Finite Population Handout
... We are comfortable with our estimate give or take almost a million people. It’s not very impressive, but that’s how it goes with the estimation of totals. You multiply a small margin of error by a very big number, and you get a big number. The estimation of totals is inherently not very precise. Thi ...
... We are comfortable with our estimate give or take almost a million people. It’s not very impressive, but that’s how it goes with the estimation of totals. You multiply a small margin of error by a very big number, and you get a big number. The estimation of totals is inherently not very precise. Thi ...
Top Ten #1
... estimate the mean number of hours worked per week by students. A sample of 49 students showed a mean of 24 hours. It is assumed that the population standard deviation is 4 hours. What is the population mean? ...
... estimate the mean number of hours worked per week by students. A sample of 49 students showed a mean of 24 hours. It is assumed that the population standard deviation is 4 hours. What is the population mean? ...
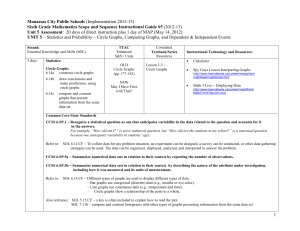
Manassas City Public Schools (4-19-07)
... CCSS 6.SP.1 ~ Recognize a statistical question as one that anticipates variability in the data related to the question and accounts for it in the answers. For example, “How old am I?” is not a statistical question, but “How old are the students in my school?” is a statistical question because one an ...
... CCSS 6.SP.1 ~ Recognize a statistical question as one that anticipates variability in the data related to the question and accounts for it in the answers. For example, “How old am I?” is not a statistical question, but “How old are the students in my school?” is a statistical question because one an ...
Document
... be found even if the size of the absolute effects are so small that they are of no clinical interest. • The fact that no significant results were found, does not mean that no difference exists. Perhaps the study had to low power to detect a true difference/effect/association. ...
... be found even if the size of the absolute effects are so small that they are of no clinical interest. • The fact that no significant results were found, does not mean that no difference exists. Perhaps the study had to low power to detect a true difference/effect/association. ...
Chi-Square and T-Tests Using SAS®: Performance and Interpretation
... whether the distribution of age is different for beach and non-beach swimmers (i.e. is there an association between swim location and age), the correct percentage to examine in the two-way table is the row percentage, which is the third number listed in each cell of the table. The row percentages ar ...
... whether the distribution of age is different for beach and non-beach swimmers (i.e. is there an association between swim location and age), the correct percentage to examine in the two-way table is the row percentage, which is the third number listed in each cell of the table. The row percentages ar ...
Data Collection and Analysis
... Measurement – Generally what questions do we ask so that we get the information we want Sampling Plan – How do we select a sample for the study such that we maximize its chances of faithfully representing the population of interest Analysis – confirming that all information being obtained is a ...
... Measurement – Generally what questions do we ask so that we get the information we want Sampling Plan – How do we select a sample for the study such that we maximize its chances of faithfully representing the population of interest Analysis – confirming that all information being obtained is a ...
Ch10 - OCCC.edu
... significant difference between the two groups this is the procedure we use. Many of the techniques and statistics that we have used in previous chapters will be used again. So it should seem very familiar how we go about studying and analyzing this type of procedure. Assumptions When Comparing Two S ...
... significant difference between the two groups this is the procedure we use. Many of the techniques and statistics that we have used in previous chapters will be used again. So it should seem very familiar how we go about studying and analyzing this type of procedure. Assumptions When Comparing Two S ...
Psychology 2010 Lecture 10 Notes: Hypothesis Testing Ch 6
... What if the mean of the lifetimes of 25 bulbs were 4999.99? Most rational people would retain null. What if the mean of the lifetimes of 25 bulbs were 1003.23 Most rational people would reject null. What if the mean of the lifetimes of 25 bulbs were 4876.44? Hmm. A gray area. Clearly we need some ru ...
... What if the mean of the lifetimes of 25 bulbs were 4999.99? Most rational people would retain null. What if the mean of the lifetimes of 25 bulbs were 1003.23 Most rational people would reject null. What if the mean of the lifetimes of 25 bulbs were 4876.44? Hmm. A gray area. Clearly we need some ru ...
1) The grade point averages for 10 randomly selected students in a
... 6) (Sec 6.3 – omit su06) A survey of 250 households showed 62 owned at least one gun. Construct a 90% confidence interval for the proportion of households that own at least one gun. A) (0.369, 0.451) B) (0.683, 0.712) C) (0.103, 0.189) D) (0.203, 0.293) ...
... 6) (Sec 6.3 – omit su06) A survey of 250 households showed 62 owned at least one gun. Construct a 90% confidence interval for the proportion of households that own at least one gun. A) (0.369, 0.451) B) (0.683, 0.712) C) (0.103, 0.189) D) (0.203, 0.293) ...
251y0244
... b. I use an average of 2 boxes of paper in a day , but it takes 5 days to get a delivery. Given the average usage over 9 days , do the following: (i) What is the probability of using at least 22 boxes in the 9 day period? (1) (ii) What is the probability of using more than 22 boxes? (1) (iii) If x i ...
... b. I use an average of 2 boxes of paper in a day , but it takes 5 days to get a delivery. Given the average usage over 9 days , do the following: (i) What is the probability of using at least 22 boxes in the 9 day period? (1) (ii) What is the probability of using more than 22 boxes? (1) (iii) If x i ...
Statistics 13 Elementary Statistics Describing Qualitative Data
... Summary of Graphical Descriptive Methods for Quantitative Data • Dot Plot: The numerical value of each quantitative measurement in the data set is represented by a dot on a horizontal scale. When data values repeat, the dots are placed above one another vertically. • Stem-and-Leaf Display: The numer ...
... Summary of Graphical Descriptive Methods for Quantitative Data • Dot Plot: The numerical value of each quantitative measurement in the data set is represented by a dot on a horizontal scale. When data values repeat, the dots are placed above one another vertically. • Stem-and-Leaf Display: The numer ...
251y0242
... b. I use an average of 2 boxes of paper in a day , but it takes 6 days to get a delivery. Given the average usage over 6 days , do the following: (i) What is the probability of using at least 5 boxes in the 6 day period? (1) (ii) What is the probability of using more than 6 boxes? (1) (iii) If x is ...
... b. I use an average of 2 boxes of paper in a day , but it takes 6 days to get a delivery. Given the average usage over 6 days , do the following: (i) What is the probability of using at least 5 boxes in the 6 day period? (1) (ii) What is the probability of using more than 6 boxes? (1) (iii) If x is ...