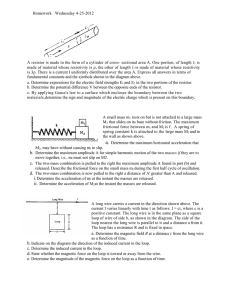
Homework Wednesday 4-25-2012 A resistor is made in the form of a
... A resistor is made in the form of a cylinder of cross- sectional area A. One portion, of length l1 is made of material whose resistivity is ρ, the other of length l 2 is made of material whose resistivity is 3ρ. There is a current I uniformly distributed over the area A. Express all answers in terms ...
... A resistor is made in the form of a cylinder of cross- sectional area A. One portion, of length l1 is made of material whose resistivity is ρ, the other of length l 2 is made of material whose resistivity is 3ρ. There is a current I uniformly distributed over the area A. Express all answers in terms ...
MAGNETIC SUSCEPTIBILITY USING A GOUY BALANCE
... top of the wooden casing. A digital balance is placed which carries a hook at the bottom for suspending the glass tube containing the material (FeCl2, or Fe2SO4). The magnetic field between the pole pieces can be varied by changing the current through the coils using a DC power supply. The magnetic ...
... top of the wooden casing. A digital balance is placed which carries a hook at the bottom for suspending the glass tube containing the material (FeCl2, or Fe2SO4). The magnetic field between the pole pieces can be varied by changing the current through the coils using a DC power supply. The magnetic ...
Chapter 25 Clicker questions.
... b. power at one voltage to the same power at another voltage. c. current from one place to another. d. voltage to useful applications. Explanation: Answers c or d are not the best choices, as is b, the more direct answer. If you answered a, OUCH! … no device creates energy! ...
... b. power at one voltage to the same power at another voltage. c. current from one place to another. d. voltage to useful applications. Explanation: Answers c or d are not the best choices, as is b, the more direct answer. If you answered a, OUCH! … no device creates energy! ...
simulation of the magnetostrictive actuator transients
... the linear dimension of a ferromagnetic element caused by magnetic field. Changes in linear dimensions of the element are different in each direction. In most cases a privileged direction in which the change is greatest can be distinguished. This type is called a linear magnetostriction [3, 5]. This ...
... the linear dimension of a ferromagnetic element caused by magnetic field. Changes in linear dimensions of the element are different in each direction. In most cases a privileged direction in which the change is greatest can be distinguished. This type is called a linear magnetostriction [3, 5]. This ...
notes
... The third term also is caused by a current, but not i1. This is evident by the fact that if we impress a voltage across the primary winding but leave the secondary open circuited (so that i1=(N2/N1)i2=0 because i2=0), we will still be able to measure a voltage across the ...
... The third term also is caused by a current, but not i1. This is evident by the fact that if we impress a voltage across the primary winding but leave the secondary open circuited (so that i1=(N2/N1)i2=0 because i2=0), we will still be able to measure a voltage across the ...
Electric Power Prac 1: Magnetic Fields Produced by
... Look at the inside of the plastic cover and describe and draw what you see. The axle of the motor can be pushed out from the other end. The axle has the commutator and the coils on it. How many metal segments are there on the commutator? ...
... Look at the inside of the plastic cover and describe and draw what you see. The axle of the motor can be pushed out from the other end. The axle has the commutator and the coils on it. How many metal segments are there on the commutator? ...
12: Electromagnetic Induction
... change in flux so EMF is zero for an instant. - As magnet exits, Lenz’s law tells us that the current must flow in the opposite direction so as to oppose motion. reversed EMF - Max induced EMF occurs on exit because magnet is moving fastest. - t2 is smaller due to greater speed. ...
... change in flux so EMF is zero for an instant. - As magnet exits, Lenz’s law tells us that the current must flow in the opposite direction so as to oppose motion. reversed EMF - Max induced EMF occurs on exit because magnet is moving fastest. - t2 is smaller due to greater speed. ...
Page|1 - askIITians
... Among the following statements, the incorrect statement is A. The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of straight lines which indicates that the magnetic field is the same at all points inside the solenoid B. The strong magnetic field produced inside the solenoid can be used to magnetise ...
... Among the following statements, the incorrect statement is A. The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of straight lines which indicates that the magnetic field is the same at all points inside the solenoid B. The strong magnetic field produced inside the solenoid can be used to magnetise ...
P - LSU Physics
... The Transformer The transformer is a device that can change the voltage amplitude of any ac signal. It consists of two coils with a different number of turns wound around a common iron core. The coil on which we apply the voltage to be changed is called the "primary" and it has N P turns. The trans ...
... The Transformer The transformer is a device that can change the voltage amplitude of any ac signal. It consists of two coils with a different number of turns wound around a common iron core. The coil on which we apply the voltage to be changed is called the "primary" and it has N P turns. The trans ...
- School Corner
... – a ferrimagnetic material is one in which the magnetic moment of the atoms on different sublattices are opposed, as in antiferromagnetism; however, in ferrimagnetic materials, the opposing moments are unequal and a spontaneous magnetization remains. METAMAGNETISM – is the increase in the magnetizat ...
... – a ferrimagnetic material is one in which the magnetic moment of the atoms on different sublattices are opposed, as in antiferromagnetism; however, in ferrimagnetic materials, the opposing moments are unequal and a spontaneous magnetization remains. METAMAGNETISM – is the increase in the magnetizat ...
Chapter 11
... coil, the total resistance may be significant • The inherent resistance is called the dc resistance or the winding resistance (RW) • When two conductors are placed side-by-side, there is always some capacitance between them • When many turns of wire are placed close together in a coil, there is a wi ...
... coil, the total resistance may be significant • The inherent resistance is called the dc resistance or the winding resistance (RW) • When two conductors are placed side-by-side, there is always some capacitance between them • When many turns of wire are placed close together in a coil, there is a wi ...
Chapter 11 - Inductors
... coil, the total resistance may be significant • The inherent resistance is called the dc resistance or the winding resistance (RW) • When two conductors are placed side-by-side, there is always some capacitance between them • When many turns of wire are placed close together in a coil, there is a wi ...
... coil, the total resistance may be significant • The inherent resistance is called the dc resistance or the winding resistance (RW) • When two conductors are placed side-by-side, there is always some capacitance between them • When many turns of wire are placed close together in a coil, there is a wi ...
Magnetism
... removed. It's as if the domains were forced to move against an internal friction among the atoms of the magnetic material. This effect is called hysteresis. The word hysteresis means "to lag behind," which describes how the change in B lags behind the change in H. We can now reverse the current thro ...
... removed. It's as if the domains were forced to move against an internal friction among the atoms of the magnetic material. This effect is called hysteresis. The word hysteresis means "to lag behind," which describes how the change in B lags behind the change in H. We can now reverse the current thro ...
Exam 2 Solutions
... The parallel combination yields a resistance of 4 Ω and thus the total resistance is 6.0 Ω. The total current is thus 24 / 6.0 = 4 A. To find the current in the 6 Ω branch, first find the voltage across it, which is the same as the voltage across the parallel combination. This voltage is determined ...
... The parallel combination yields a resistance of 4 Ω and thus the total resistance is 6.0 Ω. The total current is thus 24 / 6.0 = 4 A. To find the current in the 6 Ω branch, first find the voltage across it, which is the same as the voltage across the parallel combination. This voltage is determined ...
Flux Displacement in Rectangular Iron Sheets and Geometry
... LECTRIC MACHINES are subject to various sources of loss, the most prominent being conduction loss and iron loss. Conduction loss is reliably quantifiable, whereas iron loss is still subject to great uncertainty when designing an electrical machine. As conduction loss is the major loss source in elec ...
... LECTRIC MACHINES are subject to various sources of loss, the most prominent being conduction loss and iron loss. Conduction loss is reliably quantifiable, whereas iron loss is still subject to great uncertainty when designing an electrical machine. As conduction loss is the major loss source in elec ...