Motion in accelerated reference frames
... A translationally accelerated reference frame is usually a frame defined by a moving vehicle of some kind, such as an accelerating car or elevator. Motion in such a frame can be investigated in the same way as motion in an inertial frame provided only that the fictitious force 1.32 is added to the rea ...
... A translationally accelerated reference frame is usually a frame defined by a moving vehicle of some kind, such as an accelerating car or elevator. Motion in such a frame can be investigated in the same way as motion in an inertial frame provided only that the fictitious force 1.32 is added to the rea ...
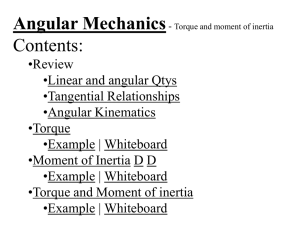
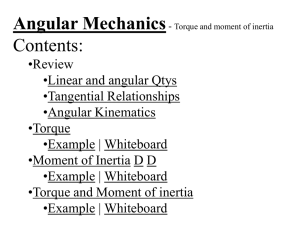
Moment of Inertia
... total of the parts: Children – use mr2 (assume they are points) MGR – use 1/2mr2 (solid cylinder) I = 3((40kg)(1.2m)2) + ½(240kg )(1.5m)2 I = 442.8 kgm2 = 440 kgm2 TOC ...
... total of the parts: Children – use mr2 (assume they are points) MGR – use 1/2mr2 (solid cylinder) I = 3((40kg)(1.2m)2) + ½(240kg )(1.5m)2 I = 442.8 kgm2 = 440 kgm2 TOC ...
Chapter 20_linear mo..
... objects of equal mass colliding in a horizontal plane and then undergoing projectile motion after the collision. Since the horizontal component of velocity remains constant for a projectile in free fall, the horizontal part of the projectile motion can be used to represent the horizontal component o ...
... objects of equal mass colliding in a horizontal plane and then undergoing projectile motion after the collision. Since the horizontal component of velocity remains constant for a projectile in free fall, the horizontal part of the projectile motion can be used to represent the horizontal component o ...
The Theory of Finite Dimensional Vector Spaces
... we say that V is finite dimensional if it is spanned by a finite set of vectors. For the remainder of this section, we will only consider finite dimensional vector spaces. Definition 4.4. The dimension of a finite dimensional vector space V is the number of elements in a basis of V . For convenience ...
... we say that V is finite dimensional if it is spanned by a finite set of vectors. For the remainder of this section, we will only consider finite dimensional vector spaces. Definition 4.4. The dimension of a finite dimensional vector space V is the number of elements in a basis of V . For convenience ...
Chapter 6
... The second condition for equilibrium asserts that if an object is in rotational equilibrium, the net torque acting on it about any axis must be zero. That is ...
... The second condition for equilibrium asserts that if an object is in rotational equilibrium, the net torque acting on it about any axis must be zero. That is ...