HP Authorized Customer
... confidence limit 248.366 lower confidence limit With a confidence interval of 99 %, the z-score is 2.576. An effective method to get our answer is: (z-value X standard deviation/10)2 (2.576 X 170.38/10)2 = 1926.067 Excel Megastat computations are as under: ...
... confidence limit 248.366 lower confidence limit With a confidence interval of 99 %, the z-score is 2.576. An effective method to get our answer is: (z-value X standard deviation/10)2 (2.576 X 170.38/10)2 = 1926.067 Excel Megastat computations are as under: ...
Estimating with Confidence
... we will use the most common ones and also learn to calculate any desired level. TESTS of SIGNIFICANCE assess the evidence for a "claim" about the population as a result of gathered data. These tests determine whether the results can be explained by chance occurrence or not and whether the results di ...
... we will use the most common ones and also learn to calculate any desired level. TESTS of SIGNIFICANCE assess the evidence for a "claim" about the population as a result of gathered data. These tests determine whether the results can be explained by chance occurrence or not and whether the results di ...
02-w11-stats250-bgunderson-chapter-3-and-4
... Does the interval in part (e) of 34.2% to 39.8% actually contain the population proportion of all adults that rate the quality of public schools as excellent? It either does or it doesn’t, but we don’t know because we don’t know the value of the population proportion. (And if we did know the value o ...
... Does the interval in part (e) of 34.2% to 39.8% actually contain the population proportion of all adults that rate the quality of public schools as excellent? It either does or it doesn’t, but we don’t know because we don’t know the value of the population proportion. (And if we did know the value o ...
DM10: Evaluation and Credibility
... Total cost/benefit – when different errors involve different costs Lift and ROC curves Error in numeric predictions ...
... Total cost/benefit – when different errors involve different costs Lift and ROC curves Error in numeric predictions ...
DM10: Evaluation and Credibility
... Total cost/benefit – when different errors involve different costs Lift and ROC curves Error in numeric predictions ...
... Total cost/benefit – when different errors involve different costs Lift and ROC curves Error in numeric predictions ...
252solnA2
... distribution. These confidence intervals are point-wise, meaning that they are calculated separately for each point on the fitted distribution without controlling for family-wise error. Usually, points outside the confidence intervals occur in the tails. In the lower half of the plot, points to the ...
... distribution. These confidence intervals are point-wise, meaning that they are calculated separately for each point on the fitted distribution without controlling for family-wise error. Usually, points outside the confidence intervals occur in the tails. In the lower half of the plot, points to the ...
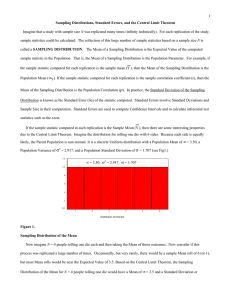
1 N SAMPLING DISTRIBUTION
... The Central Limit Theorem states that a sampling distribution of means (or sums) from random samples of N observations approximates a normal distribution regardless of the shape of the parent population as N becomes large. This has particular importance because it implies that even if data are sampl ...
... The Central Limit Theorem states that a sampling distribution of means (or sums) from random samples of N observations approximates a normal distribution regardless of the shape of the parent population as N becomes large. This has particular importance because it implies that even if data are sampl ...
Statistical Analysis of Data Collected
... When performing laboratory experiments, a certain variation in results will always occur regardless of the care taken in measuring. Though all systematic errors have been avoided, the student will notice that the values obtained will deviate from each other. Random errors are unavoidable. Variations ...
... When performing laboratory experiments, a certain variation in results will always occur regardless of the care taken in measuring. Though all systematic errors have been avoided, the student will notice that the values obtained will deviate from each other. Random errors are unavoidable. Variations ...