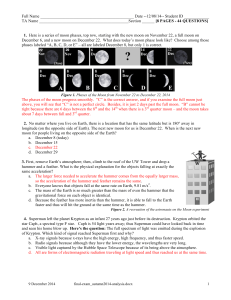
b. false - UW Canvas
... good representation of how stars “work,” we would conclude that a. the hotter the star is, the more luminous it is, and the brighter the colors will be overall. b. the cooler the star, the less luminous it is; the brighter part of the spectrum will be toward longer wavelengths. c. the luminosity of ...
... good representation of how stars “work,” we would conclude that a. the hotter the star is, the more luminous it is, and the brighter the colors will be overall. b. the cooler the star, the less luminous it is; the brighter part of the spectrum will be toward longer wavelengths. c. the luminosity of ...
Alpha Centauri 3
... elliptical orbit (e= 0.52) that takes almost 80 (79.90) years to complete and are inclined at an angle of 79.23° from the perspective of an observer on Earth (see Pourbaix et al, 2002, or 2000 in the Sixth Catalog of Orbits of Visual Binaries; and Worley and Heintz, 1983). As viewed from a hypotheti ...
... elliptical orbit (e= 0.52) that takes almost 80 (79.90) years to complete and are inclined at an angle of 79.23° from the perspective of an observer on Earth (see Pourbaix et al, 2002, or 2000 in the Sixth Catalog of Orbits of Visual Binaries; and Worley and Heintz, 1983). As viewed from a hypotheti ...
Page pour l`impression
... There is a resonance of order n/m, where n and m are two integers, if a planet makes n revolutions when the other one makes m revolutions. In Neptune's rings, the edge of the Adams ring is in a resonance 42:43 with the satellite Galatea. Resonances between the rotation motion of a body and its revol ...
... There is a resonance of order n/m, where n and m are two integers, if a planet makes n revolutions when the other one makes m revolutions. In Neptune's rings, the edge of the Adams ring is in a resonance 42:43 with the satellite Galatea. Resonances between the rotation motion of a body and its revol ...
Chapter 20
... helium flash before the star is once again in equilibrium. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... helium flash before the star is once again in equilibrium. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Learning About Stars
... camera was left on to record the movement of the stars. The North Star doesn’t appear blurry or have a trail because it is in the same position the whole time. ...
... camera was left on to record the movement of the stars. The North Star doesn’t appear blurry or have a trail because it is in the same position the whole time. ...
OUR COSMIC NEIGHBORS Story of the Stars
... A long winding stream of stars was placed by primitive man at the “top of the sky.” According to a Greek legend, Draco represents the Dragon that guarded the Golden Apples in the Garden of Hesperides. This dragon was finally killed by Hercules and was placed in the sky in a position where it would n ...
... A long winding stream of stars was placed by primitive man at the “top of the sky.” According to a Greek legend, Draco represents the Dragon that guarded the Golden Apples in the Garden of Hesperides. This dragon was finally killed by Hercules and was placed in the sky in a position where it would n ...
May 2010 - Pomona Valley Amateur Astronomers
... them up and gives the reason to the fact that the huge amounts of gases are believed to be the formation of a skewed ring of stars, which would facilitate the flow of gas, by sapping its speed so that it spirals in towards the back hole. It has been a mystery on how enough matter can reach these cos ...
... them up and gives the reason to the fact that the huge amounts of gases are believed to be the formation of a skewed ring of stars, which would facilitate the flow of gas, by sapping its speed so that it spirals in towards the back hole. It has been a mystery on how enough matter can reach these cos ...
Time From the Perspective of a Particle Physicist
... What to Remember - EW • What time during the day a star rises, is overhead, and sets changes with the seasons • look up on Star Chart (right ascension is the EastWest location) • Changes 2 hours/month • Only on the Equator can all stars be viewed from a single location Hawaii or northern Chile a ...
... What to Remember - EW • What time during the day a star rises, is overhead, and sets changes with the seasons • look up on Star Chart (right ascension is the EastWest location) • Changes 2 hours/month • Only on the Equator can all stars be viewed from a single location Hawaii or northern Chile a ...
Dear Leif - LEIF.org
... term that Wolff and Patrone retain as being dominant; in a radiative zone it is likely to be 10^5 times greater than that (I have not bothered to estimate the factors carefully -- it is hardly necessary). This is in stark contrast to the imaginary stars considered by the authors. I have not read on ...
... term that Wolff and Patrone retain as being dominant; in a radiative zone it is likely to be 10^5 times greater than that (I have not bothered to estimate the factors carefully -- it is hardly necessary). This is in stark contrast to the imaginary stars considered by the authors. I have not read on ...
1. Introduction
... In parallel with these developments, it has come to be realized that some, and probably very many, stars pulsate in more complicated manners than the Cepheids. In many instances more than one mode of oscillation is excited simultaneously in a star; these modes may include both radial overtones, in a ...
... In parallel with these developments, it has come to be realized that some, and probably very many, stars pulsate in more complicated manners than the Cepheids. In many instances more than one mode of oscillation is excited simultaneously in a star; these modes may include both radial overtones, in a ...
Dear Leif - LEIF.org
... term that Wolff and Patrone retain as being dominant; in a radiative zone it is likely to be 10^5 times greater than that (I have not bothered to estimate the factors carefully -- it is hardly necessary). This is in stark contrast to the imaginary stars considered by the authors. I have not read on ...
... term that Wolff and Patrone retain as being dominant; in a radiative zone it is likely to be 10^5 times greater than that (I have not bothered to estimate the factors carefully -- it is hardly necessary). This is in stark contrast to the imaginary stars considered by the authors. I have not read on ...
The Life And Times Of A Star
... The supergiants are also stars near the end of their lives. They have run out of hydrogen fuel in their cores. They are high mass (more than 8 solar masses). They are very large (R = 100 to 1,000) and extremely bright (L = 10,000 to 1,000,000). ...
... The supergiants are also stars near the end of their lives. They have run out of hydrogen fuel in their cores. They are high mass (more than 8 solar masses). They are very large (R = 100 to 1,000) and extremely bright (L = 10,000 to 1,000,000). ...
12/08/14-- Student ID ______ TA Name
... 24. This galaxy looks yellow-orange because there has been no star formation for a very long time. 25. These types of galaxy are likely to have on-going formation of massive stars a. elliptical, barred spiral, and irregular b. irregular and barred spiral only c. irregular, barred spiral and spiral d ...
... 24. This galaxy looks yellow-orange because there has been no star formation for a very long time. 25. These types of galaxy are likely to have on-going formation of massive stars a. elliptical, barred spiral, and irregular b. irregular and barred spiral only c. irregular, barred spiral and spiral d ...
TOOLS IN ASTRONOMY SPECTROSCOPY
... seen could be simply and naturally accounted for topographically, rendering the prevailing theory at the time, that the variations in light arose from something inside a perfect sphere, a cumbersome and unappealing alternative. 5. At half moon, a little geometry is enough to calculate the heights! G ...
... seen could be simply and naturally accounted for topographically, rendering the prevailing theory at the time, that the variations in light arose from something inside a perfect sphere, a cumbersome and unappealing alternative. 5. At half moon, a little geometry is enough to calculate the heights! G ...
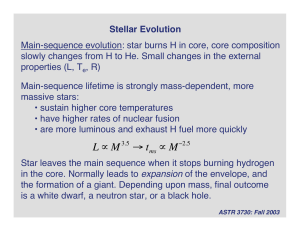
Stellar Evolution
... Explain why stars evolve off the main sequence. What happens when they leave the main sequence? How does mass affect what happens? How do stars die? Where does gold come from? ...
... Explain why stars evolve off the main sequence. What happens when they leave the main sequence? How does mass affect what happens? How do stars die? Where does gold come from? ...
The Galaxy–Dark Matter Connection
... Satellites more concentrated than centrals @ fixed stellar mass. However: Fraction of galaxies with C>3 ~ is the same! Ellipticals are not produced by environmental processes acting on satellites ...
... Satellites more concentrated than centrals @ fixed stellar mass. However: Fraction of galaxies with C>3 ~ is the same! Ellipticals are not produced by environmental processes acting on satellites ...
Lecture 30
... • Core contracts, heats up • Helium burning stars • If star is massive enough, sequence repeats for carbon burning, then oxygen, silicon etc… Dominant observational signature of post-main-sequence evolution is rapid expansion of the envelope to form a red giant star. ...
... • Core contracts, heats up • Helium burning stars • If star is massive enough, sequence repeats for carbon burning, then oxygen, silicon etc… Dominant observational signature of post-main-sequence evolution is rapid expansion of the envelope to form a red giant star. ...
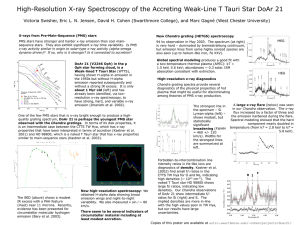
DoAr21_AAS2005 - Astronomy at Swarthmore College
... 2001) and HD 98800, which is a naked T Tauri star that has x-ray properties similar to main-sequence stars (Kastner et al. 2003). ...
... 2001) and HD 98800, which is a naked T Tauri star that has x-ray properties similar to main-sequence stars (Kastner et al. 2003). ...
2011 - Edexcel
... 5 (a) The planet Saturn is well-known for its prominent ring system. Name two other planets that have ring systems. ...
... 5 (a) The planet Saturn is well-known for its prominent ring system. Name two other planets that have ring systems. ...
AST1001.ch13
... — Use orbital properties of companion — Measure velocity and distance of orbiting gas • It’s a black hole if it’s not a star and its mass exceeds the neutron star limit (~3 MSun). ...
... — Use orbital properties of companion — Measure velocity and distance of orbiting gas • It’s a black hole if it’s not a star and its mass exceeds the neutron star limit (~3 MSun). ...
Tips on taking Astro sights
... two position lines are obtained from shore objects, her position is called a 'fix.' If they are obtained from heavenly bodies, it is called an 'observed position.' The distinction is made because a position ...
... two position lines are obtained from shore objects, her position is called a 'fix.' If they are obtained from heavenly bodies, it is called an 'observed position.' The distinction is made because a position ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.