. What is the relative motion? 28. What are motion curves? 29. A ball dropped from a height of 1.6 m on a floor re ...