L02
... function is not as easy to work with algebraically as the square function, e.g., the absolute value function is not differentiable. ...
... function is not as easy to work with algebraically as the square function, e.g., the absolute value function is not differentiable. ...
λ μ μ
... Exploring the Distribution of Sample Means by Computer Simulation This is an individual assignment. You are allowed to seek help from persons other than me for programming questions only. I reserve the right to verbally question you about your responses and assign a grade of zero if it becomes appar ...
... Exploring the Distribution of Sample Means by Computer Simulation This is an individual assignment. You are allowed to seek help from persons other than me for programming questions only. I reserve the right to verbally question you about your responses and assign a grade of zero if it becomes appar ...
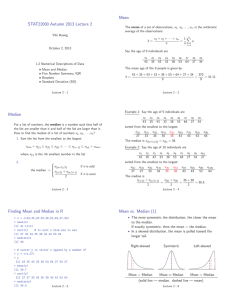
Coefficient of variation.
... The coefficient of variation measures the variability of a series of numbers independently of the unit of measurement used for these numbers. In order to do so, the coefficient od variation eliminates the unit of measurement of the standard deviation of a series of numbers by dividing it by the mean ...
... The coefficient of variation measures the variability of a series of numbers independently of the unit of measurement used for these numbers. In order to do so, the coefficient od variation eliminates the unit of measurement of the standard deviation of a series of numbers by dividing it by the mean ...
Everything is not normal,Some comparisons are not odious,The big
... more industrial bakery than the girls, so their cholesterol level are higher, as you can see if you compare the curve from girls (black) with those of children (blue). Now, if we represent the values of the girls against the values of the boys linearly, as can be seen in the figure, the dot are far ...
... more industrial bakery than the girls, so their cholesterol level are higher, as you can see if you compare the curve from girls (black) with those of children (blue). Now, if we represent the values of the girls against the values of the boys linearly, as can be seen in the figure, the dot are far ...
A class of distributions with the linear mean residual quantile
... advantage of seeking such cases is justified from the analytical and practical points of view. In data situations where a linear mean residual quantile function observed, the logical choice is the LMRQD, which being the only distribution possessing that property and not any other model, however good ...
... advantage of seeking such cases is justified from the analytical and practical points of view. In data situations where a linear mean residual quantile function observed, the logical choice is the LMRQD, which being the only distribution possessing that property and not any other model, however good ...
What`s Stat - DrJimMirabella.com
... a large collection of scores, it is best to use a statistical program such as EXCEL, SAS, Statview, SPSS, GBSTAT, MINITAB etc., where you enter the raw data into your computer and then with the mere press of a button or two, an awesome frequency table is constructed. If the data you obtained are dem ...
... a large collection of scores, it is best to use a statistical program such as EXCEL, SAS, Statview, SPSS, GBSTAT, MINITAB etc., where you enter the raw data into your computer and then with the mere press of a button or two, an awesome frequency table is constructed. If the data you obtained are dem ...