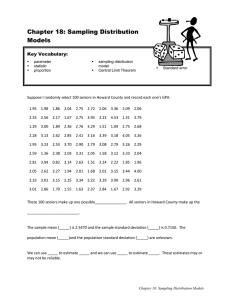
Find the new margin of error, confidence level and compare this
... • Any formula for inference is correct only in specific circumstances. • The data must be an SRS from the population. • The formula is not correct for probability sampling designs more complex than an SRS. • There is no correct method for inference from data haphazardly collected with bias of unknow ...
... • Any formula for inference is correct only in specific circumstances. • The data must be an SRS from the population. • The formula is not correct for probability sampling designs more complex than an SRS. • There is no correct method for inference from data haphazardly collected with bias of unknow ...
7.1-1
... I took a sample of the grade point averages for students in my class. For 25 students, the standard deviation of grade points was 0.65 and the mean was 2.89. The standard error for the sample was: a. 0.578. b. 0.026. ...
... I took a sample of the grade point averages for students in my class. For 25 students, the standard deviation of grade points was 0.65 and the mean was 2.89. The standard error for the sample was: a. 0.578. b. 0.026. ...
ACTIVITY SET 1 Jan - Penn State Department of Statistics
... g. The U.S. Government reported that 23% of US adults age 18-24 smoked cigarettes. Based on your confidence interval do believe that this percentage is reasonable, too high, or too low for Penn State students and explain why. Since our interval does not contain 0.23 (i.e. 23%) and is less than this ...
... g. The U.S. Government reported that 23% of US adults age 18-24 smoked cigarettes. Based on your confidence interval do believe that this percentage is reasonable, too high, or too low for Penn State students and explain why. Since our interval does not contain 0.23 (i.e. 23%) and is less than this ...
Strain Amplification in the Bone Mechanosensory
... which groups is different from which group. The procedure for finding out the difference between groups is know as making analytical comparisons. With a non significant omnibus F we are prepared to assert that there are no real differences among the means. – We can stop the analysis there. A signifi ...
... which groups is different from which group. The procedure for finding out the difference between groups is know as making analytical comparisons. With a non significant omnibus F we are prepared to assert that there are no real differences among the means. – We can stop the analysis there. A signifi ...
Sampling_MathsFest1
... Advantages of Simple Random Sampling • Every member of the population has an equal chance of being represented in the sample • The simple random sample should be representative of the population. Theoretically the only thing that can compromise its representativeness is luck • If the sample is not ...
... Advantages of Simple Random Sampling • Every member of the population has an equal chance of being represented in the sample • The simple random sample should be representative of the population. Theoretically the only thing that can compromise its representativeness is luck • If the sample is not ...
Stat200: pre7 - Sampling Distributions
... to 30 is normally distributed (bell-shaped) with a mean of 65 inches and a standard deviation of 3 inches. A random sample of 200 women was taken and the sample mean x recorded. Now IMAGINE taking MANY samples of size 200 from the population of women. For each sample we record the x . What is the sa ...
... to 30 is normally distributed (bell-shaped) with a mean of 65 inches and a standard deviation of 3 inches. A random sample of 200 women was taken and the sample mean x recorded. Now IMAGINE taking MANY samples of size 200 from the population of women. For each sample we record the x . What is the sa ...
















![[MSM04]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008529088_2-3ce1cce4ea32dddeeb96e74b738216a4-300x300.png)