Lab PDF - NMSU Astronomy
... Before this question could be answered, astronomers had to learn to distinguish stable, wellbehaved stars from their more erratic, very young or very old neighbors. They did this by plotting two basic observed quantities (brightness and color) against each other, forming a plot called a Hertzsprung ...
... Before this question could be answered, astronomers had to learn to distinguish stable, wellbehaved stars from their more erratic, very young or very old neighbors. They did this by plotting two basic observed quantities (brightness and color) against each other, forming a plot called a Hertzsprung ...
Open access - ORBi
... One of the most interesting results of the FLUOR survey so far is the possible correlation between the presence of cold dust and hot dust for solar-type stars. Another interesting result is the difference in hot exozodi occurence rate between A-type stars and solar-type stars. In order to explore the ...
... One of the most interesting results of the FLUOR survey so far is the possible correlation between the presence of cold dust and hot dust for solar-type stars. Another interesting result is the difference in hot exozodi occurence rate between A-type stars and solar-type stars. In order to explore the ...
H. Other Methods of Determining Stellar Distances
... the Solar System • From there, it was a matter of simple geometry to calculate the planet’s distance from the Sun compared to the Earth’s. ...
... the Solar System • From there, it was a matter of simple geometry to calculate the planet’s distance from the Sun compared to the Earth’s. ...
Polaris
... Polaris science. The single point of light that we see as Polaris is actually a triple star system, or three stars orbiting a common center of mass. The primary star, Polaris A, is a supergiant with about six times the mass of our sun. A close companion, Polaris Ab, orbits 2 billion miles from Polar ...
... Polaris science. The single point of light that we see as Polaris is actually a triple star system, or three stars orbiting a common center of mass. The primary star, Polaris A, is a supergiant with about six times the mass of our sun. A close companion, Polaris Ab, orbits 2 billion miles from Polar ...
Globular Clusters Dynamic Lives The
... extension of the main sequence past the cluster’s turnoff point.) Soon the helium core ignites, and the star sheds some of its envelope and enters the horizontal branch. Those that have lost only a moderate amount of mass as red giants end up on the red horizontal branch, while those that have lost ...
... extension of the main sequence past the cluster’s turnoff point.) Soon the helium core ignites, and the star sheds some of its envelope and enters the horizontal branch. Those that have lost only a moderate amount of mass as red giants end up on the red horizontal branch, while those that have lost ...
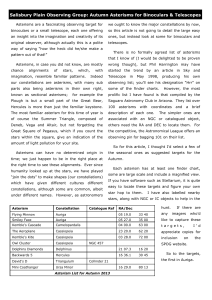
Autumn Asterisms for binoculars 2013
... (the Giraffe) is not one of the brightest constellations, but the Cascade is one of its showpiece objects, with the open cluster NGC 1502 to its end. It is an easy object in binoculars and a favourite of mine. You can find it by taking a line from Capella in Auriga ...
... (the Giraffe) is not one of the brightest constellations, but the Cascade is one of its showpiece objects, with the open cluster NGC 1502 to its end. It is an easy object in binoculars and a favourite of mine. You can find it by taking a line from Capella in Auriga ...
The Origin, Structure, and Evolution of the Stars
... in our galaxy and revolves in an orbit around the galactic center in a period of approximately 200 million years. Although the total number of stars in the galaxy is very large, the average distance between them (4 light-years) is very great. Let us assume for a moment that we can shrink the stars d ...
... in our galaxy and revolves in an orbit around the galactic center in a period of approximately 200 million years. Although the total number of stars in the galaxy is very large, the average distance between them (4 light-years) is very great. Let us assume for a moment that we can shrink the stars d ...
01 - University of Warwick
... sun-like stars, most with ages ranging from 3 million to 30 have already formed in these young solar system analogs, or they never will,” Meyer said. million years. Astronomers suspect that gas around a star may also be important for sending terrestrial, or rocky, planets like Earth The scientists u ...
... sun-like stars, most with ages ranging from 3 million to 30 have already formed in these young solar system analogs, or they never will,” Meyer said. million years. Astronomers suspect that gas around a star may also be important for sending terrestrial, or rocky, planets like Earth The scientists u ...
The Distances to the Stars
... Note that measuring such motions requires the existence of a fixed reference frame, provided by celestial objects whose motions are not detectable. Usually very distant stars will do, but for the most accurate astrometry astronomers use distant galaxies or quasars as reference points. Two thousand y ...
... Note that measuring such motions requires the existence of a fixed reference frame, provided by celestial objects whose motions are not detectable. Usually very distant stars will do, but for the most accurate astrometry astronomers use distant galaxies or quasars as reference points. Two thousand y ...
Great Migrations & other natural history tales
... Accretion disks are often found in close, interacting pairs of stars, such as the cataclysmic variables (CVs). One star, originally more massive, evolves to a compact companion: a white dwarf or perhaps a neutron star (pulsar) or a black hole. The other, originally less massive, star bloats toward ...
... Accretion disks are often found in close, interacting pairs of stars, such as the cataclysmic variables (CVs). One star, originally more massive, evolves to a compact companion: a white dwarf or perhaps a neutron star (pulsar) or a black hole. The other, originally less massive, star bloats toward ...
Celestial Sphere
... Celestial Sphere surrounding Earth aids in thinking about the position and motion of the sky ...
... Celestial Sphere surrounding Earth aids in thinking about the position and motion of the sky ...
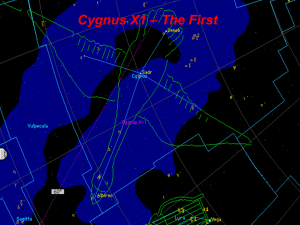
Cygnus X-1
... light years away from earth. So this means that what we are seeing, is many, many, years old. It is a very inconsistent source for X-ray emissions. The emissions of X-rays for Cygnus X-1 flicker in hundredth of a second bursts. It is also been proven that Cygnus X-1 is smaller than the Earth. Strang ...
... light years away from earth. So this means that what we are seeing, is many, many, years old. It is a very inconsistent source for X-ray emissions. The emissions of X-rays for Cygnus X-1 flicker in hundredth of a second bursts. It is also been proven that Cygnus X-1 is smaller than the Earth. Strang ...
Test Ch. 27 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes
... 25. In the last stage of stellar evolution following a supernova, stars too massive to form neutron stars may form a A. black dwarf. B. red supergiant. C. white dwarf. D. black hole. 26. In which stage of stellar evolution does combined hydrogen fusion and helium fusion cause a star’s outer shell to ...
... 25. In the last stage of stellar evolution following a supernova, stars too massive to form neutron stars may form a A. black dwarf. B. red supergiant. C. white dwarf. D. black hole. 26. In which stage of stellar evolution does combined hydrogen fusion and helium fusion cause a star’s outer shell to ...
The Origin of the Milky Way
... a huge disk, and a galactic halo surrounding both. • The diameter of the disk is 30kpc (100,000 light years). • The thickness of the disk is only 300pc (1000 light years) on average. • The total detectable mass is 200 billion solar masses. ...
... a huge disk, and a galactic halo surrounding both. • The diameter of the disk is 30kpc (100,000 light years). • The thickness of the disk is only 300pc (1000 light years) on average. • The total detectable mass is 200 billion solar masses. ...
SPECIAL REPORT
... and Saturn. That’s a problem because most of the more than 200 exoplanets astronomers know about are also giants. ...
... and Saturn. That’s a problem because most of the more than 200 exoplanets astronomers know about are also giants. ...
Procedurally Generating an Artificial Galaxy
... generating the trees themselves and place them in natural formations. The main benefit of procedurally generating something rather than making it yourself is quantity. For an artist, every tree takes time to create and place in a scene. With procedural generation, the time investment is restricted t ...
... generating the trees themselves and place them in natural formations. The main benefit of procedurally generating something rather than making it yourself is quantity. For an artist, every tree takes time to create and place in a scene. With procedural generation, the time investment is restricted t ...
Booklet 5 – Stellar Processes and Evolution
... mass allows stellar collapse to take place and the outer layers to reignite. A cross section through the star at this point would show an outer shell of hydrogen burning, an inner shell of helium burning and the core, where there is now sufficient energy for the carbon to fuse with helium into oxyge ...
... mass allows stellar collapse to take place and the outer layers to reignite. A cross section through the star at this point would show an outer shell of hydrogen burning, an inner shell of helium burning and the core, where there is now sufficient energy for the carbon to fuse with helium into oxyge ...
Into the sub-mm
... points of emission at the tips of the fingers. Although it is too early to say conclusively what the emission signifies, it is possibile that these mark the earliest phase of star formation. Modelling of the chemistry and dynamics of the finger-tip condensations has begun. The final presentation of ...
... points of emission at the tips of the fingers. Although it is too early to say conclusively what the emission signifies, it is possibile that these mark the earliest phase of star formation. Modelling of the chemistry and dynamics of the finger-tip condensations has begun. The final presentation of ...
The Sky
... Western culture originated in Mesopotamia over 5,000 years ago. – Other constellations were added by Babylonian, Egyptian, and Greek astronomers during the classical age. – Of these ancient constellations, 48 are still in use. ...
... Western culture originated in Mesopotamia over 5,000 years ago. – Other constellations were added by Babylonian, Egyptian, and Greek astronomers during the classical age. – Of these ancient constellations, 48 are still in use. ...
Using color photometry to separate transiting exoplanets from false
... limitations of the radial velocity technique. Of the 59 candidates that were identified during the 2001 campaign of OGLEIII, 7 were considered too faint for follow-up observation and only 6 of the remaining candidates had radial velocity variations less than a few km s−1 and no sign of secondary tra ...
... limitations of the radial velocity technique. Of the 59 candidates that were identified during the 2001 campaign of OGLEIII, 7 were considered too faint for follow-up observation and only 6 of the remaining candidates had radial velocity variations less than a few km s−1 and no sign of secondary tra ...
CW9_MOST_GSphot_RK_v1
... • exposure time is usually 1.5 sec (range from 0.3 to 1.5 applied) • no images are recovered, the image data is processed on board: a mean background value is removed and the signal is the sum of high signal pixels (exceeding the background and a 20 ADU threshold) • for the brightest guide stars noi ...
... • exposure time is usually 1.5 sec (range from 0.3 to 1.5 applied) • no images are recovered, the image data is processed on board: a mean background value is removed and the signal is the sum of high signal pixels (exceeding the background and a 20 ADU threshold) • for the brightest guide stars noi ...
File - Science Website
... Describe, in as much detail as you can, what forces allow a stable star to exist and how the star may eventually form a black hole. To gain full marks in this question you should write your ideas in good English. Put them into a sensible order and use the correct scientific words. ...
... Describe, in as much detail as you can, what forces allow a stable star to exist and how the star may eventually form a black hole. To gain full marks in this question you should write your ideas in good English. Put them into a sensible order and use the correct scientific words. ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.