Introduction to hypothesis testing
... in the population from which the sample was drawn, no such relationship or differences exist. [...] the statistical significance of a result tells us something about the degree to which the result is "true" (in the sense of being "representative of the population").” [http://www.statsoft.com/textboo ...
... in the population from which the sample was drawn, no such relationship or differences exist. [...] the statistical significance of a result tells us something about the degree to which the result is "true" (in the sense of being "representative of the population").” [http://www.statsoft.com/textboo ...
Exam #2 - TAMU Stat
... in Yosemite national park. 20 trees were randomly selected and measured. The p-value for the test statistic B. 0.1457 was 0.23. Your boss wants to know what the number C. 0.3085 0.23 means. It is D. 0.0228 A. the probability that the null hypothesis is true. E. 0.9772 B. the probability of making a ...
... in Yosemite national park. 20 trees were randomly selected and measured. The p-value for the test statistic B. 0.1457 was 0.23. Your boss wants to know what the number C. 0.3085 0.23 means. It is D. 0.0228 A. the probability that the null hypothesis is true. E. 0.9772 B. the probability of making a ...
Homework1
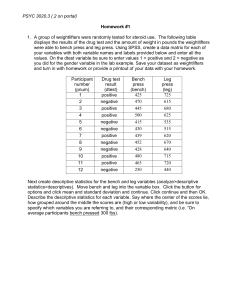
... 2. Open the breakfast.sav dataset that we used for the class presentation (it can be found on the class portal under course materials). Create a histogram of the frequency distribution for the poptart variable (analyze/descriptive statistics/frequencies). Move poptart to the variable box. Be sure to ...
... 2. Open the breakfast.sav dataset that we used for the class presentation (it can be found on the class portal under course materials). Create a histogram of the frequency distribution for the poptart variable (analyze/descriptive statistics/frequencies). Move poptart to the variable box. Be sure to ...
Powerpoint
... Tranformations must be described in the Results section of your manuscript. Effects of transformations on the validity of your t or F statistical tests is unclear. Nonparametric tests may be preferable but make probability of Type II error greater. ...
... Tranformations must be described in the Results section of your manuscript. Effects of transformations on the validity of your t or F statistical tests is unclear. Nonparametric tests may be preferable but make probability of Type II error greater. ...
hsm11a2ep_041
... 14. To mark its eighth anniversary, Pizzeria Otto has a special coupon that offers the same price on a pizza with any combination of the 8 original toppings. Each pizza must have at least one topping. How many different kinds of pizza can be ordered with the ...
... 14. To mark its eighth anniversary, Pizzeria Otto has a special coupon that offers the same price on a pizza with any combination of the 8 original toppings. Each pizza must have at least one topping. How many different kinds of pizza can be ordered with the ...
Math 140 Confidence Intervals #7 Constructing Confidence Intervals
... and 1 population proportion (percentage) Confidence intervals give two values that we think the population value is in between. To construct a confidence interval, we start with the sample value (point estimate) and then add and subtract a certain number of standard deviations from the sample value. ...
... and 1 population proportion (percentage) Confidence intervals give two values that we think the population value is in between. To construct a confidence interval, we start with the sample value (point estimate) and then add and subtract a certain number of standard deviations from the sample value. ...
Practice Exam Final KEY - Department of Statistics, Purdue University
... had never smoked regularly at any point in their lives. The researchers found a higher proportion of cancer cases among those who had smoked regularly than among those who had never smoked regularly. What type of study is this? a) An experiment but not a double-blind experiment b) A double-blind exp ...
... had never smoked regularly at any point in their lives. The researchers found a higher proportion of cancer cases among those who had smoked regularly than among those who had never smoked regularly. What type of study is this? a) An experiment but not a double-blind experiment b) A double-blind exp ...
Hypothesis Test Summary
... The null hypothesis tells us what value the parameter has, and therefore tells us something about what value we should see for our test statistic. Of course, because the test statistic is a random number, we probably won’t see exactly the value the null hypothesis says we should, even if the null hy ...
... The null hypothesis tells us what value the parameter has, and therefore tells us something about what value we should see for our test statistic. Of course, because the test statistic is a random number, we probably won’t see exactly the value the null hypothesis says we should, even if the null hy ...
Lecture 9 - Statistics
... Last day, introduced a point estimator…a statistic that estimates a population parameter Often more desirable to present a plausible range for the parameter, based on the data We will call this a confidence interval ...
... Last day, introduced a point estimator…a statistic that estimates a population parameter Often more desirable to present a plausible range for the parameter, based on the data We will call this a confidence interval ...