tut35 Magnitudes
... The IAU has defined a plutoid as a “dwarf planet” with a semi-major axis greater than Neptune. It is usually impossible to optically determine if distant KBOs are in hydrostatic equilibrium (round). The IAU assumes an object is a plutoid if its absolute magnitude, H, is +1 or brighter. Using equatio ...
... The IAU has defined a plutoid as a “dwarf planet” with a semi-major axis greater than Neptune. It is usually impossible to optically determine if distant KBOs are in hydrostatic equilibrium (round). The IAU assumes an object is a plutoid if its absolute magnitude, H, is +1 or brighter. Using equatio ...
Conference Abstract Booklet here.
... the Hubble Source Catalog (HSC) which includes 107 objects detected with WFPC2, ACS, and WFC3 instruments in at least one visit. The lightcurves extracted from the HSC are corrected for systematic effects by applying local zero-point corrections and are screened for bad measurements. For each lightc ...
... the Hubble Source Catalog (HSC) which includes 107 objects detected with WFPC2, ACS, and WFC3 instruments in at least one visit. The lightcurves extracted from the HSC are corrected for systematic effects by applying local zero-point corrections and are screened for bad measurements. For each lightc ...
Life and Death of Stars - UM Research Repository
... following y this explanations: Birth of Stars: Stars are born in giant clouds of dust and gas. Sometimes cloud shrinks because of gravity. The shrinking cloud becomes hotter until it is hot enough to produce a nuclear reaction at the core, then a star called is born. This stage is the earliest phase ...
... following y this explanations: Birth of Stars: Stars are born in giant clouds of dust and gas. Sometimes cloud shrinks because of gravity. The shrinking cloud becomes hotter until it is hot enough to produce a nuclear reaction at the core, then a star called is born. This stage is the earliest phase ...
Galaxies – Island universes
... • Galaxies form from collisions of proto-galactic clumps in the first billion years or so after the Big Bang • Many have later infalling matter which has been pulled on by nearby mass and thus doesn’t fall straight in. It settles into a rotating disk, arranging itself into a flat, roughly circularly ...
... • Galaxies form from collisions of proto-galactic clumps in the first billion years or so after the Big Bang • Many have later infalling matter which has been pulled on by nearby mass and thus doesn’t fall straight in. It settles into a rotating disk, arranging itself into a flat, roughly circularly ...
Lec2015_22
... • A number of models have suggested that IMF would be skewed to much higher masses under such conditions – “Top heavy” • If low mass stars were formed, they should be detectable today • If only high-mass stars formed, then no Population III now but study of extreme Population II stars could reveal m ...
... • A number of models have suggested that IMF would be skewed to much higher masses under such conditions – “Top heavy” • If low mass stars were formed, they should be detectable today • If only high-mass stars formed, then no Population III now but study of extreme Population II stars could reveal m ...
main sequence stars of a open cluster
... viewing so that you can see faint stars as well. Magnifying by two may help you work easily. Find Zoom up icon in the upper left of the Makali`i window; it has a picture of magnifier with a plus mark. Clicking once the icon makes the image size twice. But you can not see the whole area at a time, so ...
... viewing so that you can see faint stars as well. Magnifying by two may help you work easily. Find Zoom up icon in the upper left of the Makali`i window; it has a picture of magnifier with a plus mark. Clicking once the icon makes the image size twice. But you can not see the whole area at a time, so ...
SGL 9 NGC Galaxy magnitude 9/10 observing challenge Up for
... Object 3 – Leo triplet (Taki page 50) No not the famous one. Look half way between delta and theta Leo and then a fraction left. This group NGC3605 / NGC 3607 and NGC 3608 are part of the Leo II group of galaxies. NGC 3605 is however in the background and NGC 3607/8 (both magnitude 9) are interactin ...
... Object 3 – Leo triplet (Taki page 50) No not the famous one. Look half way between delta and theta Leo and then a fraction left. This group NGC3605 / NGC 3607 and NGC 3608 are part of the Leo II group of galaxies. NGC 3605 is however in the background and NGC 3607/8 (both magnitude 9) are interactin ...
Physics of Star Formation: Milky Way and Beyond
... Javier Ballesteros-Paredes - Gravity or Turbulence? On the origin of molecular clouds non-thermal motions The so-called Larson scaling laws found empirically in molecular clouds (MCs) have been generally interpreted as one of the main evidences that the clouds are turbulent, that such turbulence is ...
... Javier Ballesteros-Paredes - Gravity or Turbulence? On the origin of molecular clouds non-thermal motions The so-called Larson scaling laws found empirically in molecular clouds (MCs) have been generally interpreted as one of the main evidences that the clouds are turbulent, that such turbulence is ...
The colours of the Universe, the amateur astronomical spectroscopy.
... from Rspec's library at the graph which was generated in RSpec program. The main emission lines in my comet's C/2014 Q2 Lovejoy spectrum are spectral lines C2, CN, NH2, CH+, CH, CO+. Clearly visible are molecular carbon lines C 2 and cyanide CN, which are located near 4700 i 5100 Å, which are respon ...
... from Rspec's library at the graph which was generated in RSpec program. The main emission lines in my comet's C/2014 Q2 Lovejoy spectrum are spectral lines C2, CN, NH2, CH+, CH, CO+. Clearly visible are molecular carbon lines C 2 and cyanide CN, which are located near 4700 i 5100 Å, which are respon ...
compound sentences
... 1. Connor had seen many parks in his life, but he never had seen a park like this one. 2. Dad brought a pair of binoculars, and Nate used them to look for animals. 3. He saw his first live bear, and the hair stood up on his arms. 4. It was an exciting moment, but it only lasted a second. ...
... 1. Connor had seen many parks in his life, but he never had seen a park like this one. 2. Dad brought a pair of binoculars, and Nate used them to look for animals. 3. He saw his first live bear, and the hair stood up on his arms. 4. It was an exciting moment, but it only lasted a second. ...
THE PHYSICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THE STARS 1
... therefore the absolute individual masses can be derived. The double-lined eclipsing binaries are extremely important, since they are the only case providing simultaneous determinations of individual masses and radii (see Sect. 3). The best reached precisions are of the order of 1-5% ([27], [4]). Suc ...
... therefore the absolute individual masses can be derived. The double-lined eclipsing binaries are extremely important, since they are the only case providing simultaneous determinations of individual masses and radii (see Sect. 3). The best reached precisions are of the order of 1-5% ([27], [4]). Suc ...
Stellar Explosions
... A high-mass star continues to fuse elements in its core up to iron (after which the fusion reaction is energetically unfavored) As heavier elements are fused the reactions go faster and each stage is over more quickly A 20-solar-mass star will burn carbon for about 10,000 years, but its iron core la ...
... A high-mass star continues to fuse elements in its core up to iron (after which the fusion reaction is energetically unfavored) As heavier elements are fused the reactions go faster and each stage is over more quickly A 20-solar-mass star will burn carbon for about 10,000 years, but its iron core la ...
Put your title in here…
... Outline Overview of Black Holes The Stellar Disruption Event The Flare The Stellar Wind Core Remnants ...
... Outline Overview of Black Holes The Stellar Disruption Event The Flare The Stellar Wind Core Remnants ...
PDF file - Memorie della SAIt
... are commonly observed in the galactic halo. At variance with the C(N) stars commonly observed in the galactic disk, the halo C-rich stars are usually also N-rich. They are dwarfs or giants, but not AGBs. Their composition is probably due to a mass transfer process from an AGB companion. Many of thes ...
... are commonly observed in the galactic halo. At variance with the C(N) stars commonly observed in the galactic disk, the halo C-rich stars are usually also N-rich. They are dwarfs or giants, but not AGBs. Their composition is probably due to a mass transfer process from an AGB companion. Many of thes ...
Chapter 4 Galactic Chemical Evolution
... strengths of spectral lines depend on a variety of factors among which are the chemical abundances of the elements producing those spectral lines. Abundances can be measured in stellar photospheres from the strengths of absorption lines. The observed strengths of lines in a stellar spectrum depend o ...
... strengths of spectral lines depend on a variety of factors among which are the chemical abundances of the elements producing those spectral lines. Abundances can be measured in stellar photospheres from the strengths of absorption lines. The observed strengths of lines in a stellar spectrum depend o ...
Arcturus - bYTEBoss
... When he was grown up, Arcas met with the she-bear and, since obviously he didn't recognize her as his mother, he began to chase Callisto. Callisto, followed by Arcas, sheltered herself in a temple, a sacred place whose profaners were convicted to death. To avoid such fate, Zeus decided to set them i ...
... When he was grown up, Arcas met with the she-bear and, since obviously he didn't recognize her as his mother, he began to chase Callisto. Callisto, followed by Arcas, sheltered herself in a temple, a sacred place whose profaners were convicted to death. To avoid such fate, Zeus decided to set them i ...
ph709-14
... strongly in the infrared and stellar emission is weaker in this region than in the optical. Detection may be possible when the planet is especially large (considerably larger than Jupiter), widely separated from its parent star, and young (so that it is hot and emits intense infrared ...
... strongly in the infrared and stellar emission is weaker in this region than in the optical. Detection may be possible when the planet is especially large (considerably larger than Jupiter), widely separated from its parent star, and young (so that it is hot and emits intense infrared ...
Presentation file
... Like lower mass stars, could there be more than one RSG stage? warm hypergiant RSG again – extreme RSG (VY CMa) ? ...
... Like lower mass stars, could there be more than one RSG stage? warm hypergiant RSG again – extreme RSG (VY CMa) ? ...
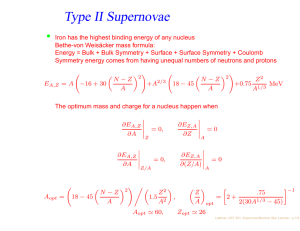
Type II Supernovae
... An observer in the orbital plane has θ = π/2 and h× = 0. The observed frequency of gravitational waves is ν = Ω/π. The intensity of gravitational waves decreases as 1/r. Consider two 1.4 M⊙ neutron stars in a binary with separation of R⊙ observed from a distance of 1 kpc: P ≃ 7000 s, ν ≃ 2.9 · 10−4 ...
... An observer in the orbital plane has θ = π/2 and h× = 0. The observed frequency of gravitational waves is ν = Ω/π. The intensity of gravitational waves decreases as 1/r. Consider two 1.4 M⊙ neutron stars in a binary with separation of R⊙ observed from a distance of 1 kpc: P ≃ 7000 s, ν ≃ 2.9 · 10−4 ...
– 1 – 1. Nucleosynthetic Yields From Various Sources
... which exceed Mc = 50M⊙ . These can reach very high temperatures at relatively low densities. Conversion of energetic photons into electron-positron pairs occurs prior to oxygen ignition. The gas is largely radiation pressure supported, so when this happens and the radiation pressure drops abruptly, ...
... which exceed Mc = 50M⊙ . These can reach very high temperatures at relatively low densities. Conversion of energetic photons into electron-positron pairs occurs prior to oxygen ignition. The gas is largely radiation pressure supported, so when this happens and the radiation pressure drops abruptly, ...
Testing the strong-field dynamics of general relativity with gravitional
... becoming available only now Analysis problem much harder From simulations that assume zero spins: 0.5% deviation at (v/c)6 beyond leading order can be seen (!) Work in progress ...
... becoming available only now Analysis problem much harder From simulations that assume zero spins: 0.5% deviation at (v/c)6 beyond leading order can be seen (!) Work in progress ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.