Descriptive Statistics
... If i is not an integer, the next integer greater than i locates the position of the pth percentile in the ranked data set. If i is an integer, the p th percentile is the average of the observations in positions i and i + 1 in the ranked data set. ...
... If i is not an integer, the next integer greater than i locates the position of the pth percentile in the ranked data set. If i is an integer, the p th percentile is the average of the observations in positions i and i + 1 in the ranked data set. ...
Intro to Statistics Toolbox Statistics Toolbox/Analysis of
... indicates that the effect of the first predictor varies from one sample to another. An F statistic as extreme as this would occur by chance only once in 10,000 times if the samples were truly equal. • The p-value for the second effect is 0.0039, which is also highly significant. This indicates that ...
... indicates that the effect of the first predictor varies from one sample to another. An F statistic as extreme as this would occur by chance only once in 10,000 times if the samples were truly equal. • The p-value for the second effect is 0.0039, which is also highly significant. This indicates that ...
SSG14 230 - public.asu.edu
... A medical researcher finds that type of cholesterol reduction program (medication, exercise, or diet) has a significant effect on LDL (the “bad” type of cholesterol) levels. To determine the amount of variance in LDL levels accounted for by type of cholesterol reduction program, she should: ...
... A medical researcher finds that type of cholesterol reduction program (medication, exercise, or diet) has a significant effect on LDL (the “bad” type of cholesterol) levels. To determine the amount of variance in LDL levels accounted for by type of cholesterol reduction program, she should: ...
Induction on Regression (Ch 15)
... – Recall: Error is the deviation from the regression line – Is dispersion of error consistent across values of X? – Definition: “homoskedasticity” = error dispersion is consistent across values of X – Opposite: “heteroskedasticity”, errors vary with X ...
... – Recall: Error is the deviation from the regression line – Is dispersion of error consistent across values of X? – Definition: “homoskedasticity” = error dispersion is consistent across values of X – Opposite: “heteroskedasticity”, errors vary with X ...
Statistics MATH-1410 Mean and Standard Deviation of Discrete Random Variables
... exactly one television, a 0.5% chance that it will own exactly six televisions, and a 62% chance that it will own no more than two televisions. We can now use the completed probability distribution to determine the mean (or the expected value) of the random variable. We are fortunate in this problem ...
... exactly one television, a 0.5% chance that it will own exactly six televisions, and a 62% chance that it will own no more than two televisions. We can now use the completed probability distribution to determine the mean (or the expected value) of the random variable. We are fortunate in this problem ...
Lecture 1
... statistical logic, it should be clear that one doesn't "prove" anything. Rather we are looking at consistency or inconsistency of the data with the hypothesis. If data is "consistent" with the hypothesis (in our example the sample mean falls between 90.2 and 109.8), then instead of proving the hypot ...
... statistical logic, it should be clear that one doesn't "prove" anything. Rather we are looking at consistency or inconsistency of the data with the hypothesis. If data is "consistent" with the hypothesis (in our example the sample mean falls between 90.2 and 109.8), then instead of proving the hypot ...
Cool Shoes: 1-Variable - The Math Projects Journal
... The Girls' Data (Day 2) The girls’ data set may be used as additional practice, however, it serves very well as an assessment for this lesson. It is suggested that the students be allowed to have their responses to the boys’ data available while working through the girls’. The analysis questions are ...
... The Girls' Data (Day 2) The girls’ data set may be used as additional practice, however, it serves very well as an assessment for this lesson. It is suggested that the students be allowed to have their responses to the boys’ data available while working through the girls’. The analysis questions are ...
MC Review
... pounds. But if its burrito is averaging more than 1.2 pounds its profits will suffer. A random sample of 42 burritos had a mean of 1.4 pounds with a standard deviation of 0.5 pounds. Based on the test of the hypotheses H0: μ = 1.2 versus Ha: μ > 1.2, which of these statements represents a logical co ...
... pounds. But if its burrito is averaging more than 1.2 pounds its profits will suffer. A random sample of 42 burritos had a mean of 1.4 pounds with a standard deviation of 0.5 pounds. Based on the test of the hypotheses H0: μ = 1.2 versus Ha: μ > 1.2, which of these statements represents a logical co ...
Directional (Circular) Statistics
... non-randomness is due to clustering. If the u’ values are greater than the higher of the u’ critical values from the Runs table of circular data it signifies that the nonrandomness is due to uniformity. If the normal approximation is used, negative Z values signify that the non-randomness is due to ...
... non-randomness is due to clustering. If the u’ values are greater than the higher of the u’ critical values from the Runs table of circular data it signifies that the nonrandomness is due to uniformity. If the normal approximation is used, negative Z values signify that the non-randomness is due to ...
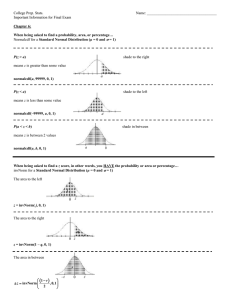
College Prep. Stats. Name: Important Information for Final Exam
... When finding a critical value, use the following calculator command: invT(area to the left, df) Example: If the given confidence level is 86%, with a sample size of 28, the degrees of freedom will be n – 1, so df = 27. α = 1 – 0.86 = 0.14, therefore, α/2 = 0.07. To find the correct critical value, f ...
... When finding a critical value, use the following calculator command: invT(area to the left, df) Example: If the given confidence level is 86%, with a sample size of 28, the degrees of freedom will be n – 1, so df = 27. α = 1 – 0.86 = 0.14, therefore, α/2 = 0.07. To find the correct critical value, f ...
srs.pdf
... definition of the k-statistics. Suppose that the components of x are independent and identically distributed random variables with distribution F . Then the expected value of the power average is E(mr (x)) = µr , the rth moment of F . Likewise, E(mrs (x)) = µr µs is the product of two moments, E(mrs ...
... definition of the k-statistics. Suppose that the components of x are independent and identically distributed random variables with distribution F . Then the expected value of the power average is E(mr (x)) = µr , the rth moment of F . Likewise, E(mrs (x)) = µr µs is the product of two moments, E(mrs ...