– 1 – 1. Cosmochronology
... of white dwarfs in clusters. These have no or very little nuclear activity, their luminosity instead comes from the slowly cooling interiors. The luminosity depends on the cooling rate. Thus the distribution with luminosity of a population of white dwarfs such as is found in old globular clusters ca ...
... of white dwarfs in clusters. These have no or very little nuclear activity, their luminosity instead comes from the slowly cooling interiors. The luminosity depends on the cooling rate. Thus the distribution with luminosity of a population of white dwarfs such as is found in old globular clusters ca ...
Upcoming Events
... When you think about the new stars forming in the Milky Way, you probably think of the giant star-forming regions like the Orion Nebula, containing thousands of new stars with light so bright it's visible to the naked eye. At over 400 parsecs (1,300 light years) distant, it's one of the most spectac ...
... When you think about the new stars forming in the Milky Way, you probably think of the giant star-forming regions like the Orion Nebula, containing thousands of new stars with light so bright it's visible to the naked eye. At over 400 parsecs (1,300 light years) distant, it's one of the most spectac ...
Name:
... CONTINUOUS spectrum shown in the spectrometer. Note that hot glowing solids, liquids, or high-density gases (such as found on the surface of a star) will produce a spectrum that contains all the ROY G. BIV colors and everything in between. CONTINUOUS SPECTRUM The CONTINUOUS spectrum is caused by gas ...
... CONTINUOUS spectrum shown in the spectrometer. Note that hot glowing solids, liquids, or high-density gases (such as found on the surface of a star) will produce a spectrum that contains all the ROY G. BIV colors and everything in between. CONTINUOUS SPECTRUM The CONTINUOUS spectrum is caused by gas ...
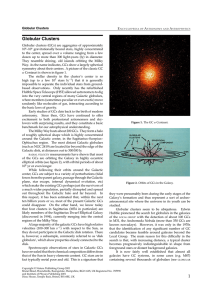
Globular Clusters
... out throughout the Galactic halo and far beyond. In this respect, it has been estimated that, within the next ten billion years or so, most of the present Galactic GCs could disappear. On the other hand, we know today that four clusters in Sagittarius (M54 in particular) are likely members of the Sa ...
... out throughout the Galactic halo and far beyond. In this respect, it has been estimated that, within the next ten billion years or so, most of the present Galactic GCs could disappear. On the other hand, we know today that four clusters in Sagittarius (M54 in particular) are likely members of the Sa ...
Name: Three Views Spectrum Simulation This simulation uses the
... CONTINUOUS spectrum shown in the spectrometer. Note that hot glowing solids, liquids, or high-density gases (such as found on the surface of a star) will produce a spectrum that contains all the ROY G. BIV colors and everything in between. CONTINUOUS SPECTRUM The CONTINUOUS spectrum is caused by gas ...
... CONTINUOUS spectrum shown in the spectrometer. Note that hot glowing solids, liquids, or high-density gases (such as found on the surface of a star) will produce a spectrum that contains all the ROY G. BIV colors and everything in between. CONTINUOUS SPECTRUM The CONTINUOUS spectrum is caused by gas ...
Binary Beauties: By John R - Black River Astronomical Society
... rotating the filter at the eyepiece or camera, the object's reflective properties can be manipulated to produce artificial color and increased contrast. The second polarized filter type is comprised of two layers of polarized material. The 2nd layer is mounted immediately above the 1st and is meant ...
... rotating the filter at the eyepiece or camera, the object's reflective properties can be manipulated to produce artificial color and increased contrast. The second polarized filter type is comprised of two layers of polarized material. The 2nd layer is mounted immediately above the 1st and is meant ...
AN ATTEMPT To prove the MOTION OF THE EARTH FROM
... observations were lyable to. As first from the shrinking and stretching of the materials wherewith their Instruments were made, I conceive a much greater angle then that of a minute may be mistaken in taking an altitude of fifty Degrees.For if the Instruments be made of Wood, 'tis manifest that moys ...
... observations were lyable to. As first from the shrinking and stretching of the materials wherewith their Instruments were made, I conceive a much greater angle then that of a minute may be mistaken in taking an altitude of fifty Degrees.For if the Instruments be made of Wood, 'tis manifest that moys ...
Observational properties of stars
... any ways). So we’ll just always make the assumption that the black body temperature is fine and we’ll just use that (so you’ll only see T and we’re not bothering with the “eff”). 2. Observed Properties of Stars 2.1 Apparent and Absolute Magnitudes When you observe a star you are often missing a larg ...
... any ways). So we’ll just always make the assumption that the black body temperature is fine and we’ll just use that (so you’ll only see T and we’re not bothering with the “eff”). 2. Observed Properties of Stars 2.1 Apparent and Absolute Magnitudes When you observe a star you are often missing a larg ...
Asteroseismic constraints on Asymmetric Dark Matter: Light particles
... best stellar laboratory for constraining DM. Nevertheless, many good laboratories are sometimes statistically more relevant than an excellent one. Kepler observed many stars showing a large number of detected oscillation modes [51]. From this set, interesting candidates for modelling have stellar fu ...
... best stellar laboratory for constraining DM. Nevertheless, many good laboratories are sometimes statistically more relevant than an excellent one. Kepler observed many stars showing a large number of detected oscillation modes [51]. From this set, interesting candidates for modelling have stellar fu ...
a MS Word version.
... 16. Describe the Hubble galaxy classification scheme. Why is a graphical representation of this galaxy classification scheme called the "tuning fork diagram"? Describe the different galaxy types and subclasses in the Hubble classification scheme. What types of galaxies are not covered by the Hubble ...
... 16. Describe the Hubble galaxy classification scheme. Why is a graphical representation of this galaxy classification scheme called the "tuning fork diagram"? Describe the different galaxy types and subclasses in the Hubble classification scheme. What types of galaxies are not covered by the Hubble ...
black hole
... dwarfs. When you surveyed the stars, you learned that white dwarfs are the second most common kind of star. (Only red dwarfs are more abundant.) The billions of white dwarfs in our galaxy must be the remains of medium-mass stars. ...
... dwarfs. When you surveyed the stars, you learned that white dwarfs are the second most common kind of star. (Only red dwarfs are more abundant.) The billions of white dwarfs in our galaxy must be the remains of medium-mass stars. ...
Bayesian mass and age estimates for transiting exoplanet host stars⋆
... more sensitive to the change in radius of a star as it evolves away from the main sequence. However, precise stellar densities can also cause problems because the broad sampling in mass, age and metallicity used for many grids of stellar models can produce poor sampling of the observed parameter spa ...
... more sensitive to the change in radius of a star as it evolves away from the main sequence. However, precise stellar densities can also cause problems because the broad sampling in mass, age and metallicity used for many grids of stellar models can produce poor sampling of the observed parameter spa ...
A Comparison of CCD Images Taken with Different Cameras Abstract
... Comparison of Images from the Different CCDs Comparison of the last three images is not straightforward for a couple of reasons. The three images are taken with different filters and with CCDs which differ in sensitivity as a function of wavelength. Equipment setup differed as did exposure time. Non ...
... Comparison of Images from the Different CCDs Comparison of the last three images is not straightforward for a couple of reasons. The three images are taken with different filters and with CCDs which differ in sensitivity as a function of wavelength. Equipment setup differed as did exposure time. Non ...
Document
... The Hertzsprung–Russell Diagram The story may be said to begin at Harvard College Observatory in the 1880s when E. C. Pickering and Annie Cannon began to analyse the emission spectra of the visible stars. The stars they examined were placed into several ‘spectral classes’, each class being designate ...
... The Hertzsprung–Russell Diagram The story may be said to begin at Harvard College Observatory in the 1880s when E. C. Pickering and Annie Cannon began to analyse the emission spectra of the visible stars. The stars they examined were placed into several ‘spectral classes’, each class being designate ...
OSP2016Level 3 Map - Oregon Star Party
... What is it? V404 Cyg is a black hole (12+/- 3 solar masses) with late K or early G type stellar companion that’s slightly smaller than the Sun, orbiting each other in less than 6.5 days. They are approximately 7800 light years away. Why you want to see it: The stellar companion is distorted into a ...
... What is it? V404 Cyg is a black hole (12+/- 3 solar masses) with late K or early G type stellar companion that’s slightly smaller than the Sun, orbiting each other in less than 6.5 days. They are approximately 7800 light years away. Why you want to see it: The stellar companion is distorted into a ...
Properties of Ellipticals and Spirals
... Velocity dispersions are responsible for the overall shape of galaxies. Oblate and Prolate Ellipticals – how that? Spiral: Velocities of stars in spirals are more ordered. Stars rotate around the galactic center in a disk surrounding it – Halo is random. Spiral galaxies are flattened by rotation (el ...
... Velocity dispersions are responsible for the overall shape of galaxies. Oblate and Prolate Ellipticals – how that? Spiral: Velocities of stars in spirals are more ordered. Stars rotate around the galactic center in a disk surrounding it – Halo is random. Spiral galaxies are flattened by rotation (el ...
Properties of Stars - Montana State University Extended University
... representative sample includes all parts of the population of the objects your are investigating in their proper proportions. The relative proportion of common things will be greater than the relative proportions of rare things. In fact, the uncommon things may not be found in a small representative ...
... representative sample includes all parts of the population of the objects your are investigating in their proper proportions. The relative proportion of common things will be greater than the relative proportions of rare things. In fact, the uncommon things may not be found in a small representative ...
SkyWatcher - Boise Astronomical Society
... Venus, Mars, and Neptune can be seen in the west and Uranus in the southwest in the evening sky. Jupiter is in the southeast at midnight. In the morning sky, Mercury and Saturn lie in the southeast and Jupiter in the southwest. Mercury is present low in the morning sky for most of the month. It brig ...
... Venus, Mars, and Neptune can be seen in the west and Uranus in the southwest in the evening sky. Jupiter is in the southeast at midnight. In the morning sky, Mercury and Saturn lie in the southeast and Jupiter in the southwest. Mercury is present low in the morning sky for most of the month. It brig ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.